Abstract
Background
Follicular bronchiolitis is a lymphoproliferative form of interstitial lung disease (ILD) defined by the presence of peribronchial lymphoid follicles. Follicular bronchiolitis has been associated with viral infection, autoimmune disease and immunodeficiency. The most common clinical manifestation is respiratory distress in infancy followed by a prolonged course with gradual improvement. We found no reports of systematic review of high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) findings in pediatric follicular bronchiolitis.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to describe the HRCT findings of follicular bronchiolitis in children and correlate these imaging findings with histopathology.
Materials and methods
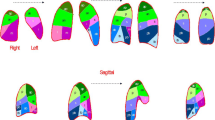
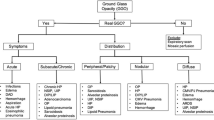
A 5-year retrospective review of all pathology-proven cases of follicular bronchiolitis was performed. Inclusion criteria were age <18 years and an HRCT within 6 months of lung biopsy. HRCTs were reviewed by three observers and scored using the system previously described by Brody et al.
Results
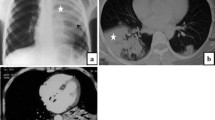
Six patients met the inclusion criteria with age range at HRCT of 7–82 months (median: 39.5 months). Pulmonary nodules (n=6) were the most common HRCT finding followed by focal consolidation (n=5), bronchiectasis (n=4) and lymphadenopathy (n=3). Tree and bud opacities and nodules on CT correlated with interstitial lymphocytic infiltrates and discrete lymphoid follicles on pathology.
Conclusion
The salient HRCT findings of childhood follicular bronchiolitis are bilateral, lower lung zone predominant pulmonary nodules and bronchiectasis with infantile onset of symptoms. These characteristic HRCT findings help differentiate follicular bronchiolitis from other forms of infantile onset ILD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kradin RL, Mark EJ (1983) Benign lymphoid disorders of the lung, with a theory regarding their development. Hum Pathol 14:857–867
Kinane BT, Mansell AL, Zwerdling RG, Lapey A, Shannon DC (1993) Follicular bronchitis in the pediatric population. Chest 104:1183–1186
Bramson RT, Cleveland R, Blickman JG, Kinane TB (1996) Radiographic appearance of follicular bronchitis in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol 166:1447–1450
Yousem SA, Colby TV, Carrington CB (1985) Follicular bronchitis/bronchiolitis. Hum Pathol 16:700–706
Howling SJ, Hansell DM, Wells AU et al (1999) Follicular bronchiolitis: thin-section CT and histologic findings. Radiology 212:637–642
Soubani AO, Uberti JP (2007) Bronchiolitis obliterans following haematopoietic stem cell transplant. Eur Respir J 29:1007–1019
Brody AS, Guillerman RP, Hay TC et al (2010) Neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy: diagnosis with high-resolution CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:238–244
Fan LL, Kozinetz CA (1997) Factors influencing survival in children with chronic interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156(3 Pt 1):939–942
Bienenstock J, Johnston N (1976) A morphologic study of rabbit bronchial lymphoid aggregates and lymphoepithelium. Lab Invest 35:343–348
Müller NL, Miller RR (1995) Diseases of the bronchioles: CT and histopathologic findings. Radiology 196:3–12
Amorosa JK, Miller RW, Laraya-Cuasay L et al (1992) Bronchiectasis in children with lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia and acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Plain film and CT observations. Pediatr Radiol 22:603–607
Sibille Y, Reynolds HY (1990) Macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils in lung defense and injury. Am Rev Respir Dis 141:471–501
Silva CI, Churg A, Müller NL (2007) Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: spectrum of high-resolution CT and pathologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:334–344
Brody AS, Sucharew H, Campbell JD et al (2005) Computed tomography correlates with pulmonary exacerbations in children with cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172:1128–1132
Jain K, Padley SPG, Goldstraw EJ et al (2007) Primary ciliary dyskinesia in the paediatric population: range and severity of radiological findings in a cohort of patients receiving tertiary care. Clin Radiol 62:986–993
Guinee DG Jr (2008) Update on pulmonary and pleural lymphoproliferative disorders. Diagn Histopathol 14:474–498
Becciolini V, Gudinchet F, Cheseaux JJ, Schnyder P (2001) Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia in children with AIDS: High-resolution CT findings. Eur Radiol 11:1015–1020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weinman, J.P., Manning, D.A., Liptzin, D.R. et al. HRCT findings of childhood follicular bronchiolitis. Pediatr Radiol 47, 1759–1765 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-017-3951-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-017-3951-5