Abstract
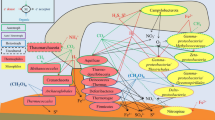
Methanogenic degradation of organic matter is an important microbial process in lake sediments. Temperature may affect not only the rate but also the pathway of CH4 production by changing the activity and the abundance of individual microorganisms. Therefore, we studied the function and structure of a methanogenic community in anoxic sediment of Lake Dagow, a eutrophic lake in north-eastern Germany. Incubation of sediment samples (in situ 7.5°C) at increasing temperatures (4, 10, 15, 25, 30°C) resulted in increasing production rates of CH4 and CO2 and in increasing steady-state concentrations of H2. Thermodynamic conditions for H2/CO2 -dependent methanogenesis were only exergonic at 25 and 30°C. Inhibition of methanogenesis with chloroform resulted in the accumulation of methanogenic precursors, i.e., acetate, propionate, and isobutyrate. Mass balance calculations indicated that less CH4 was formed via H2 at 4°C than at 30°C. Conversion of 14CO2 to 14CH4 also showed that H2/CO2 -dependent methanogenesis contributed less to total CH4 production at 4°C than at 30°C. [2–14 C]Acetate turnover rates at 4°C accounted for a higher percentage of total CH4 production than at 30°C. Collectively, these results showed a higher contribution of H2-dependent methanogenesis and a lower contribution of acetate-dependent methanogenesis at high versus low temperature. The archaeal community was characterized by cloning, sequencing, and phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA genes retrieved from the sediment. Sequences were affiliated with Methanosaetaceae, Methanomicrobiaceae, and three deeply branching euryarchaeotal clusters, i.e., group III, Rice cluster V, and a novel euryarchaeotal cluster, the LDS cluster. Terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) analysis showed that 16S rRNA genes affiliated to Methanosaetaceae (20–30%), Methanomicrobiaceae (35–55%), and group III (10–25%) contributed most to the archaeal community. Incubation of the sediment at different temperatures (4–30°C) did not result in a systematic change of the archaeal community composition, indicating that change of temperature primarily affected the activity rather than the structure of the methanogenic community.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
GB Avery CS Martens (1999) ArticleTitleControls on the stable carbon isotopic composition of biogenic methane produced in a tidal freshwater estuarine sediment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63 1075–1082 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00315-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXks12msb4%3D
GB Avery RD Shannon JR White CS Martens MJ Alperin (2003) ArticleTitleControls on methane production in a tidal freshwater estuary and a peatland: methane production via acetate fermentation and CO2 reduction. Biogeochemistry 62 19–37 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1021128400602
SM Barns CF Delwiche JD Palmer NR Pace (1996) ArticleTitlePerspectives on archaeal diversity, thermophily and monophyly from environmental rRNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93 9188–9193 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.93.17.9188 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xlt1Cntrc%3D Occurrence Handle8799176
G Billen (1982) Modelling the processes of organic matter degradation and nutrients recycling in sedimentary systems. DB Nedwell CM Brown (Eds) Sediment Microbiology Academic Press New York 1552–1982
J Brosius ML Palmer PJ Kennedy HR Noller (1978) ArticleTitleComplete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75 4801–4805 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1MXmsl2gtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle368799
DG Capone RP Kiene (1988) ArticleTitleComparison of microbial dynamics in marine and freshwater sediments: contrasts in anaerobic carbon catabolism. Limnol Oceanogr 33 725–749 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXlslGktbc%3D
T Cappenberg RA Prins (1974) ArticleTitleInterrelations between sulfate-reducing and methane-producing bacteria in bottom deposits of a fresh-water lake. III. Experiments with 14C-labeled substrates. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 40 457–469 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXot1ymuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle4546838
P Casper (1992) ArticleTitleMethane production in lakes of different trophic state. Arch Hydrobiol Beih Ergebn Limnol 37 149–154 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXhvF2lsrc%3D
P Casper (1996) ArticleTitleMethane production in littoral and profundal sediments of an oligotrophic and a eutrophic lake. Arch Hydrobiol Beih Ergebn Limnol 48 253–259 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XntFGrtbc%3D
OC Chan M Wolf D Hepperle P Casper (2002) ArticleTitleMethanogenic archaeal community in the sediment of an artificially partitioned acidic bog lake. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 42 119–129 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-6496(02)00310-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xnt1KmtLs%3D
KJ Chin R Conrad (1995) ArticleTitleIntermediary metabolism in methanogenic paddy soil and the influence of temperature. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 18 85–102 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-6496(95)00042-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXptVegt7g%3D
