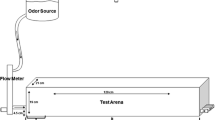
Abstract
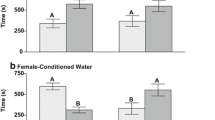
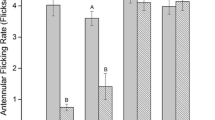
The herbicide atrazine is known to impact negatively olfactory-mediated behaviors in aquatic animals. We have shown that atrazine exposure has deleterious effects on olfactory-mediated behavioral responses to food odors in crayfish; however, recovery of chemosensory abilities post-atrazine exposure has not been investigated. We examined whether crayfish (Orconectes virilis) recovered chemosensory abilities after a 96-h exposure to sublethal, environmentally relevant concentrations of 80 ppb (µg/L) atrazine. Following treatment, we analyzed the ability of the crayfish to locate a food source using a Y-maze with one arm containing fish-flavored gelatin and the other containing unflavored gelatin. We compared the time spent in the food arm of the Y-maze, near the food source, as well as moving and walking speed of control and atrazine-treated crayfish. We also compared the number of crayfish that handled the food source and the amount of food consumed. Following 24-, 48-, and 72-h recovery periods in fresh water, behavioral trials were repeated to determine if there was any observable recovery of chemosensory-mediated behaviors. Atrazine-treated crayfish spent less time in the food arm, at the odor source, and were less successful at finding the food odor source than control crayfish for all times tested. Additionally, atrazine-treated crayfish consumed less fish-flavored than control crayfish; however, treatment did not affect locomotion. Overall, we found that crayfish are not able to recover chemosensory abilities 72 h post-atrazine exposure. Because crayfish rely heavily on their chemosensory abilities to acquire food, the negative impacts of atrazine exposure could affect population size in areas where atrazine is heavily applied.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameyaw-Akumfi C (1977) Feeding chemoreceptor sites in the crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard). Crustaceana 33:259–264. doi:10.2307/20103230
Ameyaw-Akumfi C, Hazlett BA (1975) Sex recognition in the crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Science 190:1225–1226
Andrus JM et al (2015) Spatial and temporal variation of algal assemblages in six Midwest agricultural streams having varying levels of atrazine and other physicochemical attributes. Sci Total Environ 505:65–89. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.09.033
Bardullas U, Giordano M, Rodriguez VM (2013) Atrazine is primarily responsible for the toxicity of long-term exposure to a combination of atrazine and inorganic arsenic in the nigrostriatal system of the albino rat. Neurotoxicol Teratol 40:59–66. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2013.10.003
Battaglin WA, Furlong ET, Burkhardt MR, Peter CJ (2000) Occurrence of sulfonylurea, sulfonamide, imidazolinone, and other herbicides in rivers, reservoirs and ground water in the Midwestern United States, 1998. Sci Total Environ 248:123–133. doi:10.1016/s0048-9697(99)00536-7
Belanger RM, Moore PA (2009) The role of the major chelae in the localization and sampling of female odours by male crayfish, Orconectes rusticus (Girard, 1852). Crustaceana 82:653–668. doi:10.1163/156854009x423210
Belanger RM, Peters TJ, Sabhapathy GS, Khan S, Katta J, Abraham NK (2015) Atrazine exposure affects the ability of crayfish (Orconectes rusticus) to localize a food odor source. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 68:636–645. doi:10.1007/s00244-015-0142-y
Belluck DA, Benjamin SL, Dawson T (1991) Groundwater contamination by atrazine and its metabolites: risk assessment, policy, and legal implications. ACS Symp Ser 459:254–273
Browne AM, Moore PA (2014) The effects of dublethal levels of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide (2,4-D) on feeding behaviors of the crayfish O. rusticus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 67:234–244. doi:10.1007/s00244-014-0032-8
