Abstract
Background
MRI and FDG-PET may predict the histological grading of paediatric brain-stem gliomas.
Objective
To assess MRI findings and metabolic imaging using FDG-PET of brain-stem gliomas based on histological grading.
Materials and methods
Included in the study were 20 paediatric patients (age 3–14 years, mean 8.2 years) with brain-stem glioma (five glioblastomas, ten anaplastic astrocytomas and five low-grade astrocytomas). MR images were assessed for the anatomical site of tumour origin, focality, pattern of tumour growth, and enhancement.
Results
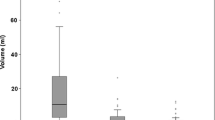
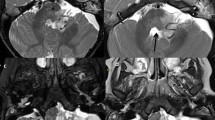
All glioblastomas were located in the pons and showed diffuse pontine enlargement with focally exophytic features. Eight anaplastic astrocytomas were located in the pons and demonstrated diffuse pontine enlargement without exophytic features. Low-grade astrocytomas were located in the pons, midbrain or medulla and showed focally exophytic growth features and peripheral enhancement. In 12 patients in whom FDG-PET was undertaken, glioblastomas showed hypermetabolic or hypometabolic lesions, anaplastic astrocytomas showed no metabolic change or hypometabolic lesions and low-grade astrocytomas showed hypometabolism compared with the cerebellum.
Conclusion
MRI findings correlated well with histological grading of brain-stem gliomas and MRI may therefore predict the histological grading. FDG-PET may be helpful in differentiating between anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastomas among high-grade tumours.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright AL, Price RA, Guthkelch AN (1983) Brain stem gliomas of children. A clinicopathological study. Cancer 52:2313–2319
Farwell R, Dohrmann GJ, Flannery JT (1977) Central nervous system tumors in children. Cancer 40:3123–3132
Fischbein NJ, Prados MD, Wara W, et al (1996) Radiologic classification of brain stem tumors: correlation of magnetic resonance imaging appearance with clinical outcome. Pediatr Neurosurg 24:9–23
Rubin G, Michowitz S, Horev G, et al (1998) Pediatric brain stem gliomas; an update. Childs Nerv Syst 14:167–173
Epstein FJ, Farmer JP (1993) Brain stem glioma growth patterns. J Neurosurg 78:408–412
Kahn AP, Hirsch JF, Vinchon M, et al (1993) Surgical management of brain stem tumor in children: results and statistical analysis of 75 cases. J Neurosurg 79:845–852
Moghrabi A, Kerby T, Tien R, et al (1995) Prognostic value of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in brain stem gliomas. Pediatr Neurosurg 23:293–298
Freeman CR, Farmer JP (1998) Pediatric brain stem gliomas: a review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 40:265–271
Jallo GI, Biser-Rohrbaugh A, Freed D (2004) Brainstem gliomas. Childs Nerv Syst 20:143–153
Lesniak MS, Klem JM, Weingart J, et al (2003) Surgical outcome following resection of contrast-enhanced pediatric brainstem gliomas. Pediatr Neurosurg 39:314–322
Freeman CR, Bourgouin PM, Sanford RA, et al (1996) Long term survivors of childhood brain stem gliomas treated with hyperfractionated radiotherapy. Clinical characteristics and treatment related toxicities. The Pediatric Oncology Group. Cancer 77:555–562
Cohen ME, Duffner PK, Heffner RR, et al (1986) Prognostic factors in brain stem gliomas. Neurology 36:602–605
Barkovich AJ, Krischer J, Kun LE, et al (1990/91) Brain stem gliomas: a classification system based on magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Neurosurg 16:73–83
Kaplan AM, Albright AL, Zimmerman RA, et al (1996) Brainstem gliomas in children. A Children’s Cancer Group review of 119 cases. Pediatr Neurosurg 24:185–192
Kane AG, Robles HA, Smirniotopoulos JG, et al (1993) Radiologic-pathologic correlation: diffuse pontine astrocytoma. AJNR 14:941–945
Bowers DC, Krause TP, Aronson LJ, et al (2001) Second surgery for recurrent pilocytic astrocytoma in children. Pediatr Neurosurg 34:229–234
Stroink AR, Hoffman HJ, Hendrick EB, et al (1987) Transependymal benign dorsally exophytic brain stem gliomas in childhood: diagnosis and treatment recommendations. Neurosurgery 20:439–444
Stroink AR, Hoffman HJ, Hendrick EB, et al (1986) Diagnosis and management of pediatric brain stem gliomas. J Neurosurg 65:745–750
Pollack IF, Hoffman HJ, Humphreys RP, et al (1993) The long-term outcome after surgical treatment of dorsally exophytic brain-stem gliomas. J Neurosurg 78:859–863
Young Poussaint T, Yousuf N, Barnes PD, et al (1999) Cervicomedullary astrocytomas of childhood: clinical and imaging follow-up. Pediatr Radiol 29:662–668
Delbeke D, Meyerowitz C, Lapidus R, et al (1995) Optimal cutoff levels of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the differentiation of low grade from high grade brain tumors with PET. Radiology 195:47–52
Padma MV, Said S, Jacobs M, et al (2003) Prediction of pathology and survival by FDG PET in gliomas. J Neurooncol 64:227–237
De Witte O, Lefranc F, Levivier M, et al (2000) FDG-PET as a prognostic factor in high-grade astrocytoma. J Neurooncol 49:157–163
Fenton LZ, Madden JR, Foreman NK (2003) Brain stem glioma in a child: false diagnosis of radiation necrosis with FDG PET. Med Pediatr Oncol 40:260–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, J.W., Kim, IO., Cheon, JE. et al. Paediatric brain-stem gliomas: MRI, FDG-PET and histological grading correlation. Pediatr Radiol 36, 959–964 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-006-0256-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-006-0256-5