Abstract
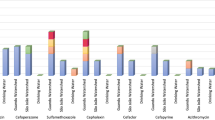
RNA methylase genes are common antibiotic resistance determinants for multiple drugs of the macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin B (MLSB) families. We used molecular methods to investigate the diversity, distribution, and abundance of MLSB methylases in waste lagoons and groundwater wells at two swine farms with a history of tylosin (a macrolide antibiotic structurally related to erythromycin) and tetracycline usage. Phylogenetic analysis guided primer design for quantification of MLSB resistance genes found in tylosin-producing Streptomyces (tlr(B), tlr(D)) and commensal/pathogenic bacteria (erm(A), erm(B), erm(C), erm(F), erm(G), erm(Q)). The near absence of tlr genes at these sites suggested a lack of native antibiotic-producing organisms. The gene combination erm(ABCF) was found in all lagoon samples analyzed. These four genes were also detected with high frequency in wells previously found to be contaminated by lagoon leakage. A weak correlation was found between the distribution of erm genes and previously reported patterns of tetracycline resistance determinants, suggesting that dissemination of these genes into the environment is not necessarily linked. Considerations of gene origins in history (i.e., phylogeny) and gene distributions in the landscape provide a useful “molecular ecology” framework for studying environmental spread of antibiotic resistance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminov RI, Chee-Sanford JC, Garrigues N, Teferedegne B, Krapac IJ, White BA, Mackie RI (2002) Development, validation, and application of PCR primers for detection of tetracycline efflux genes of gram-negative bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1786–1793
Aminov RI, Garrigues-Jeanjean N, Mackie RI (2001) Molecular ecology of tetracycline resistance: development and validation of primers for detection of tetracycline resistance genes encoding ribosomal protection proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:22–32
Aminov RI, Mackie RI (2007) Evolution and ecology of antibiotic resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 271:147–161
Benson DA, Boguski MS, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Ouellette BFF, Rapp BA, Wheeler DL (1999) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 27:12–17
Berrang ME, Ladely SR, Meinersmann RJ, Fedorka-Cray PJ (2007) Subtherapeutic tylosin phosphate in broiler feed affects Campylobacter on carcasses during processing. Poultry Sci 86:1229–1233
Berryman DI, Lyristis M, Rood JI (1994) Cloning and sequence analysis of ermQ, the predominant macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance gene in Clostridium perfringens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:1041–1046
Bryskier AJ, Butzler JP, Neu HC, Tulkens PM (1993) Macrolides: chemistry, pharmacology, and clinical uses. Arnette Blackwell, Paris
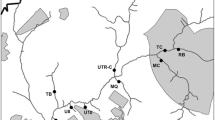
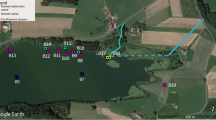
Chee-Sanford JC, Aminov RI, Krapac IJ, Garrigues-Jeanjean N, Mackie RI (2001) Occurrence and diversity of tetracycline resistance genes in lagoons and groundwater underlying two swine production facilities. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1494–1502
Chee-Sanford JC, Mackie RI, Koike S, Krapac I, Lin Y-F, Yannarell AC, Maxwell S, Aminov RI (2009) Fate and transport of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes following land application of manure waste. J Environ Qual 38:1086–1108
Chen J, Fluharty FL, St-Pierre N, Morrison M, Yu Z (2008) Technical note: occurrence in fecal microbiota of genes conferring resistance to both macrolide–lincosamide–streptogramin B and tetracyclines concomitant with feeding of beef cattle with tylosin. J Anim Sci 86:2385–2391
Chen J, Yu ZT, Michel FC, Wittum T, Morrison M (2007) Development and application of real-time PCR assays for quantification of erm genes conferring resistance to macrolides–lincosamides–streptogramin B in livestock manure and manure management systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4407–4416
Cooper AJ, Shoemaker NB, Salyers AA (1996) Erythromycin resistance gene from the Bacteroides conjugal transposon Tcr Ermr 7853 is nearly identical to ermG from Bacillus sphaericus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:506–508
D'Costa VM, McGrann KM, Hughes DW, Wright GD (2006) Sampling the antibiotic resistome. Science 311:374–377
De Graef EM, Decostere A, De Leener E, Goossens H, Baele M, Haesebrouck F (2007) Prevalence and mechanism of resistance against macrolides, lincosamides, and streptogramins among Enterococcus faecium isolates from food-producing animals and hospital patients in Belgium. Microb Drug Resist 13:135–141
De Leener E, Decostere A, De Graef EM, Moyaert H, Haesebrouck F (2005) Presence and mechanism of antimicrobial resistance among enterococci from cats and dogs. Microb Drug Resist 11:395–403
De Leener E, Martel A, Decostere A, Haesebrouck F (2004) Distribution of the erm(B) gene, tetracycline resistance genes, and TN1545-like transposons in macrolide- and lincosamide-resistant enterococci from pigs and humans. Microb Drug Resist Mechan Epidemiol Dis 10:341–345
Heuer H, Krogerrecklenfort E, Wellington EMH, Egan S, van Elsas JD, van Overbeek L, Collard JM, Guillaume G, Karagouni AD, Nikolakopoulou TL, Smalla K (2002) Gentamicin resistance genes in environmental bacteria: prevalence and transfer. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 42:289–302
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Jindal A, Kocherginskaya S, Mehboob A, Robert M, Mackie RI, Raskin L, Zilles JL (2006) Antimicrobial use and resistance in swine waste treatment systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7813–7820
