Abstract
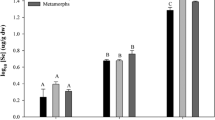
We performed an experiment in which larval gray tree frogs (Hyla chrysoscelis) were raised through metamorphosis on diets increased with a suite of elements associated with coal combustion residues (silver [Ag], arsenic [As], cadmium [Cd], chromium [Cr], copper [Cu], mercury [Hg], lead [Pb], selenium [Se], vanadium [V], and zinc [Zn]) at “low” and “high” concentrations. We quantified accumulation of metals at three life stages (mid-larval development, initiation of metamorphosis, and completion of metamorphosis) as well as effects on survival, metabolic rate, size at metamorphosis, and duration and loss of weight during metamorphosis. Most elements were accumulated in a dose-dependent pattern by some or all life stages, although this was not the case for Hg. For most elements, larval body burdens exceeded those of later life stages in some or all treatments (control, low, or high). However for Se, As, and Hg, body burdens in control and low concentrations were increased in later compared with earlier life stages. A lack of dose-dependent accumulation of Hg suggests that the presence of high concentrations of other elements (possibly Se) either inhibited accumulation or increased depuration of Hg. The duration of metamorphosis (forelimb emergence through tail resorption) was lengthened in individuals exposed to the highest concentrations of elements, but there were no other statistically significant biological effects. This study shows that patterns of accumulation and possibly depuration of metals and trace elements are complex in animals possessing complex life cycles. Further study is required to determine specific interactions affecting these patterns, in particular which elements may be responsible for affecting accumulation or retention of Hg when organisms are exposed to complex mixtures of elements.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergeron CM, Bodinof CM, Unrine JM, Hopkins WA (2010) Bioaccumulation and maternal transfer of mercury and selenium in amphibians. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:989–997
Bergeron CM, Hopkins WA, Todd BD, Hepner MJ, Unrine JM (2011) Interactive effects of maternal and dietary mercury exposure have latent and lethal consequences for amphibian larvae. Environ Sci Technol 45:3781–3787
Bjerregaard P, Fjordside S, Hansen MG, Petrova MB (2011) Dietary selenium reduces retention of methyl mercury in freshwater fish. Environ Sci Technol 45:9793–9798
Burger J, Gochfeld M, Jeitner C, Donio M, Pittfield T (2012) Interspecific and intraspecific variation in selenium:mercury molar ratios in saltwater fish from the Aleutians: potential protection on mercury toxicity by selenium. Sci Total Environ 431:46–56
Cuvin-Alarar MLA, Furness RW (1991) Mercury and selenium interaction: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 21:348–364
Dang F, Wang W-X (2011) Antagonistic interaction of mercury and selenium in a marine fish is dependent on their chemical species. Environ Sci Technol 45:3116–3122
Gosner KL (1960) A simplified table for staging anuran embryos and larvae with notes on identification. Herpetologica 16:183–190
Hopkins WA, Rowe CL, Congdon JD (1999) Elevated trace element concentrations and standard metabolic rate in banded water snakes, Nerodia fasciata, exposed to coal combustion wastes. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:1258–1263
Huang Y, Jin B, Zhong Z, Xiao R, Tang Z, Ren H (2004) Trace elements (Mn, Cr, Pb, Se, Zn, Cd and Hg) in emissions from a pulverized coal boiler. Fuel Process Technol 86:2332
Khan MAK, Wang F (2009) Mercury-selenium compounds and their toxicological significance: toward a molecular understanding of the mercury–selenium antagonism. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1567–1577
Manyin T, Rowe CL (2009) Bioenergetic effects of aqueous copper and cadmium on the grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio. Comp Biochem Physiol C 150:65–71
Marques SM, Antunes SC, Nunes B, Goncalves F, Pereira R (2011) Antioxidant response and metal accumulation in tissues of Iberian green frogs (Pelophylax perezi) inhabiting a deactivated uranium mine. Ecotoxicology 20:1315–1327
Newman MC, Alberts JJ, Greenhunt VA (1985) Geochemical factors complicating the use of aufwuchs to monitor bioaccumulation of arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper and zinc. Water Res 19:1157–1165
Peltier GL, Wright MS, Hopkins WA, Meyer JL (2009) Accumulation of trace elements and growth responses in Corbicula fluminea downstream of a coal-fired power plant. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1384–1391