KJ Chin T Lueders MW Friedrich M Klose R Conrad (2004) ArticleTitleArchaeal community structure and pathway of methane formation on rice roots. Microb Ecol 47 59–67
KJ Chin T Lukow R Conrad (1999) ArticleTitleEffect of temperature on structure and function of the methanogenic archaeal community in an anoxic rice field soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 65 2341–2349 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjs12gs7w%3D Occurrence Handle10347011
D Christensen TH Blackburn (1982) ArticleTitleTurnover of 14C-labelled acetate in marine sediments. Mar Biol 71 113–119
R Conrad (1999) ArticleTitleContribution of hydrogen to methane production and control of hydrogen concentrations in methanogenic soils and sediments [review]. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 28 193–202 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-6496(98)00086-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhvF2nsro%3D
R Conrad F Bak HJ Seitz B Thebrath HP Mayer H Schütz (1989) ArticleTitleHydrogen turnover by psychrotrophic homoacetogenic and mesophilic methanogenic bacteria in anoxic paddy soil and lake sediment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62 285–294 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-1097(89)90010-4 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXltFaitrc%3D
R Conrad TJ Phelps JG Zeikus (1985) ArticleTitleGas metabolism evidence in support of juxtapositioning between hydrogen producing and methanogenic bacteria in sewage sludge and lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 50 595–601 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XhtVWrtA%3D%3D
R Conrad B Schink TJ Phelps (1986) ArticleTitleThermodynamics of H2-producing and H2-consuming metabolic reactions in diverse methanogenic environments under in-situ conditions. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38 353–360 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-1097(86)90013-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXpvFWhug%3D%3D
R Conrad H Schütz (1988) Methods of studying methanogenic bacteria and methanogenic activities in aquatic environments. B Austin (Eds) Methods in Aquatic Bacteriology Wiley Chichester, UK 301–343
R Conrad B Wetter (1990) ArticleTitleInfluence of temperature on energetics of hydrogen metabolism in homoacetogenic, methanogenic, and other anaerobic bacteria. Arch Microbiol 155 94–98 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXlvVKktA%3D%3D
ET Degens K Mopper (1975) ArticleTitleEarly diagenesis of organic matter in marine salts. Soil Sci 119 65–72 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXhsVejs7g%3D
MA Dojka P Hugenholtz SK Haack NR Pace (1998) ArticleTitleMicrobial diversity in a hydrocarbon- and chlorinated-solvent-contaminated aquifer undergoing intrinsic bioremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 64 3869–3877 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXms1entb4%3D Occurrence Handle9758812
A Fey KJ Chin R Conrad (2001) ArticleTitleThermophilic methanogens in rice field soil. Environ Microbiol 3 295–303 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1462-2920.2001.00195.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXlt1eht70%3D Occurrence Handle11422316
A Fey R Conrad (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of temperature on carbon and electron flow and on the archaeal community in methanogenic rice field soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 66 4790–4797 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.66.11.4790-4797.2000 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXnvFyrtLw%3D Occurrence Handle11055925
K Glissmann R Conrad (2000) ArticleTitleFermentation pattern of methanogenic degradation of rice straw in anoxic paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31 117–126 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-6496(99)00091-4 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXltVCmuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10640665
YS Go SK Han IG Lee TY Ahn (2000) ArticleTitleDiversity of the domain Archaea as determined by 16S rRNA gene analysis in the sediments of Lake Soyang. Arch Hydrobiol 149 459–466 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhvV2l
R Grosskopf PH Janssen W Liesack (1998) ArticleTitleDiversity and structure of the methanogenic community in anoxic rice paddy soil microcosms as examined by cultivation and direct 16S rRNA gene sequence retrieval. Appl Environ Microbiol 64 960–969 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXhs1art74%3D Occurrence Handle9501436
TM Hoehler MJ Alperin DB Albert CS Martens (1998) ArticleTitleThermodynamic control on hydrogen concentrations in anoxic sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62 1745–1756 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00106-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXkvFWhtrc%3D
MSM Jetten AJM Stams AJB Zehnder (1990) ArticleTitleAcetate threshold and acetate activating enzymes in methanogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73 339–344 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-1097(90)90768-L Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXkvFCmur4%3D
G Jurgens F Glockner R Amann A Saano L Montonen M Likolammi U Munster (2000) ArticleTitleIdentification of novel Archaea in bacterioplankton of a boreal forest lake by phylogenetic analysis and fluorescent in situ hybridization. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 34 45–56 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-6496(00)00073-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXosVyrtL8%3D Occurrence Handle11053735
