Abstract
Characterization of complex microbial communities is frequently based on the examination of polymerase chain reaction amplified sequences from a single phylogenetic marker, usually the 16S rRNA gene. However, this commonly used target often does not offer robust resolution of species or sub-species and is thus not a sufficiently informative target for understanding microbial population dynamics occurring at the strain level. We have used the cpn60 universal target sequence to characterize Enterococcus isolates from feces of growing pigs and have shown that sub-species groups, not detected using 16S rRNA sequences, can be resolved. Furthermore, groups resolved by cpn60-based phylogenetic analysis have distinct phenotypes. We report changes in the structure and function of Enterococcus communities in pig feces sampled from individual animals at three times, from suckling through to maturity. Enterococcus faecalis was largely replaced by Enterococcus hirae between suckling and 9 weeks of age, and a shift from one sub-species group of E. hirae to another was observed in all animals between 9 and 15 weeks. Conversely, E. faecalis strains remained consistent throughout the study period. Our results demonstrate that cpn60 sequences can be used to detect strain level changes in Enterococcus populations during succession in the fecal microbiota of growing pigs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aakra A, Nyquist OL, Snipen L, Reiersen TS, Nes IF (2007) Survey of genomic diversity among Enterococcus faecalis strains by microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2207
Acinas SG, Klepac-Ceraj V, Hunt DE, Pharino C, Ceraj I, Distel DL, Polz MF (2004) Fine-scale phylogenetic architecture of a complex bacterial community. Nature 430:551
Acinas SG, Sarma-Rupavtarm R, Klepac-Ceraj V, Polz MF (2005) PCR-induced sequence artifacts and bias: insights from comparison of two 16S rRNA clone libraries constructed from the same sample. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8966
Blattner FR, Plunkett G 3rd, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF, Gregor J, Davis NW, Kirkpatrick HA, Goeden MA, Rose DJ, Mau B, Shao Y (1997) The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453
Brousseau R, Hill JE, Prefontaine G, Goh SH, Harel J, Hemmingsen SM (2001) Streptococcus suis serotypes characterized by analysis of chaperonin 60 gene sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4828
Cohan FM (2002) What are bacterial species? Annu Rev Microbiol 56:457
Devriese LA, Hommez J, Pot B, Haesebrouck F (1994) Identification and composition of the streptococcal and enterococcal flora of tonsils, intestines and faeces of pigs. J Appl Bacteriol 77:31
Devriese LA, Pot B, Collins MD (1993) Phenotypic identification of the genus Enterococcus and differentiation of phylogenetically distinct enterococcal species and species groups. J Appl Bacteriol 75:399
Dorsch M, Stackebrandt E (1992) Some modifications in the procedure of direct sequencing of PCR amplified 16S rDNA. J Microbiol Methods 16:271
Dumonceaux TJ, Hill JE, Hemmingsen SM, Van Kessel AG (2006) Characterization of intestinal microbiota and response to dietary virginiamycin supplementation in the broiler chicken. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2815
Dumonceaux TJ, Hill JE, Pelletier C, Paice MG, Van Kessel AG, Hemmingsen SM (2006) Molecular characterization of microbial communities in Canadian pulp and paper activated sludge and quantification of a novel Thiothrix eikelboomii-like bulking filament. Can J Microbiol 52:494
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (Phylogeny Infererence Package) version 3.5c, distributed by the author. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle
Gans J, Wolinsky M, Dunbar J (2005) Computational improvements reveal great bacterial diversity and high metal toxicity in soil. Science 309:1387
Goh SH, Facklam RR, Chang M, Hill JE, Tyrrell GJ, Burns EC, Chan D, He C, Rahim T, Shaw C, Hemmingsen SM (2000) Identification of Enterococcus species and phenotypically similar Lactococcus and Vagococcus species by reverse checkerboard hybridization to chaperonin 60 gene sequences. J Clin Microbiol 38:3953
Hill JE, Goh SH, Money DM, Doyle M, Li A, Crosby WL, Links M, Leung A, Chan D, Hemmingsen SM (2005) Characterization of vaginal microflora of healthy, nonpregnant women by chaperonin-60 sequence-based methods. Am J Obstet Gynecol 193:682
Hill JE, Hemmingsen SM, Goldade BG, Dumonceaux TJ, Klassen J, Zijlstra RT, Goh SH, Van Kessel AG (2005) Comparison of ileum microflora of pigs fed corn-, wheat-, or barley-based diets by chaperonin-60 sequencing and quantitative PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:867
Hill JE, Paccagnella A, Law K, Melito PL, Woodward DL, Price DL, Ng L-K, Hemmingsen SM, Goh SH (2006) Identification of Campylobacter spp. and discrimination from Helicobacter and Arcobacter spp. by direct sequencing of PCR-amplified cpn60 sequences and comparison to cpnDB, a chaperonin reference sequence database. J Med Microbiol 55:393
Hill JE, Penny SL, Crowell KG, Goh SH, Hemmingsen SM (2004) cpnDB: a chaperonin sequence database. Genome Res 14:1669
Hill JE, Seipp RP, Betts M, Hawkins L, Van Kessel AG, Crosby WL, Hemmingsen SM (2002) Extensive profiling of a complex microbial community by high-throughput sequencing. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3055
