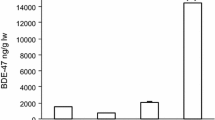
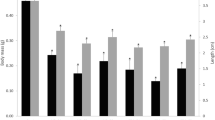
Abstract
In eight Dutch or Belgian common tern (Sterna hirundo) colonies, breeding biology and food choice were determined, and 15 second eggs were collected from three-egg clutches for artificial incubation, biochemical analysis and analysis of yolk-sac polyhalogenated hydrocarbon (PHAH) levels. Results from these analyses were combined with biological data from the eggs remaining in each clutch. In some breeding colonies severe flooding, rainy and cold weather, and extreme predation caused extensive losses of eggs and chicks. A relationship was found between yolksac mono-ortho polychlorinated biphenyl (mo-PCB) levels and main food species (fish or insects) of the adult terns before egg-laying. Colony average breeding data differed only slightly, and were difficult to relate to PHAH-levels. When the colonies were grouped after yolksac PHAH-patterns and main food species, significant differences in average egg laying date, incubation period, egg volume and chick weight could be related to differences in yolksac PHAH and retinoid levels, and hepatic ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) activity. The data from all colonies also were combined into one data-set and correlated with the biochemical parameters and PHAH levels. In summary higher yolksac PHAH levels or hepatic EROD-activity correlated with and later egg laying, prolonged incubation period and smaller eggs and chicks. Lower yolksac retinoid- and plasma thyroid hormone levels, and a higher ratio of plasma retinol over yolksac retinoids correlated with later egg laying, prolonged incubation periods and smaller chicks and eggs.
The dynamic environment of the terns had more obvious detrimental effects on breeding success than PHAHs. However, the more subtle effects observed for PHAHs could still be of importance during specific stress circumstances. To monitor site-specific reproduction effects, tree-nesting birds feeding on relatively big and non-migrating fishes would be most suitable. The use of specific biomarkers for exposure and effect is recommended to establish a causal relationship between a certain class of pollutants and an adverse biological effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts JMMJG, Denison MS, Cox MA, Schalk MAC, Garrison PA, Tullis K, De Haan LHJ, Brouwer A (1995) Species-specific antagonism of Ah receptor action by 2,2′,5,5′-tetrachloro- and 2,2′,3,3′,4,4′-hexachlorobiphenyl. Eur J Pharmacol, Env Tox Section 293:463–474
Ankley GT, Niemi GJ, Lodge KB, Harris HJ, Beaver DL, Tillitt DE, Schwartz TR, Giesy JP, Jones PD, Hagley C (1993) Uptake of planar polychlorinated biphenyls and 2,3,7,8-substituted polychlorinated dibenzofurans and dibenzo-p-dioxins by birds nesting in the Lower Fox River and Green Bay, Wisconsin Arch Environ Toxicol 24:332–344
Becker PH, Koepff C, Heidmann WA, Büthe A (1991) Schadstoffmonitoring mit Seevögeln [German]. Umweltbundesamt, Berlin, 260 pp
Becker PH, Heidmann WA, Büthe A, Frank D, Koepff C (1992) Umwelt-chemikalien in Eiern von Brutvögeln der deutschen Nordseeküste: Trends 1981–1990 [German]. J Ornithologie 2:109–124
Bosveld ATC, Gradener J, Murk AJ, Van Kampen M, Evers EHG, Brouwer A, Van den Berg M (1995) Effects of PCBs, PCDDs and PCDFs in common tern (Sterna hirundo) breeding in estuarine and coastal colonies in the Netherlands and Belgium. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:99–115
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brouwer A (1991) The role of enzymes in regulating the toxicity of xenobiotics. Role of biotransformation in PCB-induced alterations in vitamin A and thyroid hormone metabolism in laboratory and wildlife species. Biochemical Society Transactions 19:731–738
Brouwer A, Blaner WS, Kukler A, Van de Berg KJ (1988) Study on the mechanism of interference of 3,4,3′,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl with the plasma retinol-binding proteins in rodents. Chem-Biol. Interactions 68:203–217
Brouwer A, Murk AJ, Koeman JH (1990) Biochemical and physiological approaches in ecotoxicology. Functional Ecology 4:275–281
Cramp S (ed.) (1985) The Birds of the Western Palearctic, Vol. IV, Oxford University Press, Oxford
Chen L-C, Berberian I, Koch B, Mercier M, Azais-Braesco V, Glauert HP, Chow CK, Robertson LW (1992) Polychlorinated and polybrominated biphenyl congeners and retinoid levels in rat tissues: structure-activity relationships. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 114, 47–55
