Abstract
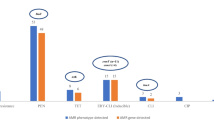
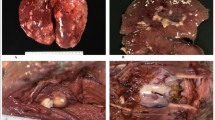
In May of 2011, a live mass stranding of 26 short-finned pilot whales (Globicephala macrorhynchus) occurred in the lower Florida Keys. Five surviving whales were transferred from the original stranding site to a nearby marine mammal rehabilitation facility where they were constantly attended to by a team of volunteers. Bacteria cultured during the routine clinical care of the whales and necropsy of a deceased whale included methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA and MRSA). In order to investigate potential sources or reservoirs of MSSA and MRSA, samples were obtained from human volunteers, whales, seawater, and sand from multiple sites at the facility, nearby recreational beaches, and a canal. Samples were collected on 3 days. The second collection day was 2 weeks after the first, and the third collection day was 2 months after the last animal was removed from the facility. MRSA and MSSA were isolated on each day from the facility when animals and volunteers were present. MSSA was found at an adjacent beach on all three collection days. Isolates were characterized by utilizing a combination of quantitative real-time PCR to determine the presence of mecA and genes associated with virulence, staphylococcal protein A typing, staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec typing, multilocus sequence typing, and pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Using these methods, clonally related MRSA were isolated from multiple environmental locations as well as from humans and animals. Non-identical but genetically similar MSSA and MRSA were also identified from distinct sources within this sample pool. PFGE indicated that the majority of MRSA isolates were clonally related to the prototype human strain USA300. These studies support the notion that S. aureus may be shed into an environment by humans or pilot whales and subsequently colonize or infect exposed new hosts.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hidron AI, Edwards JR, Patel J, Horan TC, Sievert DM, Pollock DA, Fridkin SK (2008) NHSN annual update: antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: annual summary of data reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2006–2007. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 29:996–1011. doi:10.1086/591861
Moran GJ, Amii RN, Abrahamian FM, Talan DA (2005) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in community-acquired skin infections. Emerg Infect Dis 11:928–930. doi:10.3201/eid1106.040641
Gros C, Yazdanpanah Y, Vachet A, Roussel-Delvallez M, Senneville E, Lemaire X (2012) Skin and soft tissue infections due to Panton–Valentine leukocidin producing Staphylococcus aureus. Med Mal Infect. doi:10.1016/j.medmal.2012.07.002
Hidron AI, Low CE, Honig EG, Blumberg HM (2009) Emergence of community-acquired meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain USA300 as a cause of necrotising community-onset pneumonia. Lancet Infect Dis 9:384–392. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70133-1
Miller LG, Perdreau-Remington F, Rieg G, Mehdi S, Perlroth J, Bayer AS, Tang AW, Phung TO, Spellberg B (2005) Necrotizing fasciitis caused by community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Los Angeles. N Engl J Med 352:1445–1453. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa042683
Mongkolrattanothai K, Boyle S, Kahana MD, Daum RS (2003) Severe Staphylococcus aureus infections caused by clonally related community-acquired methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant isolates. Clin Infect Dis 37:1050–1058. doi:10.1086/378277
Adem PV, Montgomery CP, Husain AN, Koogler TK, Arangelovich V, Humilier M, Boyle-Vavra S, Daum RS (2005) Staphylococcus aureus sepsis and the Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome in children. N Engl J Med 353:1245–1251. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa044194
Graham PL 3rd, Lin SX, Larson EL (2006) A U.S. population-based survey of Staphylococcus aureus colonization. Ann Intern Med 144:318–325
Kluytmans J, van Belkum A, Verbrugh H (1997) Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology, underlying mechanisms, and associated risks. Clin Microbiol Rev 10:505–520
Williams RE (1963) Healthy carriage of Staphylococcus aureus: its prevalence and importance. Bacteriol Rev 27:56–71
Armstrong-Esther CA (1976) Carriage patterns of Staphylococcus aureus in a healthy non-hospital population of adults and children. Ann Hum Biol 3:221–227
