Abstract
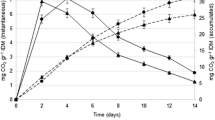
Low average temperatures and temperature fluctuations in temperate soils challenge the efficacy of microbial strains used for clean up of pollutants. In this study, we investigated the cold tolerance of Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6, a microorganism previously shown to degrade high concentrations of 4-chlorophenol at 28°C. Luciferase activity from a luc-tagged derivative of the strain (A6L) was used to monitor the metabolic status of the population during 4-chlorophenol degradation. The A6L strain could degrade 200–300 μg mL−1 4-chlorophenol in pure cultures incubated at 5°C, although rates of degradation, growth and the metabolic status of the cells were lower at 5°C compared to 28°C. When subjected to temperature fluctuations between 5 and 28°C, A6L continued to degrade 4-chlorophenol and remained active. In soil microcosm experiments, the degradation rates were significantly faster the first week at 28°C, compared to 5°C. However, this difference was no longer seen after 7 days, and equally low 4-chlorophenol concentrations were reached after 17 days at both temperatures. During 4-chlorophenol degradation in soil, CFU and luciferase activity values remained constant at both 5 and 28°C. However, once most of the 4-chlorophenol was degraded, both values decreased by 1–1.5 logarithmic values at 28°C, whereas they remained constant at 5°C, indicating a high survival of the cells at low temperatures. Because of the ability of A. chlorophenolicus A6 to degrade high concentrations of 4-chlorophenol at 5°C, together with its tolerance to temperature fluctuations and stress conditions found in soil, this strain is a promising candidate for bioaugmentation of chlorophenol-contaminated soil in temperate climates.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Alexander (1999) Inoculation. Biodegradation and Bioremediation, 2nd ed. Academic Press New York 299–323
M Alexander BK Lustigman (1966) ArticleTitleEffect of chemical structure on microbial degradation of substituted benzenes. J Agric Food Chem 14 410–413 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF28XksFWmsb8%3D
RM Atlas R Unterman (1999) Bioremediation. A Demain J Davies (Eds) Manual of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2nd ed. ASM Press Washington, DC 666–681
J Balfanz H-J Rehm (1991) ArticleTitleBiodegradation of 4-chlorophenol by adsorptive immobilized Alcaligenes sp. A 7-2 in soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35 662–668 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXlsFCqtrc%3D Occurrence Handle1367580
JA Baross RY Morita (1978) Microbial life at low temperatures: ecological aspects. D Kushner (Eds) Microbial Life in Extreme Environments Academic Press London 9–71
F Berger N Morellet F Menu P Potier (1996) ArticleTitleCold shock and cold acclimation proteins in the psychrotrophic bacterium Arthrobacter globiformis SI55. J Bacteriol 178 2999–3007 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xjt1Kmsbs%3D Occurrence Handle8655472
NT Blackburn AG Seech JT Trevors (1994) ArticleTitleSurvival and transport of lac-lux marked Pseudomonas fluorescens strain in uncontaminated and chemically contaminated soil. Sys Appl Microbiol 17 574–580
RL Crawford WW Mohn (1985) ArticleTitleMicrobiological removal of pentachlorophenol from soil using a Flavobacterium. Enzyme Microb Technol 7 617–620 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0141-0229(85)90031-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XkvVGjsg%3D%3D
RU Edgehill RK Finn (1983) ArticleTitleMicrobial treatment of soil to remove pentachlorophenol. Appl Environ Microbiol 45 1122–1125 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXhsVSgs74%3D
AM Elväng K Westerberg C Jernberg JK Jansson (2001) ArticleTitleUse of green fluorescent protein and luciferase biomarkers to monitor survival and activity of Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6 cells during degradation of 4-chlorophenol in soil. Environ Microbiol 3 32–42 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1462-2920.2001.00156.x Occurrence Handle11225721
BI Escher M Snozzi RP Schwarzenbach (1996) ArticleTitleUptake, speciation, and uncoupling activity of substituted phenols in energy transducing membranes. Environ Sci Technol 30 3071–3079 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es960153f Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xlt1eltr0%3D
A-M Gounot (1986) ArticleTitlePsychrophilic and psychrotrophic microorganisms. Experientia 42 1192–1197 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiD2Mvlt1Y%3D Occurrence Handle3536570
MM Häggblom R Valo (1995) Bioremediation of chlorophenol wastes. L Young C Cerniglia (Eds) Microbial Transformation and Degradation of Toxic Organic Chemicals Wiley-Liss New York 389–433
M Hebraud E Dubois P Potier J Labadie (1994) ArticleTitleEffect of growth temperatures on the protein levels in a psychrotrophic bacterium, Pseudomonas fragi. J Bacteriol 176 4017–4024 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXksFels7w%3D Occurrence Handle8021184
H-J Heipieper R Diefenbach H Keweloh (1992) ArticleTitleConversion of cis unsaturated fatty acids to trans, a possible mechanism for the protection of phenol-degrading Pseudomonas putida P8 from substrate toxicity. Appl Environ Microbiol 58 1847–1852 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XksVCgsro%3D Occurrence Handle1622260
