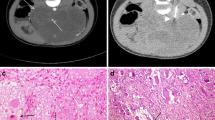
Abstract
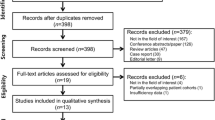
Background: Image-guided core needle biopsy is widely used in paediatric oncology, but many protocols continue to discourage this practice. No published randomized studies compare image-guided needle biopsy with surgical techniques. Objective: To perform a systematic review of the literature on image-guided core needle biopsy in paediatric oncology. Materials and methods: Several computerized databases were searched using the terms [(needle OR core) AND (biops*[ti]) AND (paediatric OR pediatric OR child OR children OR childhood OR boy OR girl)[ti]] to identify series of more than five cases of needle core biopsy for tumour diagnosis in children. Data from included studies were combined to calculate pooled estimates of adequacy, accuracy and complication rates. Results: Thirteen studies fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Overall biopsy adequacy rate (defined as sufficient to make a diagnosis) was 94% (95% CI 92–96%). The diagnostic accuracy rate in cases with adequate material (defined as achieving the correct specific diagnosis) was 94% (95% CI 92–96%). Complications requiring treatment occurred in 1%. Conclusions: Available pooled data suggest that about 95% of image-guided needle core biopsies provide an adequate sample for diagnosis of malignant disease in childhood. In such cases, the pathological diagnosis is correct in about 95%. Complications are rare.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garrett KM, Fuller CE, Santana VM, et al (2005) Percutaneous biopsy of pediatric solid tumors. Cancer 104:644–652
Guimaraes AC, Chapchap P, de Camargo B, et al (2003) Computed tomography-guided needle biopsies in pediatric oncology. J Pediatr Surg 38:1066–1068
Skoldenberg EG, Jakobson AA, Elvin A, et al (2002) Diagnosing childhood tumors: a review of 147 cutting needle biopsies in 110 children. J Pediatr Surg 37:50–56
Hussain HK, Kingston JE, Domizio P, et al (2001) Imaging-guided core biopsy for the diagnosis of malignant tumors in pediatric patients. AJR 176:43–47
Sklair-Levy M, Lebensart PD, Applbaum YH, et al (2001) Percutaneous image-guided needle biopsy in children–summary of our experience with 57 children. Pediatr Radiol 31:732–736
Willman JH, White K, Coffin CM (2001) Pediatric core needle biopsy: strengths and limitations in evaluation of masses. Pediatr Dev Pathol 4:46–52
Bain G, Bearcroft PW, Berman LH, et al (2000) The use of ultrasound-guided cutting-needle biopsy in paediatric neck masses. Eur Radiol 10:512–515
Connolly BL, Chait PG, Duncan DS, et al (1999) CT-guided percutaneous needle biopsy of small lung nodules in children. Pediatr Radiol 29:342–346
Hugosson CO, Nyman RS, Cappelen-Smith JM, et al (1999) Ultrasound-guided biopsy of abdominal and pelvic lesions in children. A comparison between fine-needle aspiration and 1.2-mm needle core biopsy. Pediatr Radiol 29:31–36
Somers JM, Lomas DJ, Hacking JC, et al (1993) Radiologically-guided cutting needle biopsy for suspected malignancy in childhood. Clin Radiol 48:236–240
Saarinen UM, Wikstrom S, Koskimies O, et al (1991) Percutaneous needle biopsy preceding preoperative chemotherapy in the management of massive renal tumors in children. J Clin Oncol 9:406–415
Klose KC, Mertens R, Alzen G, et al (1991) CT-guided percutaneous large-bore biopsies in benign and malignant pediatric lesions. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 14:78–83
Sabbah R, Ghandour M, Ali A, et al (1981) Tru-cut needle biopsy of abdominal tumors in children: a safe and diagnostic procedure. Cancer 47:2533–2535
Chang CC, Shidham VB (2003) Molecular genetics of pediatric soft tissue tumors: clinical application. J Mol Diagn 5:143–154
Shimada H, Stram DO, Chatten J, et al (1995) Identification of subsets of neuroblastomas by combined histopathologic and N-myc analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:1470–1476
Simon T, Spitz R, Faldum A, et al (2004) New definition of low-risk neuroblastoma using stage, age, and 1p and MYCN status. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 26:791–796
Mora J, Cheung NK, Chen L, et al (2001) Survival analysis of clinical, pathologic, and genetic features in neuroblastoma presenting as locoregional disease. Cancer 91:435–442
Pinarli FG, Danaci M, Tander B, et al (2004) Bilateral adrenal cystic neuroblastoma with superior vena cava syndrome and massive intracystic haemorrhage. Pediatr Radiol 34:746–749
Squire R, Willetts I (1999) Problems with biopsying solid tumours in children (abstract). Med Pediatr Oncol 34:344
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sebire, N.J., Roebuck, D.J. Pathological diagnosis of paediatric tumours from image-guided needle core biopsies: a systematic review. Pediatr Radiol 36, 426–431 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-006-0123-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-006-0123-4