Abstract
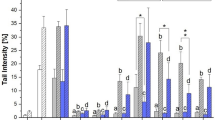
The gastrointestinal tract is the main target of exposure to mycotoxin fumonisin B1 (FB1), common natural contaminant in food. Previous studies reported that proliferating cells are more sensitive than confluent cells to the toxic effect of FB1. This study aims to investigate, by dose- and time-dependent experiments on human colon proliferating intestinal cell line (HT-29), the modifications induced by FB1 at concentrations ranging from 0.25 to 69 μM. The choice of highest FB1 concentration considered the low toxicity previously reported on intestinal cell lines, whereas the lowest one corresponded to the lower FBs levels permitted by European Commission Regulation. Different functional parameters were tested such as cell proliferation, oxidative status, immunomodulatory effect and changes in membrane microviscosity. In addition FB1-FITC localization in this cell line was assessed by using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Lipid peroxidation induction was the main and early (12 h) effect induced by FB1 at concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 69 μM, followed by inhibition of cell proliferation (up to 8.6 μM), the immunomodulatory effect (up to 17.2 μM), by assessing IL-8 secretion, and increase in membrane microviscosity (up to 34.5 μM). The toxic effects observed in different functional parameters were not dose-dependent and could be the consequence of the FB1 intracytoplasmatic localization as confirmed by confocal microscopy results. The different timescales and concentrations active of different functional parameters could suggest different cellular targets of FB1.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abado-Becognee K, Mobio TA, Ennamany R, Fleurat-Lessard F, Shier WT et al (1998) Cytotoxicity of fumonisin B1: implication of lipid peroxidation and inhibition of protein and DNA syntheses. Arch Toxicol 72(4):233–236
Bouhet S, Oswald IP (2007) The intestine as a possible target for fumonisin toxicity. Mol Nutr Food Res 51:925–931
Bouhet S, Hourcade E, Loiseau N, Fikry A, Martinez S et al (2004) The mycotoxin Fumonisin B1 alters the proliferation and the barrier function of porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Toxicol Sci 77:165–171
Bouhet S, Le Dorze E, Peres S, Fairbrother JM, Oswald IP (2006) Mycotoxin fumonisin B1 selectively down-regulates the basal IL-8 expression in pig intestine: in vivo and in vitro studies. Food Chem Toxicol 44:1768–1773
Caloni F, Spotti M, Pompa G, Zucco F, Stammati A et al (2002) Evaluation of fumonisin B1 and its metabolites absorption and toxicity on intestinal cells line Caco-2. Toxicon 40:1181–1188
Domijian AM, Abramov AY (2011) Fumonisin B1 inhibits mitochondrial respiration and deregulates calcium homeostasis- implication to mechanism of cell toxicity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:892–904
Ferrante MC, Meli R, Mattace Raso G, Esposito E, Severino L et al (2002) Effect of fumonisin B1 on structure and function of macrophage plasma membrane. Toxicol Lett 129(3):181–187
Galvano F, Campisi A, Russo A, Galvano G, Palumbo M et al (2002a) DNA damage in astrocytes exposed to fumonisin B1. Neurochem Res 27(4):345–351
Galvano F, Russo A, Cardile V, Galvano G, Vanella A et al (2002b) DNA damage in human fibroblasts exposed to fumonisin B1. Food Chem Toxicol 40(1):25–31
Gelderblom W, Marasas W (2012) Controversies in fumonisin mycotoxicology and risk assessment. Hum Exp Toxicol 31:215–235
Haugland RP (1996) Handbook of fluorescent probes and research chemicals. Molecular Probes Inc., Eugene
International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS) (2000) In: Marasas WFO, Miller JD, Riley RT, Visconti A (eds) Environmental Health Criteria 219. Fumonisin B1. World Health Organization, Geneva
Kouadio JH, Mobio TA, Baudrimont I, Moukha S, Dano SD et al (2005) Comparative study of cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by deoxynivalenol, zearalenone or fumonisin B1 in human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Toxicology 213:56–65
Kuhry JG, Duportail G, Bronner C, Laustriat G (1985) Plasma membrane fluidity measurements on whole living cells by fluorescence anisotropy of trimethylammoniumdiphenylhexatriene. Biochim Biophys Acta 845(1):60–67
Liu BH, Yu FY, Chan MH, Yang YL (2002) The effects of mycotoxins, fumonisin B1 and aflatoxin B1, on primary swine alveolar macrophages. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 180(3):197–204
Loikkanen JJ, Naarala J, Savolainen KM (1998) Modification of glutamate-induced oxidative stress by lead: the role of extracellular calcium. Free Radic Biol Med 24(2):377–384
Mahmoodi M, Alizadeh AM, Sohanaki H, Rezaei N, Amini-Najafi F et al (2012) Impact of fumonisin B1 on the production of inflammatory cytokines by gastric and colon cell lines. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 11(2):165–173
Meca G, Ruiz MJ, Fernandez-Franzón M, Ritieni A, Manes J (2010) Isolation, purification, LC-MS/MS characterization and reactive oxygen species induced by fumonisin B1 in VERO cells. Food Chem Toxicol 48(10):2891–2897