Inoue R, Tsukahara T, Nakanishi N, Ushida K (2005) Development of the intestinal microbiota in the piglet. J Gen Appl Microbiol 51:257
Jian W, Zhu L, Dong X (2001) New approach to phylogenetic analysis of the genus Bifidobacterium based on partial HSP60 gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1633
Jordan IK, Rogozin IB, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (2002) Microevolutionary genomics of bacteria. Theor Popul Biol 61:435
Kohara T, Hayashi S, Hamatsuka J, Nishitani Y, Masuda Y, Osawa R (2007) Intra-specific composition and succession of Bifidobacterium longum in human feces. Syst Appl Microbiol 30:165
Mackie RI, Sghir A, Gaskins HR (1999) Developmental microbial ecology of the neonatal gastrointestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr 69:1035S
Maidak BL, Cole JR, Lilburn TG, Parker CT Jr, Saxman PR, Farris RJ, Garrity GM, Olsen GJ, Schmidt TM, Tiedje JM (2001) The RDP-II (Ribosomal Database Project). Nucleic Acids Res 29:173
Makarova KS, Koonin EV (2007) Evolutionary genomics of lactic acid bacteria. J Bacteriol 189:1199
McBride SM, Fischetti VA, Leblanc DJ, Moellering RC Jr, Gilmore MS (2007) Genetic diversity among Enterococcus faecalis. PLoS ONE 2:e582
Minana-Galbis D, Urbizu-Serrano A, Farfan M, Fuste MC, Loren JG (2009) Phylogenetic analysis and identification of Aeromonas species based on sequencing of the cpn60 universal target. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. doi:ijs.0.005413-005410
Ott SJ, Musfeldt M, Wenderoth DF, Hampe J, Brant O, Folsch UR, Timmis KN, Schreiber S (2004) Reduction in diversity of the colonic mucosa associated bacterial microflora in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 53:685
Paulsen IT, Banerjei L, Myers GS, Nelson KE, Seshadri R, Read TD, Fouts DE, Eisen JA, Gill SR, Heidelberg JF, Tettelin H, Dodson RJ, Umayam L, Brinkac L, Beanan M, Daugherty S, DeBoy RT, Durkin S, Kolonay J, Madupu R, Nelson W, Vamathevan J, Tran B, Upton J, Hansen T, Shetty J, Khouri H, Utterback T, Radune D, Ketchum KA, Dougherty BA, Fraser CM (2003) Role of mobile DNA in the evolution of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. Science 299:2071
Perna NT, Plunkett G 3rd, Burland V, Mau B, Glasner JD, Rose DJ, Mayhew GF, Evans PS, Gregor J, Kirkpatrick HA, Posfai G, Hackett J, Klink S, Boutin A, Shao Y, Miller L, Grotbeck EJ, Davis NW, Lim A, Dimalanta ET, Potamousis KD, Apodaca J, Anantharaman TS, Lin J, Yen G, Schwartz DC, Welch RA, Blattner FR (2001) Genome sequence of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Nature 409:529
Perriere G, Gouy M (1996) WWW-query: an on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Biochimie 78:364
Pieper R, Janczyk P, Zeyner A, Smidt H, Guiard V, Souffrant WB (2008) Ecophysiology of the developing total bacterial and Lactobacillus communities in the terminal small intestine of weaning piglets. Microb Ecol 56:474
Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A (2000) EMBOSS: the European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet 16:276
Savage DC (1977) Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Microbiol 31:107
Solheim M, Aakra A, Snipen LG, Brede DA, Nes IF (2009) Comparative genomics of Enterococcus faecalis from healthy Norwegian infants. BMC Genomics 10:194
Staden R, Beal KF, Bonfield JK (2000) The Staden package, 1998. Methods Mol Biol 132:115
Swords WE, Wu CC, Champlin FR, Buddington RK (1993) Postnatal changes in selected bacterial groups of the pig colonic microflora. Biol Neonate 63:191
Wall R, Fitzgerald G, Hussey S, Ryan T, Murphy B, Ross P, Stanton C (2007) Genomic diversity of cultivable Lactobacillus populations residing in the neonatal and adult gastrointestinal tract. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:127
Xu J (2006) Microbial ecology in the age of genomics and metagenomics: concepts, tools, and recent advances. Mol Ecol 15:1713
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge John Harding and Crissie Baker for collection of pig fecal samples and Champika Fernando for assistance with statistical analysis. Funding for this work was provided by an NSERC Discovery Grant and a grant from the WCVM Vitamin Fund to JEH. Additional support was provided by NSERC Undergraduate Research Award (AHR) and the University of Saskatchewan (CJV & ARD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This manuscript is dedicated to Dr. Roland Brousseau who passed away too soon in May 2008.
Catherine J. Vermette and Amanda H. Russell contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure 1
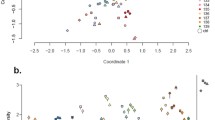
a Carbon source utilization profiles for Enterococcus hirae isolates. Only carbon sources that were utilized by at least one isolate are shown. Assignment to strain group is based on cpn60 phylogenetic analysis (Fig. 2). b Carbon source utilization profiles for Enterococcus faecalis isolates. Only carbon sources that were utilized by at least one isolate are shown. Assignment to strain group is based on cpn60 phylogenetic analysis (Fig. 2) (XLS 160 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vermette, C.J., Russell, A.H., Desai, A.R. et al. Resolution of Phenotypically Distinct Strains of Enterococcus spp. in a Complex Microbial Community Using cpn60 Universal Target Sequencing. Microb Ecol 59, 14–24 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9601-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9601-1