Wertheim HF, Verveer J, Boelens HA, van Belkum A, Verbrugh HA, Vos MC (2005) Effect of mupirocin treatment on nasal, pharyngeal, and perineal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus in healthy adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:1465–1467. doi:10.1128/AAC.49.4.1465-1467.2005
Vandenesch F, Naimi T, Enright MC, Lina G, Nimmo GR, Heffernan H, Liassine N, Bes M, Greenland T, Reverdy ME, Etienne J (2003) Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying Panton–Valentine leukocidin genes: worldwide emergence. Emerg Infect Dis 9:978–984. doi:10.3201/eid0908.030089
Knight GM, Budd EL, Whitney L, Thornley A, Al-Ghusein H, Planche T, Lindsay JA (2012) Shift in dominant hospital-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (HA-MRSA) clones over time. J Antimicrob Chemother 67:2514–2522. doi:10.1093/jac/dks245
Herold BC, Immergluck LC, Maranan MC, Lauderdale DS, Gaskin RE, Boyle-Vavra S, Leitch CD, Daum RS (1998) Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children with no identified predisposing risk. JAMA 279:593–598
Baggett HC, Hennessy TW, Rudolph K, Bruden D, Reasonover A, Parkinson A, Sparks R, Donlan RM, Martinez P, Mongkolrattanothai K, Butler JC (2004) Community-onset methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus associated with antibiotic use and the cytotoxin Panton–Valentine leukocidin during a furunculosis outbreak in rural Alaska. J Infect Dis 189:1565–1573. doi:10.1086/383247
Nguyen DM, Mascola L, Brancoft E (2005) Recurring methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in a football team. Emerg Infect Dis 11:526–532. doi:10.3201/eid1104.041094
Hardy KJ, Oppenheim BA, Gossain S, Gao F, Hawkey PM (2006) A study of the relationship between environmental contamination with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and patients’ acquisition of MRSA. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 27:127–132. doi:10.1086/500622
Uhlemann AC, Knox J, Miller M, Hafer C, Vasquez G, Ryan M, Vavagiakis P, Shi Q, Lowy FD (2011) The environment as an unrecognized reservoir for community-associated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300: a case–control study. PLoS One 6:e22407. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022407
Desai R, Pannaraj PS, Agopian J, Sugar CA, Liu GY, Miller LG (2011) Survival and transmission of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from fomites. Am J Infect Control 39:219–225. doi:10.1016/j.ajic.2010.07.005
Henderson DK (2006) Managing methicillin-resistant staphylococci: a paradigm for preventing nosocomial transmission of resistant organisms. Am J Infect Control 34:S46–S54. doi:10.1016/j.ajic.2006.05.228, discussion S64-73
Ho SS, Tse MM, Boost MV (2012) Effect of an infection control programme on bacterial contamination of enteral feed in nursing homes. J Hosp Infect 82:49–55. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2012.05.002
Feil EJ, Cooper JE, Grundmann H, Robinson DA, Enright MC, Berendt T, Peacock SJ, Smith JM, Murphy M, Spratt BG, Moore CE, Day NP (2003) How clonal is Staphylococcus aureus? J Bacteriol 185:3307–3316. doi:10.1128/JB.185.11.3307-3316.2003
Dancer SJ (2008) The effect of antibiotics on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 61:246–253. doi:10.1093/jac/dkm465
Rehm SJ, Tice A (2010) Staphylococcus aureus: methicillin-susceptible S. aureus to methicillin-resistant S. aureus and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus. Clin Infect Dis 51(Suppl 2):S176–S182. doi:10.1086/653518
Malachowa N, DeLeo FR (2010) Mobile genetic elements of Staphylococcus aureus. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:3057–3071. doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0389-4
McDougal LK, Steward CD, Killgore GE, Chaitram JM, McAllister SK, Tenover FC (2003) Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing of oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from the United States: establishing a national database. J Clin Microbiol 41:5113–5120. doi:10.1128/JCM.41.11.5113-5120.2003
Enright MC, Day NP, Davies CE, Peacock SJ, Spratt BG (2000) Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 38:1008–1015
Maiden MC, Bygraves JA, Feil E, Morelli G, Russell JE, Urwin R, Zhang Q, Zhou J, Zurth K, Caugant DA, Feavers IM, Achtman M, Spratt BG (1998) Multilocus sequence typing: a portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3140–3145
