Abstract
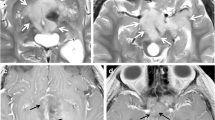
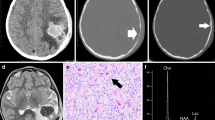
Objective. To compare 201thallium (T1) uptake and SPECT with MRI in children with brainstem gliomas. Materials and methods. Ten children with brainstem gliomas were prospectively evaluated by 201Tl-SPECT and MRI. Histological verification was obtained in eight children – two died prior to surgery. Quantitative thallium uptake index (UI) was obtainable in five cases and was compared to tumour grade. In addition, two patients with known benign brainstem lesions (neurofibromatosis and tuberculoma) were similarly prospectively evaluated. Results. All children with brainstem glioma accumulated thallium. (Mean U1 3.23, 100 % sensitivity). The single patient with brainstem tuberculoma also accumulated thallium (UI 2.80, 91.7 % specificity). There was no correlation between thallium uptake and tumour grade. Uptake could not be conclusively correlated with the following MR features: gadolinium enhancement, exophytic or intrinsic gliomas, necrosis and location of glioma within the brainstem. Conclusions. 201Tl-SPECT is a promising imaging adjunct in the assessment of childhood brainstem gliomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 May 1997 Accepted: 16 January 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadvi, S., Sheik Ebrahim, F. & Corr, P. The value of 201thallium-SPECT imaging in childhood brainstem gliomas. Pediatric Radiology 28, 575–579 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002470050418
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002470050418