OR Kotsyurbenko AN Nozhevnikova GA Zavarzin (1993) ArticleTitleMethanogenic degradation of organic matter by anaerobic bacteria at low temperature. Chemosphere 27 1745–1761 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0045-6535(93)90155-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXkt12m
KM Kuivila JW Murray AH Devol (1989) ArticleTitleMethane production, sulfate reduction and competition for substrates in the sediments of Lake Washington. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53 409–416 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(89)90392-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXktFaitLs%3D
WT Liu TL Marsh H Cheng LJ Forney (1997) ArticleTitleCharacterization of microbial diversity by determining terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms of genes encoding 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63 4516–4522 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXnt12ntbs%3D Occurrence Handle9361437
BJ MacGregor DP Moser EW Alm KH Nealson DA Stahl (1997) ArticleTitleCrenarchaeota in Lake Michigan sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 63 1178–1181 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhsFSms7o%3D Occurrence Handle9055434
AN Nozhevnikova OR Kotsyurbenko MV Simankova (1994) Acetogenesis at low temperature. HL Drake (Eds) Acetogenesis Chapman & Hall New York 416–431
B Nüsslein KJ Chin W Eckert R Conrad (2001) ArticleTitleEvidence for anaerobic syntrophic acetate oxidation during methane production in the profundal sediment of subtropical Lake Kinneret (Israel). Environ Microbiol 3 460–470 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1462-2920.2001.00215.x Occurrence Handle11553236
B Nüsslein R Conrad (2000) ArticleTitleMethane production in eutrophic Lake Plusssee: seasonal change, temperature effect and metabolic processes in the profundal sediment. Arch Hydrobiol 149 597–623
B Nüsslein W Eckert R Conrad (2003) ArticleTitleStable isotope biogeochemistry of methane formation in profundal sediments of Lake Kinneret (Israel). Limnol Oceanogr 48 1439–1446
RJ Parkes J Taylor D Joerck-Ramberg (1984) ArticleTitleDemonstration, using Desulfobacter sp., of two pools of acetate with different biological availabilities in marine pore water. Mar Biol 83 271–276 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXkt1Krtrg%3D
S Schulz R Conrad (1996) ArticleTitleInfluence of temperature on pathways to methane production in the permanently cold profundal sediment of Lake Constance. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 20 1–14 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-6496(96)00009-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjsVOktbw%3D
K Smalla N Cresswell LC Mendonca-Hagler A Wolters JD van Elsas (1993) ArticleTitleRapid DNA extraction protocol from soil for polymerase chain reaction-mediated amplification. J Appl Bacteriol 74 78–85 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXit1Kks7g%3D
AJM Stams (1994) ArticleTitleMetabolic interactions between anaerobic bacteria in methanogenic environments. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 66 271–294 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXjs1yhu7s%3D Occurrence Handle7747937
O Strunk W Ludwig (2000) ARB Software Package Version 2.5b Technische Universität München Germany
B Thamdrup DE Canfield (2000) Benthic respiration in aquatic sediments. OE Sala RB Jackson HA Mooney RW Howarth (Eds) Methods in Ecosystem Science Springer New York 86–103
RK Thauer K Jungermann K Decker (1977) ArticleTitleEnergy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 41 100–180 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXktVajtLs%3D Occurrence Handle860983
S Weber T Lueders MW Friedrich R Conrad (2001) ArticleTitleMethanogenic populations involved in the degradation of rice straw in anoxic paddy soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38 11–20 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-6496(01)00168-4 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XitVyi
P Westermann (1994) ArticleTitleThe effect of incubation temperature on steady-state concentrations of hydrogen and volatile fatty acids during anaerobic degradation in slurries from wetland sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 13 295–302 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-6496(94)90067-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXit1Kjtrs%3D
CR Woese O Kandler ML Wheelis (1990) ArticleTitleTowards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87 4576–4579 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BB1c%2FktFw%3D Occurrence Handle2112744
AJB Zehnder (1978) Ecology of methane formation. R Mitchell (Eds) Water Pollution Microbiology Wiley New York 349–376
K Zepp Falz C Holliger R Grosskopf W Liesack AN Nozhevnikova B Müller B Wehrli D Hahn (1999) ArticleTitleVertical distribution of methanogens in the anoxic sediment of Rotsee (Switzerland). Appl Environ Microbiol 65 2402–2408 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3nvVSnuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10347020
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Nüsslein for supplying the sediment samples of Lake Plußsee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glissman, K., Chin, KJ., Casper, P. et al. Methanogenic Pathway and Archaeal Community Structure in the Sediment of Eutrophic Lake Dagow: Effect of Temperature. Microb Ecol 48, 389–399 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-2027-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-2027-2