Spratt BG (1999) Multilocus sequence typing: molecular typing of bacterial pathogens in an era of rapid DNA sequencing and the internet. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:312–316. doi:10.1016/S1369-5274(99)80054-X
Oliveira DC, de Lencastre H (2002) Multiplex PCR strategy for rapid identification of structural types and variants of the mec element in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:2155–2161. doi:10.1128/AAC.46.7.2155-2161.2002
Milheirico C, Oliveira DC, de Lencastre H (2007) Update to the multiplex PCR strategy for assignment of mec element types in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:3374–3377. doi:10.1128/AAC.00275-07
Milheirico C, Oliveira DC, de Lencastre H (2007) Multiplex PCR strategy for subtyping the staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type IV in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: ‘SCCmec IV multiplex’. J Antimicrob Chemother 60:42–48. doi:10.1093/jac/dkm112
Katayama Y, Ito T, Hiramatsu K (2000) A new class of genetic element, staphylococcus cassette chromosome mec, encodes methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:1549–1555
Tristan A, Bes M, Meugnier H, Lina G, Bozdogan B, Courvalin P, Reverdy ME, Enright MC, Vandenesch F, Etienne J (2007) Global distribution of Panton–Valentine leukocidin-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, 2006. Emerg Infect Dis 13:594–600. doi:10.3201/eid1304.061316
Takano T, Higuchi W, Otsuka T, Baranovich T, Enany S, Saito K, Isobe H, Dohmae S, Ozaki K, Takano M, Iwao Y, Shibuya M, Okubo T, Yabe S, Shi D, Reva I, Teng LJ, Yamamoto T (2008) Novel characteristics of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains belonging to multilocus sequence type 59 in Taiwan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:837–845. doi:10.1128/AAC.01001-07
Boyle-Vavra S, Ereshefsky B, Wang CC, Daum RS (2005) Successful multiresistant community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus lineage from Taipei, Taiwan, that carries either the novel Staphylococcal chromosome cassette mec (SCCmec) type VT or SCCmec type IV. J Clin Microbiol 43:4719–4730. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.9.4719-4730.2005
Karahan ZC, Tekeli A, Adaleti R, Koyuncu E, Dolapci I, Akan OA (2008) Investigation of Panton–Valentine leukocidin genes and SCCmec types in clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Turkey. Microb Drug Resist 14:203–210. doi:10.1089/mdr.2008.0811
Koreen L, Ramaswamy SV, Graviss EA, Naidich S, Musser JM, Kreiswirth BN (2004) spa typing method for discriminating among Staphylococcus aureus isolates: implications for use of a single marker to detect genetic micro- and macrovariation. J Clin Microbiol 42:792–799
Cai Y, Kong F, Wang Q, Tong Z, Sintchenko V, Zeng X, Gilbert GL (2007) Comparison of single- and multilocus sequence typing and toxin gene profiling for characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 45:3302–3308. doi:10.1128/JCM.01082-07
Kim J-S, Song W, Kim H-S, Cho HC, Lee KM, Choi M-S, Kim E-C (2006) Association between the methicillin resistance of clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, their staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) subtype classification, and their toxin gene profiles. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 56:289–295. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2006.05.003
Tristan A, Ying L, Bes M, Etienne J, Vandenesch F, Lina G (2003) Use of multiplex PCR to identify Staphylococcus aureus adhesins involved in human hematogenous infections. J Clin Microbiol 41:4465–4467
Monecke S, Luedicke C, Slickers P, Ehricht R (2009) Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in asymptomatic carriers. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28:1159–1165. doi:10.1007/s10096-009-0752-2
Monecke S, Ehricht R, Slickers P, Tan HL, Coombs G (2009) The molecular epidemiology and evolution of the Panton–Valentine leukocidin-positive, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain USA300 in Western Australia. Clin Microbiol Infect 15:770–776. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02792.x
Tenover FC, Goering RV (2009) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain USA300: origin and epidemiology. J Antimicrob Chemother 64:441–446. doi:10.1093/jac/dkp241
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2003) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections among competitive sports participants—Colorado, Indiana, Pennsylvania, and Los Angeles County, 2000–2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 52:793–795