Cummins JE (1988) Extinction: the PCB threat to marine mammals. Ecologist 18:193–195
Koeman JH, Van Velzen-Blad HCW, De Vries R, Vos JG (1973) Effects of PCB and DDE in cormorants and evaluation of PCB residues from an experimental study. J Reprod Fert Suppl 19:353–364
Fox GA, Weseloh DV, Kubiak TJ, Erdman TC (1991) Reproductive outcomes in colonial fish-eating birds: a biomarker for developmental toxicants in Great Lakes food chains. I. Historical and ecotoxicological perspectives. J Great Lakes Res 17:158–167
Fox GA (1993) What have biomarkers told us about the effect of contaminants on the health of fish-eating birds in the Great Lakes? The theory and a literature review. J Great Lakes Res 19(4): 722–736
Friedman A, Sklan D (1989) Antigen-specific immune response impairment in the chick as influenced by dietary vitamin A. J Nutr 119:790–795
Gilbertson M (1974) Pollutants in breeding herring gulls in the lower Great Lakes. Can Field-Naturalist 88:273–280
Gilbertson M (1989) Effects on fish and wildlife populations. In: Kimbrough and Jensen (eds) Halogenated Biphenyls, Terphenyls, Naphtalenes, Dibenzodioxines and Related Products. Elsevier 103–127
Gilbertson M, Fox GA (1977) Pollutant-associated embryonic mortality of Great Lakes herring gulls. Environ Pollut 12:211–216
Hays H (1978) Timing and breeding success in three- to seven-year-old Common Terns. Ibis 120: 127–128
Hoffman DJ, Rattner BA, Sileo L, Docherty D, Kubiak TJ (1987) Embryotoxicity, teratogenicity, and aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in forster's terns on Green Bay, Lake Michigan. Environ Res 42:176–9
Hoffman DJ, Smith GJ, Rattner BA (1993) Biomarkers of contaminant exposure in Common terns and Black-crowned night herons in the Great Lakes. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1095–1103
Hoyt DF (1979) Practical methods for estimating volume and fresh weight of bird eggs. Auk 96:73–77
Klaassen M (1992) The naive proficient. Metabolic responses to problems of climate and food availability. Thesis, Univ. Groningen
Klamer J, Laane RWPM, Marquenie JM (1991) Sources and fate of PCBs in the North Sea: a review of available data. Wat Sci Technol 24:77–85
Kubiak TJ, Harris HJ, Smith LM, Schwartz TR, Stalling DL, Trick JA, Sileo L, Dochetry DE, Erdman TC (1989) Microcontaminants and reproductive impairment of the forster's tern on Green Bay, Lake Michigan-1983. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18:706–722
Leatherland JF, Sonstegard RA (1978) Lowering of serum thyroxine and triiodothyronine levels in yearling Coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch, by dietary Mirex and PCBs. J Fish Res Board Canada 35:1285–1289
Morse DC, Koeter HWBM, Smits van Prooijen AE, Brouwer A (1992) Interference of polychlorinated biphenyls in thyroid hormone metabolism: possible neurotoxic consequences in fetal and neonatal rats. Chemosphere 25:165–168
Morse DC, Brouwer A (1995) Fetal, neonatal and longterm alterations in hepatic retinoid levels following maternal polychlorinated biphenyl exposure in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 131: 175–182
Murk AJ, Bosveld ATC, Van den Berg M, Brouwer A (1994a) Effects of polyhalogenated aromatic hydrocarbons (PHAHs) on biochemical parameters in chicks of the common tern (Sterna hirundo). Aquat Toxicol 30:91–115
Murk AJ, Van den Berg JHJ, Fellinger M, Rozemeijer MJC, Swennen C, Duiven P, Boon JP, Brouwer A, Koeman JH (1994b) Toxic and biochemical effects of 3,3′, 4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl (CB77) and clophen A50 on eider ducklings (Somateria mollissima) in semifield experiment. Environ Pollut 86:21–30
Murk AJ, Legler L, Denison MS, Giesy JP, Van der Guchte CJ, Brouwer A (1996) Chemical-activated Luciferase gene expression (CA-LUX): a novel in vitro bioassay for Ah receptor active compounds in sediments and pore water. Fund Appl Toxicol (Submitted)
Nisbet ICT (1973) Courtship-feeding, egg-size and breeding success in Common terns. Nature 241:141–142
Nisbet ICT (1977) Courtship-feeding and clutch size in Common terns Sterna hirundo. In: Stonehouse, B. and C. Perrins (Eds.). Evolutionary Ecology. Macmillan Press Ltd
Nisbet ICT (1978) Population models for common terns in Massachusetts. Bird Banding 49:50–58
Pijnappel WWM, Hendriks HFJ, Folkers GE, Van den Brink CE, Dekker EJ, Edelenbosch C, Van der Saag PT, Durston AJ (1993) The retinoid ligand 4-oxo-retinoic acid is a highly active modulator of positional specification. Nature 366:340–344