Comber SDW (1999) Abiotic persistence of atrazine and simazine in water. Pestic Sci 55:696–702
Cook ME, Moore PA (2008) The effects of the herbicide metolachlor on agonistic behavior in the crayfish, Orconectes rusticus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55:94–102. doi:10.1007/s00244-007-9088-z
Cowan CM, Thai J, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Nicholson DW, Kaufmann SH, Roskams AJ (2001) Caspases 3 and 9 send a pro-apoptotic signal from synapse to cell body in olfactory receptor neurons. J Neurosci 21:7099–7109
Creed RP Jr (1994) Direct and indirect effects of crayfish grazing in a stream community. Ecology 75:2091–2103. doi:10.2307/1941613
Dorn NJ, Wojdak JM (2004) The role of omnivorous crayfish in littoral communities. Oecologia 140:150–159. doi:10.1007/s00442-004-1548-9
EPA (2003) Decision documents for atrazine. United States Environmental Protection Agency. http://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/REDs/atrazine_combined_docs.pdf. Accessed 10 Aug 2015
EPA (2007) Atrazine: Chemical Summary. United States Environmental Protection Agency. http://www.epa.gov/teach/chem_summ/Atrazine_summary.pdf. Accessed 19 Jan 2015
EPA (2013) Atrazine updates. US Environmental Protection Agency. http://www.epa.gov/pesticides/reregistration/atrazine/atrazine_update.htm. Accessed 3 Aug 2015
EPA (2014) Atrazine updates: 2014 atrazine ecological exposure monitoring program data. United States Environmental Protection Agency. http://www.regulations.gov/#!documentDetail;D=EPA-HQ-OPP-2003-0367-0303. Accessed 19 Jul 2015
Fedotov VP (2009) Systems of chemoperception in decapod crayfish. J Evol Biochem Physiol 45:1–26. doi:10.1134/S0022093009010013
Frey JW (2001) Occurrence, distribution, loads of selected pesticides in streams in the Lake Erie-St. Clair basin, 1996–1998. National Water Quality Assessment Program, Branch of Information Services, US Geological Survey, Denver, CO
Giri T, Dunham DW (2000) Female crayfish (Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852)) use both antennular rami in the localization of male odour. Crustaceana 73:447–458
Hazlett BA (1990) Source and nature of disturbance-chemical system in crayfish. J Chem Ecol 16:2263–2275. doi:10.1007/bf01026936
Helfrich LA, Weigmann DL, Hipkins P, Stinson ER (1996) Pesticides and aquatic animals: a guide to reducing impacts on aquatic systems. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, pp 420–103. https://pubs.ext.vt.edu/420/420-013/420-013_pdf.pdf. Accessed 6 Aug 2015
Huang P, Yang J, Ning J, Wang M, Song Q (2015) Atrazine triggers DNA damage response and induces DNA double-strand breaks in MCF-10A cells. Int J Mol Sci 16:14353–14368. doi:10.3390/ijms160714353
Jablonowski ND, Schaffer A, Burauel P (2011) Still present after all these years: persistence plus potential toxicity raise questions about the use of atrazine. Environ Sci Pollut R 18:328–331. doi:10.1007/s11356-010-0431-y
Keller TA, Moore PA (1999) Effects of ontogeny and odors on behavior: the influence of crayfish size and fish odors on crayfish movement. Mar Freshw Behav Phys 33:35–50
Kiely T, Donaldson D, Grube A (2004) Pesticide industry sales and usage: 2000 and 2001 market estimates. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington
Klaine SJ, Hinman ML, Winkelmann DA, Sauser KR, Martin JR, Moore LW (1988) Characterization of agricultural nonpoint pollution—pesticide migration in a west tennessee watershed. Environ Toxicol Chem 7:609–614. doi:10.1002/etc.5620070802
Kolok AS, Jeffries MKS, Knight L, Snow DD, Bartelt-Hunt SL (2014) The hourglass: a conceptual framework for the transport of biologically active compounds from agricultural landscapes(1). J Am Water Resour As 50:266–274. doi:10.1111/jawr.12158