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2001) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin or soft tissue infections in a state prison—Mississippi, 2000. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 50:919–922
Moran GJ, Krishnadasan A, Gorwitz RJ, Fosheim GE, McDougal LK, Carey RB, Talan DA (2006) Methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections among patients in the emergency department. N Engl J Med 355:666–674. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa055356
Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J, Petit S, Gershman K, Ray S, Harrison LH, Lynfield R, Dumyati G, Townes JM, Craig AS, Zell ER, Fosheim GE, McDougal LK, Carey RB, Fridkin SK (2007) Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA 298:1763–1771. doi:10.1001/jama.298.15.1763
Seybold U, Kourbatova EV, Johnson JG, Halvosa SJ, Wang YF, King MD, Ray SM, Blumberg HM (2006) Emergence of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 genotype as a major cause of health care-associated blood stream infections. Clin Infect Dis 42:647–656. doi:10.1086/499815
Otter JA, French GL (2006) Nosocomial transmission of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an emerging threat. Lancet Infect Dis 6:753–755. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70636-3
Wannet WJ, Heck ME, Pluister GN, Spalburg E, van Santen MG, Huijsdans XW, Tiemersma E, de Neeling AJ (2004) Panton–Valentine leukocidin positive MRSA in 2003: the Dutch situation. Euro Surveill 9:28–29
Larsen A, Stegger M, Goering R, Sorum M, Skov R (2007) Emergence and dissemination of the methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 clone in Denmark (2000–2005). Euro Surveill 12(2)
Blanco R, Tristan A, Ezpeleta G, Larsen AR, Bes M, Etienne J, Cisterna R, Laurent F (2011) Molecular epidemiology of Panton–Valentine leukocidin-positive Staphylococcus aureus in Spain: emergence of the USA300 clone in an autochthonous population. J Clin Microbiol 49:433–436. doi:10.1128/JCM.02201-10
Rolo J, Miragaia M, Turlej-Rogacka A, Empel J, Bouchami O, Faria NA, Tavares A, Hryniewicz W, Fluit AC, de Lencastre H (2012) High genetic diversity among community-associated Staphylococcus aureus in Europe: results from a multicenter study. PLoS One 7:e34768. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034768
Passalacqua KD, Satola SW, Crispell EK, Read TD (2012) A mutation in the PP2C phosphatase gene in a Staphylococcus aureus USA300 clinical isolate with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin and daptomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:5212–5223. doi:10.1128/AAC.05770-11
Como-Sabetti K, Harriman KH, Buck JM, Glennen A, Boxrud DJ, Lynfield R (2009) Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: trends in case and isolate characteristics from six years of prospective surveillance. Public Health Rep 124:427–435
Han LL, McDougal LK, Gorwitz RJ, Mayer KH, Patel JB, Sennott JM, Fontana JL (2007) High frequencies of clindamycin and tetracycline resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pulsed-field type USA300 isolates collected at a Boston ambulatory health center. J Clin Microbiol 45:1350–1352. doi:10.1128/JCM.02274-06
Diep BA, Carleton HA, Chang RF, Sensabaugh GF, Perdreau-Remington F (2006) Roles of 34 virulence genes in the evolution of hospital- and community-associated strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis 193:1495–1503. doi:10.1086/503777
Kennedy AD, Otto M, Braughton KR, Whitney AR, Chen L, Mathema B, Mediavilla JR, Byrne KA, Parkins LD, Tenover FC, Kreiswirth BN, Musser JM, DeLeo FR (2008) Epidemic community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: recent clonal expansion and diversification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:1327–1332. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710217105
Miller LG, Eells SJ, Taylor AR, David MZ, Ortiz N, Zychowski D, Kumar N, Cruz D, Boyle-Vavra S, Daum RS (2012) Staphylococcus aureus colonization among household contacts of patients with skin infections: risk factors, strain discordance, and complex ecology. Clin Infect Dis 54:1523–1535. doi:10.1093/cid/cis213
Patel M, Waites KB, Hoesley CJ, Stamm AM, Canupp KC, Moser SA (2008) Emergence of USA300 MRSA in a tertiary medical centre: implications for epidemiological studies. J Hosp Infect 68:208–213. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2007.12.010