Jost BH, Trinh HT, Songer JG, Billington SJ (2004) A second tylosin resistance determinant, Erm B, in Arcanobacterium pyogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:721–727
Koike S, Krapac IG, Oliver HD, Yannarell AC, Chee-Sanford JC, Aminov RI, Mackie RI (2007) Monitoring and source tracking of tetracycline resistance genes in lagoons and groundwater adjacent to swine production facilities. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4813–4823
Krapac I, Dey WS, Smyth CA, Roy WR (1998) Impacts of bacteria, metals, and nutrients on groundwater at two hog confinement facilities. In: Proceedings of Animal feeding operations on groundwater: issues, impact, and solutions: a conference for the future. National Ground Water Association, St. Louis, MO, pp. 29–50
Krapac IG, Koike S, Meyer MT, Snow DD, Chou SFJ, Mackie RI, Roy WR, Chee-Sanford JC (2004) Long-term monitoring of the occurrence of antibiotic resistance genes in groundwater near swine confinement facilities. Proceedings of the 4th International conference on pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting chemicals in water. National Ground Water Association, Minneapolis, MN, pp. 158–172
Ladely SR, Harrison MA, Fedorka-Cray PJ, Berrang ME, Englen MD, Meinersmann RJ (2007) Development of macrolide-resistant Campylobacter in broilers administered subtherapeutic or therapeutic concentrations of tylosin. J Food Prot 70:1945–1951
Larson TH, Krapac IG, Dey WS, Suchomski CJ (1997) Electromagnetic terrain conductivity surveys used to screen swine confinement facilities for groundwater contamination. Presented at the Proceedings of the symposium on the application of geophysics to engineering and environmental problems, Reno, NV
Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical ecology, second English ed. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Liu MF, Kirpekar F, van Wezel GP, Douthwaite S (2000) The tylosin resistance gene tlrB of Streptomyces fradiae encodes a methyltransferase that targets G748 in 23S rRNA. Mol Microbiol 37:811–820
Mackie RI, Koike S, Krapac I, Chee-Sanford J, Maxwell S, Aminov RI (2006) Tetracycline residues and tetracycline resistance genes in groundwater impacted by swine production facilities. Anim Biotechnol 17:157–176
McEwen SA (2006) Antibiotic use in animal agriculture: what have we learned and where are we going? Anim Biotechnol 17:239–250
Miller DN (2001) Evaluation of gel filtration resins for the removal of PCR-inhibitory substances from soils and sediments. J Microbiol Methods 44:49–58
Portillo A, Ruiz-Larrea F, Zarazaga M, Alonso A, Martinez JL, Torres C (2000) Macrolide resistance genes in Enterococcus spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:967–971
R Development Core Team (2005) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rasmussen JL, Odelson DA, Macrina FL (1986) Complete nucleotide sequence and transcription of ermF, a macrolide–lincosamide–streptogramin B resistance determinant from Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol 168:523–533
Roberts MC (2002) Resistance to tetracycline, macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin, trimethoprim, and sulfonamide drug classes. Mol Biotechnol 20:261–283
Roberts MC (2008) Update on macrolide–lincosamide–streptogramin, ketolide, and oxazolidinone resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 282:147–159
Roberts MC, Sutcliffe J, Courvalin P, Jensen LB, Rood J, Seppala H (1999) Nomenclature for macrolide and macrolide–lincosamide–streptogramin B resistance determinants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:2823–2830
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Salyers A, Shoemaker NB (2006) Reservoirs of antibiotic resistance genes. Anim Biotechnol 17:137–146
Singer RS, Ward MP, Maldonado G (2006) Can landscape ecology untangle the complexity of antibiotic resistance? Nat Rev Microbiol 4:943–952
Sutcliffe J, Grebe T, TaitKamradt A, Wondrack L (1996) Detection of erythromycin-resistant determinants by PCR. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:2562–2566
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tsai YL, Olson BH (1991) Rapid method for direct extraction of DNA from soil and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1070–1074
Wegener HC (2003) Antibiotics in animal feed and their role in resistance development. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:439–445
Witte W (2000) Ecological impact of antibiotic use in animals on different complex microflora: environment. Int J Antimicrob Agents 14:321–325
Yu ZT, Michel FC, Hansen G, Wittum T, Morrison M (2005) Development and application of real-time PCR assays for quantification of genes encoding tetracycline resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6926–6933
Zhou JZ, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:316–322
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by funding from the USDA NRI Competitive Grants Program 26.0 (award nos. 2001-35102-10774 and 2005-35102-16424). Support was also provided by the Scottish Government Rural and Environmental Research and Analysis Directorate and by Hatch funding to the Agricultural Experimental Station at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S. Koike, R. I. Aminov, and A. C. Yannarell contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koike, S., Aminov, R.I., Yannarell, A.C. et al. Molecular Ecology Of Macrolide–Lincosamide–Streptogramin B Methylases in Waste Lagoons and Subsurface Waters Associated with Swine Production. Microb Ecol 59, 487–498 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9610-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9610-0