Peterson JD, Peterson VA, Mendonca MT (2008) Growth and developmental effects of coal combustion residues on Southern Leopard Frog (Rana sphenocephala) tadpoles exposed throughout metamorphosis. Copeia 2008:499–503
Pryor GS, Bjorndal KA (2005) Symbiotic fermentation, digesta passage, and gastrointestinal morphology in bullfrog tadpoles (Rana catesbeiana). Physiol Biochem Zool 78:201–215
Raimondo SM, Rowe CL, Congdon JD (1998) Exposure to coal ash impacts swimming behavior and predator avoidance in larval bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana). J Herpetol 32:289–292
Roe JH, Hopkins WA, Jackson BP (2005) Species and stage-specific differences in trace element tissue concentrations in amphibians: implications for the disposal of coal combustion wastes. Environ Pollut 136:353–363
Rowe CL, Kinney OM, Fiori AP, Congdon JD (1996) Oral deformities in tadpoles (Rana catesbeiana) associated with coal ash deposition: effects on grazing ability and growth. Freshw Biol 37:723–730
Rowe CL, Kinney OM, Nagle RD, Congdon JD (1998a) Elevated maintenance costs in an anuran (Rana catesbeiana) exposed to a mixture of trace elements during the embryonic and early larval periods. Physiol Zool 71:27–35
Rowe CL, Kinney OM, Congdon JD (1998b) Oral deformities in tadpoles of the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) caused by conditions in a polluted habitat. Copeia 1998:244–246
Rowe CL, Hopkins WA, Zehnder C, Congdon JD (2001a) Metabolic costs incurred by crayfish (Procambarus acutus) in a trace element-polluted habitat: further evidence of a common response among diverse taxonomic groups. Comp Biochem Physiol C 129:275–283
Rowe CL, Hopkins WA, Coffman V (2001b) Failed recruitment of southern toads (Bufo terrestris) in a trace element-contaminated breeding habitat: direct and indirect effects that may lead to a local population sink. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 40:399–405
Rowe CL, Hopkins WA, Congdon JD (2002) Ecotoxicological implications of aquatic disposal of coal combustion residues in the United States: a review. Environ Monit Assess 80:207–276
Rowe CL, Heyes A, Hopkins WA (2009) Effects of dietary vanadium on growth and lipid storage in a larval anuran: results from studies employing ad libitum and rationed feeding. Aquat Toxicol 91:179–186
Rowe CL, Heyes A, Hilton J (2011) Differential patterns of accumulation and depuration of dietary selenium and vanadium during metamorphosis in the gray treefrog (Hyla versicolor). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:336–342
Snodgrass JW, Hopkins WA, Roe JH (2003) Relationships among developmental stage, metamorphic timing, and concentrations of elements in bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana). Environ Toxicol Chem 22:1597–1604
Snodgrass JW, Hopkins WA, Broughton J, Gwinn D, Baionno JA, Burger J (2004) Species-specific responses of developing anurans to coal combustion wastes. Aquat Toxicol 66:171–182
Snodgrass JW, Hopkins WA, Jackson BP, Baionno JA, Broughton J (2005) Influence of larval period on responses of overwintering green frog (Rana clamitans) larvae exposed to contaminated sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:1508–1514
Sørmo EG, Ciesielski TM, Øverjordet IB, Lierhagen, Eggen GS, Berg T, Jenssen BM (2011) Selenium moderates mercury toxicity in free-ranging freshwater fish. Environ Sci Technol 45:6561–6566
Unrine JM, Jagoe CH (2004) Dietary mercury exposure and bioaccumulation in southern leopard frog (Rana sphenocephala) larvae. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:2956–2963
Unrine JM, Hopkins WA, Romanek CS, Jackson BP (2007) Bioaccumulation of trace elements in omnivorous amphibian larvae: implications for amphibian health and contaminant transport. Environ Poll 149:182–192
Yang DY, Chen YW, Gunn JM, Belzile N (2008) Selenium and mercury in organisms: interactions and mechanisms. Environ Rev 16:71–92
Acknowledgments
P. Conrad was supported by the National Science Foundation Research Experience for Undergraduates Program 0754609 administered by Maryland Sea Grant. This is contribution No. 4810 of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Heyes, A., Rowe, C.L. & Conrad, P. Differential Patterns of Accumulation and Retention of Dietary Trace Elements Associated With Coal Ash During Larval Development and Metamorphosis of an Amphibian. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 66, 78–85 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9957-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-013-9957-6