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2009) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin infections from an elephant calf—San Diego, California, 2008. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 58:194–198
Haenni M, Saras E, Chatre P, Medaille C, Bes M, Madec JY, Laurent F (2012) A USA300 variant and other human-related methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains infecting cats and dogs in France. J Antimicrob Chemother 67:326–329. doi:10.1093/jac/dkr499
Vitale CB, Gross TL, Weese JS (2006) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in cat and owner. Emerg Infect Dis 12:1998–2000. doi:10.3201/eid1212.060725
Rohr U, Kaminski A, Wilhelm M, Jurzik L, Gatermann S, Muhr G (2009) Colonization of patients and contamination of the patients’ environment by MRSA under conditions of single-room isolation. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212:209–215. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2008.05.003
Sexton T, Clarke P, O’Neill E, Dillane T, Humphreys H (2006) Environmental reservoirs of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in isolation rooms: correlation with patient isolates and implications for hospital hygiene. J Hosp Infect 62:187–194. doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2005.07.017
Charoenca N, Fujioka RS (1993) Assessment of staphylococcus bacteria in Hawaii marine recreational waters. Water Sci Technol 27:283–289
Yoshpe-Purer Y, Golderman S (1987) Occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Israeli coastal water. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1138–1141
Shah AH, Abdelzaher AM, Phillips M, Hernandez R, Solo-Gabriele HM, Kish J, Scorzetti G, Fell JW, Diaz MR, Scott TM, Lukasik J, Harwood VJ, McQuaig S, Sinigalliano CD, Gidley ML, Wanless D, Ager A, Lui J, Stewart JR, Plano LR, Fleming LE (2011) Indicator microbes correlate with pathogenic bacteria, yeasts and helminthes in sand at a subtropical recreational beach site. J Appl Microbiol 110:1571–1583. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05013.x
Abdelzaher AM, Wright ME, Ortega C, Hasan AR, Shibata T, Solo-Gabriele HM, Kish J, Withum K, He G, Elmir SM, Bonilla JA, Bonilla TD, Palmer CJ, Scott TM, Lukasik J, Harwood VJ, McQuaig S, Sinigalliano CD, Gidley ML, Wanless D, Plano LR, Garza AC, Zhu X, Stewart JR, Dickerson JW, Yampara-Iquise H, Carson C, Fleisher JM, Fleming LE (2011) Daily measures of microbes and human health at a non-point source marine beach. J Water Health 9:443–457. doi:10.2166/wh.2011.146
Papadakis JA, Mavridou A, Richardson SC, Lampiri M, Marcelou U (1997) Bather-related microbial and yeast populations in sand and seawater. Water Res 31:799–804
Sinigalliano CD, Fleisher JM, Gidley ML, Solo-Gabriele HM, Shibata T, Plano LR, Elmir SM, Wanless D, Bartkowiak J, Boiteau R, Withum K, Abdelzaher AM, He G, Ortega C, Zhu X, Wright ME, Kish J, Hollenbeck J, Scott T, Backer LC, Fleming LE (2010) Traditional and molecular analyses for fecal indicator bacteria in non-point source subtropical recreational marine waters. Water Res 44:3763–3772. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.04.026
Goodwin KD, McNay M, Cao Y, Ebentier D, Madison M, Griffith JF (2012) A multi-beach study of Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, and enterococci in seawater and beach sand. Water Res 46:4195–4207. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.04.001
Levin-Edens E, Soge OO, No D, Stiffarm A, Meschke JS, Roberts MC (2012) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Northwest marine and freshwater recreational beaches. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 79:412–420. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01229.x
Soge OO, Meschke JS, No DB, Roberts MC (2009) Characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococcus spp. isolated from US West Coast public marine beaches. J Antimicrob Chemother 64:1148–1155. doi:10.1093/jac/dkp368
Robinton ED, Mood EW (1966) A quantitative and qualitative appraisal of microbial pollution of water by swimmers: a preliminary report. J Hyg (Lond) 64:489–499
Plano LR, Garza AC, Shibata T, Elmir SM, Kish J, Sinigalliano CD, Gidley ML, Miller G, Withum K, Fleming LE, Solo-Gabriele HM (2011) Shedding of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from adult and pediatric bathers in marine waters. BMC Microbiol 11:5. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-11-5
Elmir SM, Wright ME, Abdelzaher A, Solo-Gabriele HM, Fleming LE, Miller G, Rybolowik M, Peter Shih MT, Pillai SP, Cooper JA, Quaye EA (2007) Quantitative evaluation of bacteria released by bathers in a marine water. Water Res 41:3–10. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2006.10.005
