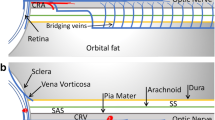
Abstract
Retinal hemorrhages are an integral part of the evaluation of abusive head trauma (AHT). Timely detection of retinal hemorrhage not only facilitates the diagnosis of AHT, but has the potential to prevent further abuse to the child and the siblings and to identify the abuser. The gold standard for diagnosing retinal hemorrhage is a dilated fundoscopy exam, which requires pharmacological dilation. As such, there is a small percentage of patients for whom the dilated fundoscopy exam might be delayed. Evolving literature suggests that MRI, specifically susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI), of the orbits might provide an alternative diagnostic tool for noninvasively detecting retinal hemorrhages, particularly when there is a delay in administering the dilated fundoscopy exam. In this paper we review the utility of SWI for detecting retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma, including discussion of diagnostic limitations and future research.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vinchon M, De Foort-Dhellemmes S, Desurmont M, Delestret I (2010) Confessed abuse versus witnessed accidents in infants: comparison of clinical, radiological, and ophthalmological data in corroborated cases. Childs Nerv Syst 26:637–645
Choudhary AK, Servaes S, Slovis TL et al (2018) Consensus statement on abusive head trauma in infants and young children. Pediatr Radiol 48:1048–1065
Bhardwaj G, Chowdhury V, Jacobs MB et al (2010) A systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of ocular signs in pediatric abusive head trauma. Ophthalmology 117:983–992.e17
Levin AV (2010) Retinal hemorrhage in abusive head trauma. Pediatrics 126:961–970
Caffey J (1974) The whiplash shaken infant syndrome: manual shaking by the extremities with whiplash-induced intracranial and intraocular bleedings, linked with residual permanent brain damage and mental retardation. Pediatrics 54:396–403
Guthkelch AN (1971) Infantile subdural haematoma and its relationship to whiplash injuries. Br Med J 2:430–431
Maguire SA, Kemp AM, Lumb RC, Farewell DM (2011) Estimating the probability of abusive head trauma: a pooled analysis. Pediatrics 128:550–564
Binenbaum G, Forbes BJ (2014) The eye in child abuse: key points on retinal hemorrhages and abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol 44:571–577
Kubal W (2008) Imaging of orbital trauma. Radiographics 28:1729–1739
Beavers AJ, Stagner AM, Allbery SM et al (2015) MR detection of retinal hemorrhages: correlation with graded ophthalmologic exam. Pediatr Radiol 45:1363–1371
Nandigam RNK, Dickerson BC (2009) MR imaging detection of cerebral microbleeds: effect of susceptibility-weighted imaging, section thickness, and field strength. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:338–343
Thamburaj K, Soni A, Frasier LD et al (2019) Susceptibility-weighted imaging of retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol 49:210–216
Zuccoli G, Panigrahy A, Haldipur A et al (2013) Susceptibility weighted imaging depicts retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma. Neuroradiology 55:889–893
Alvarez-Linera J (2008) 3 T MRI: advances in brain imaging. Eur J Radiol 67:415–426
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Online Supplementary Material 1
Imaging in an 11-week-old boy with abusive head trauma. There is susceptibility of the posterior globes bilaterally, representing retinal hemorrhage on axial susceptibility-weighted imaging (M4V 874 kb)
Online Supplementary Material 2
Imaging in an 11-week-old boy with abusive head trauma. Oblique susceptibility-weighted imaging reformats show multiple foci of susceptibility, representing retinal hemorrhage up to the ora serrata (M4V 1,007 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, A., Mirsky, D.M., Mankad, K. et al. Neuroimaging of retinal hemorrhage utilizing adjunct orbital susceptibility-weighted imaging. Pediatr Radiol 51, 991–996 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-020-04897-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-020-04897-6