C Jernberg JK Jansson (2002) ArticleTitleImpact of 4-chlorophenol contamination and/or inoculation with the 4-chlorophenol-degrading strain, Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6L, on soil bacterial community structure. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 42 387–397 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-6496(02)00356-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XoslGitbY%3D
PG Jones RA VanBogelen FC Neidhardt (1987) ArticleTitleInduction of proteins in response to low temperature in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 169 2092–2095 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXktVCjsro%3D Occurrence Handle3553157
CM Kramer MM Kory (1992) ArticleTitleBacteria that degrade p-chlorophenol isolated from a continuous culture system. Can J Microbiol 38 34–37 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XitlWmurw%3D Occurrence Handle1581863
MM Laine KS Jørgensen (1997) ArticleTitleEffective and safe composting of chlorophenol-contaminated soil in pilot scale. Environ Sci Technol 31 371–378 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es960176u Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmtVyjsw%3D%3D
K Leung D Errampalli M Cassidy H Lee JT Trevors H Okamura HJ Bach B Hall (1997) A case study of bioremediation of polluted soil: biodegradation and toxicity of chlorophenols in soil. Modern Soil Microbiology Marcel Dekker New York 577–605
S Liu JE Graham L Bigelow PDI Morse BJ Wilkinson (2002) ArticleTitleIdentification of Listeria monocytogenes genes expressed in response to growth at low temperature. Appl Environ Microbiol 68 1697–1705 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.68.4.1697-1705.2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XivFGltLw%3D Occurrence Handle11916687
S Liu JM Suflita (1993) ArticleTitleEcology and evolution of microbial populations for bioremediation. Trends Biotechnol 11 344–352 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXms1Kjsrk%3D Occurrence Handle7764181
ES Melin KT Järvinen JA Puhakka (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of temperature on chlorophenol biodegradation kinetics in fluidized-bed reactors with different biomass carriers. Wat Res 32 81–90 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00184-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXhvVCm
DB Nedwell (1999) ArticleTitleEffect of low temperature on microbial growth: lowered affinity for substrates limits growth at low temperature. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 30 101–111 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-6496(99)00030-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmt1emur8%3D Occurrence Handle10508935
ME Roberts WE Inniss (1992) ArticleTitleThe synthesis of cold shock proteins and cold acclimation proteins in the psychrophilic bacterium Aquaspirillum arcticum. Curr Microbiol 25 275–278 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXjs1Sj
NJ Russell (1984) ArticleTitleMechanisms of thermal adaptation in bacteria: blueprints for survival. TIBS 9 108–112 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0968-0004(84)90106-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXitVKiurs%3D
B Stenberg M Johansson M Pell K Sjödahl-Svensson J Stenström L Torstensson (1998) ArticleTitleMicrobial biomass and activities in soil as affected by frozen and cold storage. Soil Biol Biochem 30 393–402 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(97)00125-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXhvFWrsLc%3D
R Valo M Salkinoja-Salonen (1986) ArticleTitleBioreclamation of chlorophenol-contaminated soil by composting. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 25 68–75 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXhsFWlsro%3D
K Westerberg AM Elvöng E Stackebrandt JK Jansson (2000) ArticleTitleArthrobacter chlorophenolicus sp. nov., a new species capable of degrading high concentrations of 4-chlorophenol. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50 2083–2092 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXls1GgtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11155983
LG Whyte SJ Slagman F Pietrantonio L Bourbonniere SF Koval JR Lawrence WE Inniss CW Greer (1999) ArticleTitlePhysiological adaptations involved in alkane assimilation at a low temperature by Rhodococcus sp. strain Q15. Appl Environ Microbiol 65 2961–2968 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXktlemtL4%3D Occurrence Handle10388690
T-M Xie K Abrahamsson E Fogelqvist B Josefsson (1986) ArticleTitleDistribution of chlorophenolics in a marine environment. Environ Sci Technol 20 457–463 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XhsFGntrw%3D
Acknowledgment
This work was funded by The Swedish Foundation for Strategic Environmental Research (MISTRA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Backman, A., Jansson, J. Degradation of 4-Chlorophenol at Low Temperature and during Extreme Temperature Fluctuations by Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6. Microb Ecol 48, 246–253 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-2026-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-2026-3