Plano LRW, Shibata T, Garza AC, Kish J, Fleisher JM, Sinigalliano CD, Gidley ML, Withum K, Elmir SM, Hower S, Jackson CR, Barrett JB, Cleary T, Davidson M, Davis J, Mukherjee S, Fleming LE, Solo-Gabriele HM (2013) Human-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from a subtropical recreational marine beach. Microb Ecol. doi:10.1007/S00248-013-0216-1
Mazet JAK, Hunt TD, Ziccardi MH (2004) Assessment of the risk of zoonotic disease transmission to marine mammal workers and the public: survey of occupational risks. Final report prepared for United States Marine Mammal Commission (K005486-01). UC, Davis
Charoenca N, Fujioka RS (1995) Association of staphylococcal skin infections and swimming. Water Sci Technol 31:11–17
Hasman H, Moodley A, Guardabassi L, Stegger M, Skov RL, Aarestrup FM (2010) spa type distribution in Staphylococcus aureus originating from pigs, cattle and poultry. Vet Microbiol 141:326–331. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.09.025
Espinosa-Gongora C, Chrobak D, Moodley A, Bertelsen MF, Guardabassi L (2012) Occurrence and distribution of Staphylococcus aureus lineages among zoo animals. Vet Microbiol 158:228–231. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.01.027
Faires MC, Gehring E, Mergl J, Weese JS (2009) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in marine mammals. Emerg Infect Dis 15:2071–2072. doi:10.3201/eid1512.090220
Walther B, Wieler LH, Friedrich AW, Hanssen AM, Kohn B, Brunnberg L, Lubke-Becker A (2008) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from small and exotic animals at a university hospital during routine microbiological examinations. Vet Microbiol 127:171–178. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.07.018
O’Mahony R, Abbott Y, Leonard FC, Markey BK, Quinn PJ, Pollock PJ, Fanning S, Rossney AS (2005) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolated from animals and veterinary personnel in Ireland. Vet Microbiol 109:285–296. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2005.06.003
Weese JS, Archambault M, Willey BM, Hearn P, Kreiswirth BN, Said-Salim B, McGeer A, Likhoshvay Y, Prescott JF, Low DE (2005) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in horses and horse personnel, 2000–2002. Emerg Infect Dis 11:430–435. doi:10.3201/eid1103.040481
Khanna T, Friendship R, Dewey C, Weese JS (2008) Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization in pigs and pig farmers. Vet Microbiol 128:298–303. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.10.006
Seguin JC, Walker RD, Caron JP, Kloos WE, George CG, Hollis RJ, Jones RN, Pfaller MA (1999) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus outbreak in a veterinary teaching hospital: potential human-to-animal transmission. J Clin Microbiol 37:1459–1463
Weese JS, DaCosta T, Button L, Goth K, Ethier M, Boehnke K (2004) Isolation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from the environment in a veterinary teaching hospital. J Vet Intern Med 18:468–470
Aklilu E, Zakaria Z, Hassan L, Hui Cheng C (2012) Molecular relatedness of methicillin-resistant S. aureus isolates from staff, environment and pets at university veterinary hospital in malaysia. PLoS One 7:e43329. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0043329
van Duijkeren E, Wolfhagen MJ, Box AT, Heck ME, Wannet WJ, Fluit AC (2004) Human-to-dog transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Emerg Infect Dis 10:2235–2237. doi:10.3201/eid1012.040387
Dierauf LA, Gulland FMD (2001) CRC handbook of marine mammal medicine. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hohn AA, Southeast Fisheries Science Center (U.S.) (2006) Report on marine mammal unusual mortality event UMESE0501Sp: multispecies mass stranding of pilot whales (Globicephala macrorhynchus), Minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata), and Dwarf sperm whales (Kogia sima) in North Carolina on 15–16 January 2005. U.S. Dept. of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Marine Fisheries Service, Southeast Fisheries Science Center, Miami
Hall JD, Gilmartin WG, Mattsson JL (1971) Investigation of a Pacific pilot whale stranding on San Clemente Island. J Wildl Dis 7:324–327
Colgrove GS, Migaki G (1976) Cerebral abscess associated with stranding in a dolphin. J Wildl Dis 12:271–274
