Abstract
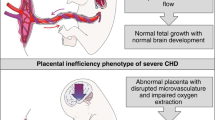
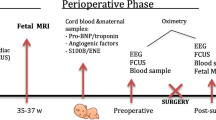
Complex congenital heart disease (CCHD) is associated with impaired neurodevelopmental outcomes. Peri- and post-operative factors are known contributors while the impact of the prenatal environment is not yet delineated. Variations in fetal circulation, seen in transposition of the great arteries (TGA) and single ventricular physiology (SVP), are associated with placenta abnormalities. These abnormalities may be associated with placental insufficiency, a risk factor for poor neurodevelopmental outcomes. We hypothesized there is a correlation between placental pathology and impaired neurodevelopmental outcomes in patients with CCHD. We performed a single center retrospective cohort study with patients with TGA and SVP from 2010 to 2017 at Children’s Wisconsin. Patient variables were obtained from the medical record. Bayley Scales of Infant Development Third Edition standard scores for cognitive, motor, and language performance were collected from neurodevelopmental visits. Placenta pathology reports were reviewed with tabulation of predetermined anatomical and pathological characteristics. We identified 79 patients in our cohort and 61 (77.2%) had abnormal placentas. There was no significant difference between the two groups in any demographic or clinical variables. For cognitive and motor performance, without adjusting for the covariates, infants with placental abnormalities had significantly lower scores compared to infants without (p = 0.026, p = 0.045 respectively). Conversely, there was no significant difference in language scores between the two groups (p = 0.12). Placenta abnormalities are common in patients with CCHD, and placenta abnormalities are associated with impaired neurodevelopmental outcomes. These results underscore the complex causal pathways of neurodevelopmental impairment in infants with CCHD and offer opportunities for targeted postnatal developmental interventions after discharge.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wernovsky G, Licht DJ (2016) Neurodevelopmental outcomes in children with congenital heart disease—what can we impact? pediatric critical care medicine. J Soc Crit Care Med World Fed Pediatric Intensive Crit Care Soc 17(8 1):S232–S242. https://doi.org/10.1097/PCC.0000000000000800
Brosig CL, Bear L, Allen S, Simpson P, Zhang L, Frommelt M, Mussatto KA (2018) Neurodevelopmental outcomes at 2 and 4 years in children with congenital heart disease. Congenit Heart Dis 13(5):700–705. https://doi.org/10.1111/chd.12632
Brosig CL, Bear L, Allen S, Hoffmann RG, Pan A, Frommelt M, Mussatto KA (2017) Preschool neurodevelopmental outcomes in children with congenital heart disease. J Pediatr 183:80-86.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.12.044
Zun Z, Limperopoulos C (2018) Placental perfusion imaging using velocity-selective arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med 80(3):1036–1047. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.27100
Olive EL, Xiao E, Natale DR, Fisher SA (2018) Oxygen and lack of oxygen in fetal and placental development, feto-placental coupling, and congenital heart defects. Birth Defects Res 110(20):1517–1530. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdr2.1430
Albalawi A, Brancusi F, Askin F, Ehsanipoor R, Wang J, Burd I, Sekar P (2017) Placental characteristics of fetuses with congenital heart disease. J Ultrasound Med 36(5):965–972. https://doi.org/10.7863/ultra.16.04023
Leon RL, Mir IN, Herrera CL et al (2021) Neuroplacentology in congenital heart disease: placental connections to neurodevelopmental outcomes. Pediatr Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-021-01521-7
Rychik J, Goff D, McKay E, Mott A, Tian Z, Licht DJ, William Gaynor J (2018) Characterization of the placenta in the newborn with congenital heart disease: distinctions based on type of cardiac malformation. Pediatric Cardiol 39(6):1165–1171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-018-1876-x
Courtney et al. Abnormalities of placental development and function are associated with the different fetal growth patterns of hypoplastic left heart syndrome and transposition of the great arteries
Jones HN, Olbrych SK, Smith KL, Cnota JF, Habli M, Ramos-Gonzales O, Owens KJ et al (2015) Hypoplastic left heart syndrome is associated with structural and vascular placental abnormalities and leptin dysregulation. Placenta 36(10):1078–1086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2015.08.003
