Abstract
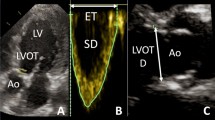
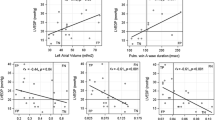
Echocardiography is used to measure the therapeutic effectiveness of heart failure therapy in adults and children. The purposes of this study were (1) to assess baseline echocardiographic predictors of clinical outcome, (2) to investigate changes in echocardiographic parameters, and (3) to compare these echocardiographic changes with changes in plasma levels of b-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) in a population of children with systemic ventricular dysfunction and symptomatic heart failure treated with carvedilol or placebo. All available baseline and 6-month echocardiograms from Pediatric Carvedilol Trial (PCT) participants (carvedilol n = 161; placebo n = 55) were reviewed. Systolic and diastolic sphericity index (SI; n = 110), TEI index (n = 145), and systemic ventricular dP/dt (n = 70) were measured. The PCT composite definition of clinical outcome (i.e., worsened, improved, or unchanged) was used. For all patients, baseline TEI index was a predictor of worsened outcome. Only children treated with carvedilol showed a significant decrease in systolic SI (P ≤ 0.0001), diastolic SI (P ≤ 0.0001), and TEI index (P = 0.02). An inverse correlation between changes in BNP and changes in dP/dt (r = –0.45, P = 0.04) was found only in the carvedilol group. In conclusion, TEI index predicted outcome in children with systemic ventricular dysfunction and heart failure. Carvedilol may have a beneficial effect on reversal of left ventricular remodeling and global ventricular function in pediatric heart failure.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung N, Nishimura RA, Holmes DR Jr, Tajik AJ (1992) Measurement of left ventricular dp/dt by simultaneous Doppler echocardiography and cardiac catheterization. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 5:147–152
Doust JA, Pietrzak E, Dobson A, Glasziou P (2005) How well does B-type natriuretic peptide predict death and cardiac events in patients with heart failure: systematic review. Br Med J 330:625
Dujardin KS, Tei C, Yeo TC, Hodge DO, Rossi A, Seward JB (1998) Prognostic value of a Doppler index combining systolic and diastolic performance in idiopathic-dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol 82:1071–1076
Eidem BW, Tei C, O’Leary PW, Cetta F, Seward JB (1998) Nongeometric quantitative assessment of right and left ventricular function: myocardial performance index in normal children and patients with Ebstein anomaly. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 11:849–856
Harjai KJ, Scott L, Vivekananthan K, Nunez E, Edupuganti R (2002) The Tei index: a new prognostic index for patients with symptomatic heart failure. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 15:864–868
Kolias TJ, Aaronson KD, Armstrong WF (2000) Doppler-derived dP/dt and −dP/dt predict survival in congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 36:1594–1599
Lowes BD, Gill EA, Abraham WT, Larrain JR, Robertson AD, Bristow MR et al (1999) Effects of carvedilol on left ventricular mass, chamber geometry, and mitral regurgitation in chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol 83:1201–1205
Mangat J, Carter C, Riley G, Foo Y, Burch M (2009) The clinical utility of brain natriuretic peptide in paediatric left ventricular failure. Eur J Heart Fail 11:48–52
McMahon CJ, Nagueh SF, Eapen RS, Dreyer WJ, Finkelshtyn I, Cao X et al (2004) Echocardiographic predictors of adverse clinical events in children with dilated cardiomyopathy: a prospective clinical study. Heart 90:908–915
Packer M, Bristow MR, Cohn JN, Colucci WS, Fowler MB, Gilbert EM et al (1996) The effect of carvedilol on morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure U.S. Carvedilol Heart Failure Study Group. N Engl J Med 334:1349–1355
Packer M, Fowler MB, Roecker EB, Coats AJ, Katus HA, Krum H et al (2002) Effect of carvedilol on the morbidity of patients with severe chronic heart failure: results of the carvedilol prospective randomized cumulative survival (COPERNICUS) study. Circulation 106:2194–2199
Senior R, Basu S, Kinsey C, Schaeffer S, Lahiri A (1999) Carvedilol prevents remodeling in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 137:646–652
Shaddy RE, Boucek MM, Hsu DT, Boucek RJ, Canter CE, Mahony L et al (2007) Carvedilol for children and adolescents with heart failure: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 298:1171–1179
Silver MA, Maisel A, Yancy CW, McCullough PA, Burnett JC Jr, Francis GS et al (2004) BNP Consensus Panel 2004: a clinical approach for the diagnostic, prognostic, screening, treatment monitoring, and therapeutic roles of natriuretic peptides in cardiovascular diseases. Congest Heart Fail 10:1–30
Tani LY, Minich LL, Williams RV, Shaddy RE (2005) Ventricular remodeling in children with left ventricular dysfunction secondary to various cardiomyopathies. Am J Cardiol 96:1157–1161
Tatli E, Kurum T (2005) A controlled study of the effects of carvedilol on clinical events, left ventricular function and proinflammatory cytokines levels in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Can J Cardiol 21:344–348
Tei C (1995) New non-invasive index for combined systolic and diastolic ventricular function. J Cardiol 26:135–136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petko, C., Minich, L.L., Everitt, M.D. et al. Echocardiographic Evaluation of Children With Systemic Ventricular Dysfunction Treated With Carvedilol. Pediatr Cardiol 31, 780–784 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-010-9700-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-010-9700-2