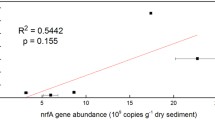
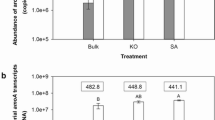
Abstract
Levels of inorganic nitrogen species (ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate), ammonia oxidation potential (AOP), and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) were studied in the sediments of a 50-km-long segment of an ephemeral stream in the Negev desert, receiving untreated wastewater. Water analysis in downstream sampling points showed reductions of 91.7% in biological oxygen demand, 87.7% in chemical oxygen demand, 73.9% in total nitrogen, and 72.8% in total ammonia nitrogen. Significant AOP levels in the sediment were detected mainly in the fall and spring seasons. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of AOB 16S rRNA gene fragments showed that in most sampling points, the streambed was dominated by Nitrosospira cluster 3 strains similar to those dominating the stream bank’s soils and sediments in nearby springs. Nitrosomonas strains introduced by discharged wastewater and others dominated some sections of the stream characterized by high organic carbon levels. The results suggest that climatic conditions in the Negev desert select for AOB belonging to Nitrosospira cluster 3, and these conditions dominate the aquatic environment effect along most of the stream sections. In addition, the nitrification–denitrification processes were not sufficient to reduce nitrogen levels in the sediment and prevent the eutrophication of some sections of the stream ecosystem. Thus, the discharge of high nitrogen wastewater into desert streams should be done carefully as it may endanger the already fragile ecosystem.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aakra A, Utaker JB, Nes IF, Bakken LR (1999) An evaluated improvement of the extinction dilution method for isolation of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 39:23–31
Anderson NJ, Rippey B (1994) Monitoring lake recovery from point-source eutrophication: the use of diatom-inferred epilimnetic total phosphorus and sediment chemistry. Freshwater Biol 32:625–639
APHA (1985) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. APHA AWWA WPCF, Washington
Avrahami S, Conrad R, Braker G (2002) Effect of soil ammonium concentration on N2O release and on the community structure of ammonia oxidizers and denitrifiers. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5685–5692
Avrahami S, Liesack W, Conrad R (2003) Effects of temperature and fertilizer on activity and community structure of soil ammonia oxidizers. Environ Microbiol 5:691–705
Bothe H, Jost G, Schloter M, Ward BB, Witzel K-P (2000) Molecular analysis of ammonia oxidation and denitrification in natural environments. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:673–690
Boyd CE (1995) Bottom soils, sediment and pond aquaculture. Chapman & Hall, New York
Carpenter SR, Caraco NF, Correll DL, Howarth RW, Sharpley AN, Smith VH (1998) Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol Appl 8:559–568
Cébron A, Coci M, Garnier J, Laanbroek HJ (2004) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoretic analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacterial community structure in the lower Seine River: impact of Paris wastewater effluents. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6726–6737
De Bie M, Speksnijder AGCL, Kowalchuk GA, Schurman T, Zwart G, Stephen JR, Diekmann OE, Laanbroek HJ (2001) Shifts in the dominant populations of ammonia-oxidizing beta -subclass Proteobacteria along the eutrophic Schelde Estuary. Aquatic Microb Ecol 23:225–236
Ferree MA, Shannon RD (2001) Evaluation of a second derivative UV/visible spectroscopy technique for nitrate and total nitrogen analysis of wastewater samples. Water Res 35:327–332
Fromin N, Hamelin J, Tarnawski S, Roesti D, Jourdain-Miserez K, Forestier N, Teyssier-Cuvelle S, Gillet M, Aragno F, Rossi P (2002) Statistical analysis of denaturing gel electrophoresis (DGE) fingerprinting patterns. Environ Microbiol 4:634–643
Geets J, Boon N, Verstraete W (2006) Strategies of aerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria for coping with nutrient and oxygen fluctuations. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 58:1–13
Gerards S, Duyts H, Laanbroek HJ (1998) Ammonium-induced inhibition of ammonium-starved Nitrosomonas europaea cells in soil and sand slurries. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 26:269–280
Hassan MA, Egozi R (2001) Impact of wastewater discharge on the channel morphology of ephemeral streams. Earth Surf Processes Landf 26:1285–1302
Hastings RC, Ceccherini MT, Miclaus N, Saunders JR, Bazzicalupo M, McCarthy AJ (1997) Direct molecular biological analysis of ammonia oxidising bacteria populations in cultivated soil plots treated with swine manure. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 23:45–54
Horz H-P, Barbrook A, Field CB, Bohannan BJM (2004) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria respond to multifactorial global change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:15136–15141
Jongman RHG, Ter Braak CJF, Van Tongeren OFR (1995) Data analysis in community and landscape ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Koops H-P, Pommerening-Roser A (2001) Distribution and ecophysiology of the nitrifying bacteria emphasizing cultured species. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 37:1–9
Koops H-P, Purkhold U, Pommerening-Roser A, Timmermann G, Wagner M (2003) The lithoautotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. In: Dworkin M et al. (eds) The prokaryotes: an evolving electronic resource for the microbiological community, 3rd edn, release 3, 13. Springer, New-York. http://link.springer-ny.com/link/service/books/10125/