Meli R, Ferrante MC, Raso GM, Cavaliere M, Di Carlo R et al (2000) Effect of fumonisin B1 on inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in LPS-stimulated J774 A.1 cells. Life Sci 67(23):2845–2853
Minervini F, Fornelli F, Flynn KM (2004) Toxicity and apoptosis induced by the mycotoxins nivalenol, deoxynivalenol and fumonisin B1 in a human erythroleukemia cell line. Toxicol In Vitro 18(1):21–28
Minervini F, Fornelli F, Lucivero G, Romano C, Visconti A (2005) T-2 toxin immunotoxicity on human B and T lymphoid cell lines. Toxicology 210:81–91
Mobio TA, Tavan E, Baudrimont I, Anane R, Carratú MR et al (2003) Comparative study of the toxic effects of fumonisin B1 in rat C6 glioma cells and p53-null mouse embryo fibroblasts. Toxicology 183(1–3):65–75
Myburg RB, Needhi N, Chuturgoon AA (2009) The ultrastructural effects and immunolocalisation of fumonisin B1 on cultured oesophageal cancer cells (SNO). S Afr J Sci 105(5–6):212–222
Riley RT, Voss KA, Norred WP, Sharma RP, Wang E, Merrill AH Jr (1998) Fumonisins: mechanism of mycotoxicity. Rev Méd Vét 149(6):617–626
Riley RT, Enongene E, Voss KA, Norred KA, Meredith FI et al (2001) Sphingolipid perturbations as mechanisms for fumonisin carcinogenesis. Environ Health Perspect 109(2):301–308
Schmelz EM, Dombrink-Kurtzman MA, Roberts PC, Kozutsumi Y, Kawasaki T et al (1998) Induction of apoptosis of fumonisin B1 in HT-29 cells is mediated by the accumulation of endogenous free sphingoid bases. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 148:252–260
SCOOP (2003) Collection of occurrence data of Fusarium toxins in food and assessment of dietary intake by the population of EU member States. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/food/fs/scoop/task3210.pdf. Accessed 13 Feb 2014
Shepard GS, Thiel PG, Sydenham EW, Alberts JF, Cawood ME (1994) Distribution and excretion of a single dose of the mycotoxin fumonisin B1 in a non-human primate. Toxicon 32(6):735–741
Shephard GS, Thiel PG, Sydenham EW, Savard ME (1995) Fate of a single dose of 14C-labelled fumonisin B1 in vervet monkeys. Nat Toxins 3:145–150
Shier WT (2000) The fumonisin paradox: a review of research on oral bioavailability of fumonisin B1, a mycotoxin produced by Fusarium moniliforme. J Toxicol Toxin Rev 19:161–187
Shinitzky M, Barenholz Y (1978) Fluidity parameters of lipid regions determined by fluorescence polarization. Biochim Biophys Acta 515:367–394
Soriano JM, Gonzalez L, Català AI (2005) Mechanism of action of sphingolipids and their metabolites in the toxicity of fumonisin B1. Prog Lipid Res 44:345–356
Stockmann-Juvala H, Mikkola J, Naarala J, Loikkanen J, Elovaara E et al (2004a) Fumonisin B1-induced toxicity and oxidative damage in U-118MG glioblastoma cells. Toxicology 202:173–183
Stockmann-Juvala H, Mikkola J, Naarala J, Loikkanen J, Elovaara E et al (2004b) Oxidative stress induced by fumonisin B1 in continuous human and rodent neural cell cultures. Free Radic Res 38:933–942
Theumer MG, Clop EM, Rubinstein HR, Perillo MA (2008) The lipid-mediated hypothesis of fumonisin B1 toxicodynamics tested in model membrane. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 64:22–33
Theumer MG, Canepa MC, Lopez AG, Mary VS, Dambolena JS, Rubinstein HR (2010) Suchronic mycotoxicoses in Wistar rats: assessment of the in vivo and in vitro genotoxicity induced by fumonisins and aflatoxin B1 and oxidative stress biomarker status. Toxicology 268:104–110
Van der Westhuizen L, Shepard GS, Burger HM, Rheeder JP et al (2011) Fumonisin B1 as a urinary biomarker of exposure in a maize intervention study among South African subsistence farmers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 20:483–489
World Health Organization and International Agency for Research on Cancer (1993) Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk to humans. Some naturally occurring substances: Food items and constituents, heterocyclic aromatic amines and mycotoxins. IARC, Lyon, pp 445–466
Yin JJ, Smith MJ, Eppley RM, Troy AL, Page SW et al (1996) Effects of fumonisin B1 and (hydrolyzed) fumonisin backbone AP1 on membranes: a spin-label study. Arch Biochem Biophys 335(1):13–22
Yin JJ, Smith MH, Eppley RM, Page SW, Sphon JA (1998) Effects of fumonisin B1 on lipid peroxidation in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1371:134–142
Yoo HS, Norred WP, Showker J, Riley RT (1996) Elevated sphingoid bases and complex sphingolipid depletion as contributing factors in Fumonisin-induced cytotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 138:211–218
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by EC KBBE-2007-222690-2 Novel Integrated Strategies for worldwide mycotoxin reduction in food and feed chains (MycoRed).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minervini, F., Garbetta, A., D’Antuono, I. et al. Toxic Mechanisms Induced by Fumonisin B1 Mycotoxin on Human Intestinal Cell Line. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 67, 115–123 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0004-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0004-z