Lahman SE, Moore PA (2015) Olfactory sampling recovery following sublethal copper exposure in the rusty crayfish. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol, Orconectes rusticus. doi:10.1007/s00128-015-1623-4
Lahman SE, Trent KR, Moore PA (2015) Sublethal copper toxicity impairs chemical orientation in the crayfish, Orconectes rusticus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:369–377. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.022
Lerch RN, Blanchard PE, Thurman EM (1998) Contribution of hydroxylated atrazine degradation products to the total atrazine load in midwestern streams. Environ Sci Technol 32:40–48. doi:10.1021/es970447g
Liu XM, Shao JZ, Xiang LX, Chen XY (2006) Cytotoxic effects and apoptosis induction of atrazine in a grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) cell line. Environ Toxicol 21:80–89. doi:10.1002/tox.20159
Lodge DM, Kershner MW, Aloi JE, Covich AP (1994) Effects of an omnivorous crayfish (Orconectes rusticus) on a freshwater littoral food web. Ecology 75:1265–1281. doi:10.2307/1937452
Miller SM, Sweet CW, Depinto JV, Hornbuckle KC (2000) Atrazine and nutrients in precipitation: results from the Lake Michigan mass balance study. Environ Sci Technol 34:55–61. doi:10.1021/es990486n
Mitchell PD (2014) Market-level assessment of the economic benefits of atrazine in the United States. Pest Manag Sci 70:1684–1696. doi:10.1002/ps.3703
Momot WT (1995) Redefining the role of crayfish in aquatic ecosystems. Rev Fish Sci 3:33–63. doi:10.1080/10641269509388566
Momot WT, Gowing H, Jones PD (1978) Dynamics of crayfish and their role in ecosystems. Am Midl Nat 99:10–35. doi:10.2307/2424930
Monteclaro HM, Anraku K, Uno S, Koyama J, Matsuoka T, Yan HY (2011) Sensitivity of crayfish Procambarus clarkii antennules to hydrodynamic stimuli is reduced during diazinon exposure. Zool Stud 50:145–154
Moore A, Lower N (2001) The impact of two pesticides on olfactory-mediated endocrine function in mature male Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) parr. Comp Biochem Physiol B 129:269–276. doi:10.1016/s1096-4959(01)00321-9
Moore A, Waring CP (1998) Mechanistic effects of a triazine pesticide on reproductive endocrine function in mature male Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) parr. Pestic Biochem Phys 62:41–50. doi:10.1006/pest.1998.2366
Nieves-Puigdoller K, Bjornsson BT, McCormick SD (2007) Effects of hexazinone and atrazine on the physiology and endocrinology of smolt development in Atlantic salmon. Aquat Toxicol 84:27–37. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.05.011
NRDC (2006) Atrazine contamination in Indiana. National Resources Defense Council http://docs.nrdc.org/health/files/hea_07091201b.pdf
Rohr JR, McCoy KA (2010) A qualitative meta-analysis reveals consistent effects of atrazine on freshwater fish and amphibians. Environ Health Perspect 118:20–32. doi:10.1289/ehp.0901164
Roses N, Poquet M, Munoz I (1999) Behavioural and histological effects of atrazine on freshwater molluscs (Physa acuta Drap. and Ancylus fluviatilis Mull. Gastropoda). J Appl Toxicol 19:351–356. doi:10.1002/(sici)1099-1263(199909/10)19:5<351:aid-jat588>3.0.co;2-h
Rowe CL, Hopkins WA, Zehnder C, Congdon JD (2001) Metabolic costs incurred by crayfish (Procambarus acutus) in a trace element-polluted habitat: further evidence of similar responses among diverse taxonomic groups. Comp Biochem Physiol C 129:275–283. doi:10.1016/s1532-0456(01)00204-6
Saglio P, Trijasse S (1998) Behavioral responses to atrazine and diuron in goldfish. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 35:484–491
Sass JB, Colangelo A (2006) European Union bans atrazine, while the United States negotiates continued use. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 12:260–267
Scribner EA, Battaglin WA, Goolsby DA, Thurman EM (2000) Changes in herbicide concentrations in Midwestern streams in relation to changes in use, 1989-1998. Sci Total Environ 248:255–263.