Kowalchuk G, Stephen J, De Boer W, Prosser J, Embley T, Woldendorp JW (1997) Analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria of the beta subdivision of the class Proteobacteria in coastal sand dunes by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and sequencing of PCR-amplified 16S ribosomal DNA fragments. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1489–1497
Kowalchuk GA, Bodelier PLE, Heilig GHJ, Stephen JR, Laanbroek HJ (1998) Community analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, in relation to oxygen availability in soils and root-oxygenated sediments, using PCR, DGGE and oligonucleotide probe hybridization. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 27:339–350
Kowalchuk GA, Stienstra AW, Heilig GHJ, Stephen JR, Woldendorp JW (2000) Changes in the community structure of ammonia oxidizing bacteria during secondary succession of calcareous grasslands. Environ Microbiol 2:99–110
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR (2001) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: a model for molecular microbial ecology. Annu Rev of Microbiol 55:485–529
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Legendre P, Gallagher E (2001) Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 129:271–280
Leps J, Smilauer P (1999) Multivariate analysis of ecological data. Faculty of Biological Sciences, University of South Bohemia, Ceske Budejovice
Mahmood S, Freitag TE, Prosser JI (2006) Comparison of PCR primer-based strategies for characterization of ammonia oxidizer communities in environmental samples. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 56:482–493
McCaig AE, Embley TM, Prosser JI (1994) Molecular analysis of enrichment cultures of marine ammonia oxidisers. FEMS Microbiol Lett 120:363–367
Montuelle B, Balandras B, Volat B, Feray C (2003) Effect of wastewater treatment plant discharges on the functional nitrifying communities in river sediments. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manag 6:381–390
Nakamura Y, Satoh H, Kindaichi T, Okabe S (2006) Community structure, abundance, and in situ activity of nitrifying bacteria in river sediments as determined by the combined use of molecular techniques and microelectrodes. Environ Sci Technol 40:1532–1539
Nejidat A (2005) Nitrification and occurrence of salt-tolerant nitrifying bacteria in the Negev desert soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52:21–29
Nicol GW, Schleper C (2006) Ammonia-oxidizing Crenarchaeota: important players in the nitrogen cycle? Trends Microbiol 14:207–212
Oved T, Shaviv A, Goldrath T, Mandelbaum RT Minz D (2001) Influence of effluent irrigation on community composition and function of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3426–3433
Princic A, Mahne I, Megusar F, Paul EA, Tiedje JM (1998) Effects of pH and oxygen and ammonium concentrations on the community structure of nitrifying bacteria from wastewater. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3584–3590
Purkhold U, Pommerening-Roser A, Juretschko S, Schmid MC, Koops H-P, Wagner M (2000) Phylogeny of all recognized species of ammonia oxidizers based on comparative 16S rRNA and amoA sequence analysis: implications for molecular diversity surveys. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5368–5382
Shapira DA, Mazor G (2004) Pollutants loadings in streams: a comparison between the years 1994, 2000, 2001 and 2003. The Israeli Ministry of the Environment, Jerusalem in Hebrew
Shoaf W, Lium B (1976) Improved extraction of chlorophyll a and b from algae using dimethyl sulfoxide. Limnol Oceanogr 21:926–928
Smith VH, Tilman GD, Nekola JC (1999) Eutrophication: impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ Pollut 100:179–196
Soil and Plant Analysis Council (2000) Soil analysis handbook of reference methods. CRC, Boca Raton
Stamatakis A, Ludwig T, Meier H (2005) RAxML-III: a fast program for maximum likelihood-based inference of large phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 21(4):456–463
Stehr G, Bottcher B, Dittberner P, Rath G, Koops H-P (1995) The ammonia-oxidizing nitrifying population of the River Elbe estuary. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 17:177–186
Stephen JR, Kowalchuk GA, Brun M-AV, McCaig AE, Phillips CJ, Embley TM, Prosser JI (1998) Analysis of beta -subgroup proteobacterial ammonia oxidizer populations in soil by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis and hierarchical phylogenetic probing. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2958–2965
Tal A, Al Khatib N, Asaf L, Assi A, Nassar A, Abu Sadah M, Gazith A, Laronne JB, Zeev R, Hirshkovitz Y, Halawani D, Nagouker N, Angel R, Akerman H, Diabat M (2006) Watershed modeling: biomonitoring and economic analysis to determine optimal restoration strategies for transboundary streams. AIES, Eilot
Ter Braak CJF, Smilauer P (1998) Canoco 4. Centre for Biometry Wageningen, Wageningen
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wilhelm R, Abeliovich A, Nejidat A (1998) Effect of long-term ammonia starvation on the oxidation of ammonia and hydroxylamine by Nitrosomonas europaea. J Biochem (Tokyo) 124:811–815
Yuan F, Ran W, Shen Q, Wang D (2005) Characterization of nitrifying bacteria communities of soils from different ecological regions of China by molecular and conventional methods. Biol Fertil Soils 41:22–27
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Middle East Research and Cooperation (MERC) Program of the U.S. Agency for International Development: Buraeu for Economic Growth, Agriculture and Trade. Project number M23-019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angel, R., Asaf, L., Ronen, Z. et al. Nitrogen Transformations and Diversity of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria in a Desert Ephemeral Stream Receiving Untreated Wastewater. Microb Ecol 59, 46–58 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9555-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-009-9555-3