Acevedo-Whitehouse K, Rocha-Gosselin A, Gendron D (2010) A novel non-invasive tool for disease surveillance of free-ranging whales and its relevance to conservation programs. Anim Conserv 13:217–225. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1795.2009.00326.x
Buck JD, Spotte S (1986) Microbiology of captive white-beaked dolphins (Lagenorhynchus albirostris) with comments on epizootics. Zoo Biol 5:321–329
Schaefer AM, Goldstein JD, Reif JS, Fair PA, Bossart GD (2009) Antibiotic-resistant organisms cultured from Atlantic bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) inhabiting estuarine waters of Charleston, SC and Indian River Lagoon, FL. EcoHealth 6:33–41. doi:10.1007/s10393-009-0221-5
Pier AC, Takayama AK, Miyahara AY (1970) Cetacean nocardiosis. J Wildl Dis 6:112–118
Fravel V, Van Bonn W, Rios C, Gulland F (2011) Meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a harbour seal (Phoca vitulina). Vet Rec 169:155. doi:10.1136/vr.d4199
Geraci JR, Lounsbury VJ (2005) Marine mammals ashore: a field guide for strandings, 2nd edn. Bational Aquarium in Baltimore, Baltimore
Shibata T, Solo-Gabriele HM, Fleming LE, Elmir S (2004) Monitoring marine recreational water quality using multiple microbial indicators in an urban tropical environment. Water Res 38:3119–3131
Boehm AB, Griffith J, McGee C, Edge TA, Solo-Gabriele HM, Whitman R, Cao Y, Getrich M, Jay JA, Ferguson D, Goodwin KD, Lee CM, Madison M, Weisberg SB (2009) Faecal indicator bacteria enumeration in beach sand: a comparison study of extraction methods in medium to coarse sands. J Appl Microbiol 107:1740–1750. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04440.x
United States Environmental Protection Agency (2002) Method 1600: membrane filter test method for enterococci in water. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, D. C
Vancraeynest D, Hermans K, Haesebrouck F (2004) Genotypic and phenotypic screening of high and low virulence Staphylococcus aureus isolates from rabbits for biofilm formation and MSCRAMMs. Vet Microbiol 103:241–247. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2004.09.002
Harmsen D, Claus H, Witte W, Rothganger J, Turnwald D, Vogel U (2003) Typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a university hospital setting by using novel software for spa repeat determination and database management. J Clin Microbiol 41:5442–5448
Ribot EM, Fair MA, Gautom R, Cameron DN, Hunter SB, Swaminathan B, Barrett TJ (2006) Standardization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for the subtyping of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, and Shigella for PulseNet. Foodborne Pathog Dis 3:59–67. doi:10.1089/fpd.2006.3.59
Bartels MD, Boye K, Rhod Larsen A, Skov R, Westh H (2007) Rapid increase of genetically diverse methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Copenhagen, Denmark. Emerg Infect Dis 13:1533–1540. doi:10.3201/eid1310.070503
Boye K, Westh H (2011) Variations in spa types found in consecutive MRSA isolates from the same patients. FEMS Microbiol Lett 314:101–105. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02151.x
Mertz PM, Cardenas TC, Snyder RV, Kinney MA, Davis SC, Plano LR (2007) Staphylococcus aureus virulence factors associated with infected skin lesions: influence on the local immune response. Arch Dermatol 143:1259–1263. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.10.1259
Speziale P, Pietrocola G, Rindi S, Provenzano M, Provenza G, Di Poto A, Visai L, Arciola CR (2009) Structural and functional role of Staphylococcus aureus surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules of the host. Future Microbiol 4:1337–1352. doi:10.2217/fmb.09.102
Tenover FC, McAllister S, Fosheim G, McDougal LK, Carey RB, Limbago B, Lonsway D, Patel JB, Kuehnert MJ, Gorwitz R (2008) Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from nasal cultures collected from individuals in the United States in 2001 to 2004. J Clin Microbiol 46:2837–2841. doi:10.1128/JCM.00480-08
Nubel U, Roumagnac P, Feldkamp M, Song JH, Ko KS, Huang YC, Coombs G, Ip M, Westh H, Skov R, Struelens MJ, Goering RV, Strommenger B, Weller A, Witte W, Achtman M (2008) Frequent emergence and limited geographic dispersal of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:14130–14135. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804178105
Waring GT, Josephson E, Maze-Foley K, Rosel PE, (eds) (2012) U.S. Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico marine mammal stock assessments 2011. NOAA technical memorandum NMFS-NE; 221
Vasconcelos GJ, Swartz RG (1976) Survival of bacteria in seawater using a diffusion chamber apparatus in situ. Appl Environ Microbiol 31:913–920
