Abstract
Background
Heterotaxy with polysplenia is associated with many cardiovascular anomalies including the occasional occurrence of congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts (CEPS). Missing this anomaly can lead to inappropriate and ineffective therapy.
Objective
To emphasize the importance and associated anatomy of CEPS in conjunction with heterotaxy with polysplenia.
Materials and methods
Review of three young children who presented with cyanosis and pulmonary hypertension without a cardiac etiology. They were known (1) or discovered (2) to have heterotaxy with polysplenia.
Results
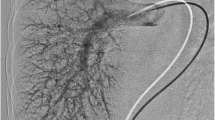
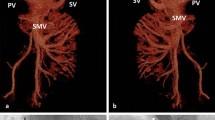
There was absence of the intrahepatic inferior vena cava (IVC) with azygos or hemiazygos continuation in all three cases. In spite of normal liver function, they were discovered to have large portosystemic shunts, splenorenal in location, along with diffuse peripheral pulmonary arterial dilatation suggestive of CEPS (Abernethy malformation) with hepatopulmonary or, more accurately, portopulmonary syndrome. All CEPS were ipsilateral to the spleens. Patency of the portal veins in these cases allowed for percutaneous shunt closure with resolution of cyanosis.
Conclusion
CEPS is associated with heterotaxy with polysplenia and can be symptomatic because of pulmonary arteriovenous (AV) shunting. Portal and hepatic vein patency are critical for determining feasibility of CEPS closure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Towbin A, Newman B (2007) Syndromes and chromosonal anomalies. In: Slovis T (ed) Caffey’s pediatric diagnostic imaging. Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1605–1610
Papagiannis J, Kanter RJ, Effman EL et al (1993) Polysplenia with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Pediatr Cardiol 14:127–129
Kinane TB, Westra SJ (2004) Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 31-2004. A four-year-old boy with hypoxemia. New Engl J Med 351:1667–1675
De BK, Sen S, Biswas PK et al (2002) Occurrence of hepatopulmonary syndrome in Budd-Chiari syndrome and the role of venous decompression. Gastroenterology 122:897–903
Murray CP, Yoo SJ, Babyn PS (2003) Congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Pediatr Radiol 33:614–620
Alvarez AE, Ribeiro AF, Hessel G et al (2002) Abernethy malformation: one of the etiologies of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Pediatr Pulmonol 34:391–394
Gupta NA, Abramowsky C, Pillen T et al (2007) Pediatric hepatopulmonary syndrome is seen with polysplenia/interrupted inferior vena cava and without cirrhosis. Liver Transpl 13:680–686
Hoeper M, Krowka MJ, Strassburg CP (2004) Portopulmonary hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Lancet 363:1461–1468
Fewtrell MS, Noble-Jamieson G, Revell S et al (1994) Intrapulmonary shunting in the biliary atresia/polysplenia syndrome: reversal after liver transplantation. Arch Dis Child 70:501–504
Barbe T, Losay J, Grimon G et al (1995) Pulmonary arteriovenous shunting in children with liver disease. J Pediatr 126:571–579
Gurses D, Ulger Z, Levent E et al (2006) A very rare case of polysplenia syndrome with congenital diffuse pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas. Turk J Pediatr 48:96–99
McAdams HP, Erasmus J, Crockett R et al (1996) The hepatopulmonary syndrome: radiologic findings in 10 patients. AJR 166:1379–1385
Oh KS, Bender TM, Bowen A et al (1983) Plain radiographic, nuclear medicine and angiographic observations of hepatogenic pulmonary angiodysplasia. Pediatr Radiol 13:111–115
Krowka MJ, Dickson ER, Cortese DA (1993) Hepatopulmonary syndrome. clinical observations and lack of therapeutic response to somatostatin analogue. Chest 104:515–521
Krowka MJ (2000) Hepatopulmonary syndromes. Gut 46:1–4
Srivastava D, Preminger T, Lock JE et al (1995) Hepatic venous blood and the development of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations in congenital heart disease. Circulation 92:1217–1222
Newman B, Effmann E (2007) Lung masses. In: Slovis T (ed) Caffey’s pediatric diagnostic imaging. Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1300–1303
Spencer LT, Langham MR, Hoyer MH et al (2000) Resolution of hypoxemia in a liver transplant recipient after ligation of a portosystemic shunt. J Pediatr 137:575–577
Ikeda S, Sera Y, Ohshiro H et al (1999) Surgical indications for patients with hyperammonemia. J Pediatr Surg 34:1012–1015
Alonso J, Sierre S, Lipsich J et al (2004) Endovascular treatment of congenital portal vein fistulas with the Amplatzer occlusion device. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15:989–993
Jones FD, Kuo PC, Johnson LB et al (1999) The coexistence of portopulmonary hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Anesthesiology 90:626–630
Ioachimescu OC, Mehta AC, Stoller JK (2007) Hepatopulmonary syndrome following portopulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 29:1277–1280
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newman, B., Feinstein, J.A., Cohen, R.A. et al. Congenital extrahepatic portosystemic shunt associated with heterotaxy and polysplenia. Pediatr Radiol 40, 1222–1230 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-009-1508-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-009-1508-y