Solomon KR, Carr JA, Du Preez LH, Giesy JP, Kendall RJ, Smith EE (2008) Effects of atrazine on fish, amphibians, and aquatic reptiles: a critical review. Crit Rev Toxicol 38:721–772. doi:10.1080/10408440802116496
Thurman EM, Goolsby DA, Meyer MT, Kolpin DW (1991) Herbicides in surface waters of the Midwestern United States—the effect of spring flush. Environ Sci Technol 25:1794–1796. doi:10.1021/es00022a018
Thurman EM, Goolsby DA, Meyer MT, Mills MS, Pomes ML, Kolpin DW (1992) A reconnaissance study of herbicides and their metabolites in surface-water of the Midwestern United States using immunoassay and gas-chromatography mass-spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol 26:2440–2447. doi:10.1021/es00036a016
Tierney KB, Singh CR, Ross PS, Kennedy CJ (2007) Relating olfactory neurotoxicity to altered olfactory-mediated behaviors in rainbow trout exposed to three currently-used pesticides. Aquat Toxicol 81:55–64. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.11.006
Tierney KB, Sampson JL, Ross PS, Sekela MA, Kennedy CJ (2008) Salmon olfaction is impaired by an environmentally realistic pesticide mixture. Environ Sci Technol 42:4996–5001. doi:10.1021/es800240u
Tomba AM, Keller TA, Moore PA (2001) Foraging in complex odor landscapes: chemical orientation strategies during stimulation by conflicting chemical cues. J N Am Benthol Soc 20:211–222
USGS (2007) The quality of our nation’s waters: Pesticides in the nation’s streams and ground water, 1992–2001. United States Geological Survey. http://pubs.usgs.gov/circ/2005/1291/. Accessed 7 Aug 2015
Usio N, Townsend CR (2002) Functional significance of crayfish in stream food webs: roles of omnivory, substrate heterogeneity and sex. Oikos 98:512–522. doi:10.2307/3547192
Velisek J, Kouba A, Stara A (2013) Acute toxicity of triazine pesticides to juvenile signal crayfish (Pacifastacus leniusculus). Neuroendocrinol Lett 34:31–36
Vogel JR, Majewski MS, Capel PD (2008) Pesticides in rain in four agricultural watersheds in the United States. J Environ Qual 37:1101–1115. doi:10.2134/jeq2007.0079
Walther JS (2003) Surface water pesticide contamination in the upper Terrebonne Basin of Louisiana. Master’s thesis, Louisiana State University
Wolf MC, Moore PA (2002) Effects of the herbicide metolachlor on the perception of chemical stimuli by Orconectes rusticus. J N Am Benthol Soc 21:457–467. doi:10.2307/1468482
Wolf MC, Voigt R, Moore PA (2004) Spatial arrangement of odor sources modifies the temporal aspects of crayfish search strategies. J Chem Ecol 30:501–517. doi:10.1023/b:joec.0000018625.83906.95
Wu M, Quirindongo M, Sass J, Wetzler A (2010) Still poisoning the well. Atrazine continues to contaminate surface water and drinking water in the United States. http://www.nrdc.org/health/atrazine/files/atrazine10.pdf. Accessed 19 Jul 2015
Xu XB, Shi YJ, Lu YL, Zheng XQ, Ritchie RJ (2015) Growth inhibition and altered gene transcript levels in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 69:1–7. doi:10.1007/s00244-014-0125-4
Zar JH (2010) Biostatistical Analysis, 5th edn. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River
Zhu LS, Dong XL, Xie H, Wang J, Wang JH, Su J, Yu CW (2011) DNA damage and effects on glutathione-S-transferase activity induced by atrazine exposure in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Toxicol 26:480–488. doi:10.1002/tox.20575
Zulandt Schneider RA, Huber R, Moore PA (2001) Individual and status recognition in the crayfish, Orconectes rusticus: the effects of urine release on fight dynamics. Behaviour 138:137–153. doi:10.1163/15685390151074348
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Paul A. Moore and the members of the Laboratory for Sensory Ecology Bowling Green State University for the use of their Y-maze and for their continued support. Additionally, they acknowledge Madison Kirby for help collecting data and other contributions to this research project and are thankful for grants from the University of Detroit Mercy to both Rachelle M. Belanger and Noor K. Abraham.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belanger, R.M., Mooney, L.N., Nguyen, H.M. et al. Acute Atrazine Exposure has Lasting Effects on Chemosensory Responses to Food Odors in Crayfish (Orconectes virilis). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 70, 289–300 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0234-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0234-8