Mohammed RL, Echeverry A, Stinson CM, Green M, Bonilla TD, Hartz A, McCorquodale DS, Rogerson A, Esiobu N (2012) Survival trends of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Clostridium perfringens in a sandy South Florida beach. Mar Pollut Bull 64:1201–1209. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.03.010
Thurlow LR, Joshi GS, Richardson AR (2012) Virulence strategies of the dominant USA300 lineage of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA). FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 65:5–22. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2012.00937.x
King MD, Humphrey BJ, Wang YF, Kourbatova EV, Ray SM, Blumberg HM (2006) Emergence of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA 300 clone as the predominant cause of skin and soft-tissue infections. Ann Intern Med 144:309–317
Tenover FC, McDougal LK, Goering RV, Killgore G, Projan SJ, Patel JB, Dunman PM (2006) Characterization of a strain of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus widely disseminated in the United States. J Clin Microbiol 44:108–118. doi:10.1128/JCM.44.1.108-118.2006
Tenover FC, Tickler IA, Goering RV, Kreiswirth BN, Mediavilla JR, Persing DH (2012) Characterization of nasal and blood culture isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from patients in United States Hospitals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:1324–1330. doi:10.1128/AAC.05804-11
Batra R, Eziefula AC, Wyncoll D, Edgeworth J (2008) Throat and rectal swabs may have an important role in MRSA screening of critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 34:1703–1706. doi:10.1007/s00134-008-1153-1
Bitterman Y, Laor A, Itzhaki S, Weber G (2010) Characterization of the best anatomical sites in screening for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 29:391–397. doi:10.1007/s10096-009-0869-3
Eveillard M, de Lassence A, Lancien E, Barnaud G, Ricard JD, Joly-Guillou ML (2006) Evaluation of a strategy of screening multiple anatomical sites for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at admission to a teaching hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 27:181–184. doi:10.1086/500627
Jarraud S, Cozon G, Vandenesch F, Bes M, Etienne J, Lina G (1999) Involvement of enterotoxins G and I in staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome and staphylococcal scarlet fever. J Clin Microbiol 37:2446–2449
Loughman JA, Fritz SA, Storch GA, Hunstad DA (2009) Virulence gene expression in human community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Infect Dis 199:294–301. doi:10.1086/595982
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Marine Mammal Conservancy for their assistance and cooperation during this study. We thank Alexander Costidis for performing the whale necropsy as well as the staff at the FWC Fish and Wildlife Research Institute, Marine Mammal Pathobiology Laboratory. We are grateful to Ari Bennett, Julie Hollenbeck, Heather Coit, Sharon Plano, Rebecca Weeks, Havek Kavoblock, Ryan Phillips, Danielle DeHowitt, and the Florida Department of Health for their assistance during the sample collections. We thank Dr. Helena Solo-Gabriele and Faiza Benahmed, for assistance in processing and storing samples. Thanks to Carlton Woods at Micrim Laboratory, Inc. for isolating MRSA from the whale samples and facilitating the transfer to University of Miami Miller School of Medicine. We also thank the Palm Beach Infectious Disease Institute for providing S. aureus clinical isolates for comparison. Additionally, we thank the Hollings Scholarship Program of the NOAA Office of Education for their support of the Hollings Scholar students involved in this project. Marine Mammal samples were collected as either diagnostic clinical samples or as salvage samples under NMFS Permit No. 932-1905/MA-009526. This publication represents the personal opinions of the authors and is not the official position of the contributing federal government agencies. No official endorsement of any product or commercial laboratory is made or implied by its use in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hower, S., Phillips, M.C., Brodsky, M. et al. Clonally Related Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Short-Finned Pilot Whales (Globicephala macrorhynchus), Human Volunteers, and a Bayfront Cetacean Rehabilitation Facility. Microb Ecol 65, 1024–1038 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0178-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0178-3