Rossaert G, Dirksen S, Boudewijn TJ, Meire PM, Ysebaert T, Evers EHG, Meininger PL (1993) Effects of PCBs, PCDDs and PCDFs on reproductive success, and morphological, physiological and biochemical parameters in chicks of the Common Tern (Sterna hirundo); Part I: field study. Report DGW-93.010, The Hague, 126 pp
Rutten AAJJL, Falke HE, Catsburg JF, Topp R, Blaauboer BJ, Van Holsteijn I, Doorn L, Van Leeuwen FXR (1987) Interlaboratory comparison of total cytochrome P-450 and protein determinations in rat liver microsomes. Reinvestigation of assay conditions. Arch Toxicol 61:27–7
Safe S (1990) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzo furans (PCDFs), and related compounds: Environmental and mechanistic considerations with support the development of toxic equivalence factors (TEFs). Crit Rev Toxicol 21(10):51–88
Safe S (1994) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): Environmental impact, biochemical and toxic responses, and implications for riskassessment. Crit Rev Toxicol 24:87–149
Sharp PJ, Klandorf H (1985) Environmental and physiological factors controlling thyroid function in galliformes. The endocrine system and the environment. Follett BK, Ishii S, Chandola A (eds). Japan Sci. Soc. Press, Tokyo/Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 175–188
Smith LM, Schwartz TR, Feltz K, Kubiak TJ (1990) Determination and occurence of AHH-active polychlorinated biphenyls, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran in Lake Michigan sediment and biota. Chemosphere 21:1063–1085
Spear PA, Moon TW, Peakall DB (1985) Liver retinoid concentrations in natural populations of herring gulls (Larus argentatus) contaminated by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and in ring doves (Streptopelia risoria) injected with a dioxin analogue. Can J Zool 64:204–207
Spear PA, Garcin H, Narbonne JF (1988) Increased retinoic acid metabolism following 3,3′, 4,4′, 5,5′-hexabromobiphenyl injection. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 66:1181–1186
Spear PA, Bourbonnais DH, Norstrom RJ, Moon TW (1990) Yolk retinoids (vitamin A) in eggs of the Herring gull and correlations with polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1053–1061
Stienen EWM, Brenninkmeijer A (1992) Ecologisch profiel van de visdief (Sterna hirundo) [Dutch]. RIN-rapport 92/18, Arnhem, 128 pp
Stronkhorst J, Ysebaert TJ, Smedes F, Meininger PL, Dirksen SR, Boudewijn Th (1993) Contaminants in eggs of some waterbird species from the Scheldt estuary, SW Netherlands. Mar Pollut Bull 26:572–578
Ten Brink BJE, Hosper SH, Colijn F (1991) A quatitative method for description and assessment of ecosystems: the AMOEBA-approach Mar Pollut Bull 23:265–270
Thompson JN (1970) The role of vitamin A in reproduction. In J.H.F. DeLuca and Suttie (eds) The Fat-Soluble Vitamins, p 267–281. The University of Wisconsin Pres, Madison, WI
Tillitt DE, Ankley GT, Giesy JP, Ludwig JP, Kurita-Matsuba H, Weseloh DV, Ross PS, Bishop CA, Sileo L, Stromborg KL, Larson J, Kubiak TJ (1992) Polychlorinated biphenyl residues and egg mortality in double-crested cormorants from the Great Lakes. Environ Toxicol Chem 11:1281–1288
Van den Berg M, Craane BLHJ, Sinnege T, Van Mourik S, Dirksen S, Boudewijn Th, Van der Gaag M, Lutke-Schipholt IJ, Spenkelink B, Brouwer A (1995) Biochemical and toxic effects of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), dibenzo-p-dioxines (PCDDs) and dibenzofurans (PCDFs) in the cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo) after in ovo exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 13:803–816
Vethaak AD (1992) Epidemiology of diseases in flounder (Platichthys flesus L.) in Dutch coastal waters, with particular reference to environmental stress factors. PhD Thesis, chapter 2. University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Walker CH (1990) Persistent pollutants in fish-eating sea birds-bioaccumulation, metabolism and effects. Aquat Toxicol 17:293–324
Wobeser GA, Kost W (1992) Starvation, staphylococcosis, and vitamin A deficiency among mallards, overwintering in Saskatchewan. J Wildl Dis 28:215–222
Zile MH (1992) Vitamin A homeostasis endangered by environmental pollutants. Proc Soc Exper Biol Med 201:141–153.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murk, A.J., Boudewijn, T.J., Meininger, P.L. et al. Effects of polyhalogenated aromatic hydrocarbons and related contaminants on common tern reproduction: Integration of biological, biochemical, and chemical data. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 31, 128–140 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203917
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00203917