Kinnear C, Haranal M, Shannon P, Jaeggi E, Chitayat D, Mital S (2019) Abnormal fetal cerebral and vascular development in hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Prenat Diagn 39(1):38–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.5395
Yamamoto Y, Khoo NS, Brooks PA, Savard W, Hirose A, Hornberger LK (2013) Severe left heart obstruction with retrograde arch flow influences fetal cerebral and placental blood flow. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 42(3):294–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.12448
Godfrey ME, Friedman KG, Drogosz M, Rudolph AM, Tworetzky W (2017) Cardiac output and blood flow redistribution in fetuses with D-loop transposition of the great arteries and intact ventricular septum: insights into pathophysiology. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 50(5):612–617. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.17370
Bayley N (2006) The bayley scales of infant development-III. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Courtney JA, Cnota JF, Jones HN (2018) The role of abnormal placentation in congenital heart disease; cause, correlate, or consequence?”. Front Physiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01045
Miremberg H, Gindes L, Schreiber L, Sternfeld AR, Bar J, Kovo M (2019) The association between severe fetal congenital heart defects and placental vascular malperfusion lesions. Prenat Diagn 39(11):962–967. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.5515
Burton GJ, Jauniaux E (2018) Development of the human placenta and fetal heart: synergic or independent? Front Physiol 9:373. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00373
Cohen J, Rychik J, Salva J (2021) The placenta as the window to congenital heart disease. Curr Opin Cardiol 36(1):56–60. https://doi.org/10.1097/HCO.0000000000000816
Maslen CL (2018) Recent advances in placenta-heart interactions. Front Physiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00735
Linask KK (2013) The heart-placenta axis in the first month of pregnancy: induction and prevention of cardiovascular birth defects. J Pregnancy. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/320413
Andescavage NN, Limperopoulos C (2021) Placental abnormalities in congenital heart disease. Translat Pediatr. 10(8):2148–2156. https://doi.org/10.21037/tp-20-347
Wang B, Zeng H, Liu J, Sun M (2021) Effects of prenatal hypoxia on nervous system development and related diseases. Front Neurosci 15:755554. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.755554
Yockey LJ, Iwasaki A (2018) Role of interferons and cytokines in pregnancy and fetal development. Immunity 49(3):397–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.07.017
Wardinger JE, S. Ambati (2022) Placental insufficiency. In StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563171/
Derridj N, Guedj R, Calderon J, Houyel L, Lelong N, Bertille N, Goffinet F, Bonnet D, Khoshnood B (2021) Long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes of children with congenital heart defects. J Pediatrics 237:109-114.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.06.032
Acknowledgements
Statistical support was provided through the Division of Quantitative Health Sciences. We would like to thank the Divisions of Pediatric Cardiology and Neonatology for their support as well as the Master’s in Clinical and Translational Research program through the Medical College of Wisconsin and the Clinical and Translational Science Institute of Southeast Wisconsin.
Funding
No funding was utilized for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DS was the primary author of the manuscript text and prepared figures 1-2 and the tables. JZ and KY performed the statistical analysis and data for tables 1-4 and prepared figure 3. AR contributed to data analysis. M.F developed the project. SC contributed to drafting of the manuscript and provided supervision in all aspects throughout the project. All authors reviewed the manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interests.
Informed Consent
This was a retrospective study for which no data was generated, and a waiver of consent was approved by our IRB.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Segar, D.E., Zhang, J., Yan, K. et al. The Relationship Between Placental Pathology and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Complex Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatr Cardiol 44, 1143–1149 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-022-03018-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-022-03018-4