Abstract
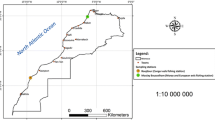
In the light of the alarming decline of the European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) population, there is an urgent need to define ecological indicators for eel habitat quality. Due to an increasing shortage of glass eels available for local stock enhancement, the decision of whether restocking is a valuable management tool to increase high-quality silver eel escapement to the sea needs to be evaluated. Organic contaminants, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), are among the major threats to fish in their habitat. Therefore, the aim of the investigation presented here was to examine metabolites of PAHs in eel bile as one possible marker for habitat quality. In total, 170 yellow eels were collected in the rivers Rhine, Ems, Weser, Elbe, Havel, Schlei, Eider, Trave, Warnow, Peene, Uecker, and Oder in 2009. PAH metabolites in eel bile were analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Metabolites of pyrene and phenanthrene were investigated. Concentrations of PAH metabolites in eel bile varied significantly between several rivers, with the highest mean concentrations of 1-hydroxypyrene and 1-hydroxyphenanthrene in eel bile from the river Trave (2421 and 632 ng/ml). Moreover, huge differences in the ratio of 1-hydroxypyrene to 1-hydroxyphenanthrene, with the highest mean value in eel bile from the river Ems (7.43) and the lowest mean value in eel bile from the river Uecker (0.70), indicate different sources of PAH contamination. A comparative analysis of PAH-metabolite contamination of eels in different river systems is seen as a first step toward a classification of freshwater habitats for restocking purposes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas E, Baussant T, Balk L, Liewenborg B, Andersen OK (2000a) PAH metabolites in bile, cytochrome P4501A and DNA adducts as environmental risk parameters for chronic oil exposure: a laboratory experiment with Atlantic cod. Aquat Toxicol 51:241–258
Aas E, Beyer J, Goksoyr A (2000b) Fixed wavelength fluorescence (FF) of bile as a monitoring tool for polyaromatic hydrocarbon exposure in fish: an evaluation of compound specificity, inner filter effect and signal interpretation. Biomarkers 5:9–23
Ariese F, Kok SJ, Verkaik M, Gooijer C, Velthorst NH, Hofstraat JW (1993) Synchronous fluorescence spectrometry of fish bile: a rapid screening method for the biomonitoring of PAH exposure. Aquat Toxicol 26:273–286
Ariese F, Burgers I, Oudhoff K, Rutten T, Stroomberg G, Vethaak D (1997) Comparison of analytical approaches for PAH metabolites in fish bile samples for marine and estuarine monitoring. Institute for Environmental Studies, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, R-97/9, p 29
Au DWT, Wu RSS, Zhou BS, Lam PKS (1999) Relationship between ultrastructural changes and EROD activities in liver of fish exposed to benzo[a]pyrene. Environ Pollut 104:235–247
Beyer J, Jonsson G, Porte C, Krahn MM, Ariese F (2010) Analytical methods for determining metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) pollutants in fish bile: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 30:224–244
Brack W, Altenburger R, Ensenbach U, Möder M, Segner H, Schuurmann G (1999) Bioassay-directed identification of organic toxicants in river sediment in the industrial region of Bitterfeld (Germany) – a contribution to hazard assessment. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 37:164–174
Brumley CM, Haritos VS, Ahokas JT, Holdway DA (1998) The effects of exposure, duration and feeding status on fish bile metabolites: implications for biomonitoring. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 39:147–153
Buet A, Banas D, Vollaire Y, Coulet E, Roche H (2006) Biomarker responses in European eel (Anguilla anguilla) exposed to persist organic pollutants. A field study in the Vaccarès lagoon (Camargue, France). Chemosphere 65:1846–1858
Buhler DR, Williams DE (1989) Enzymes involved in metabolism of PAH by fishes and other aquatic animals: oxidative enzymes (or phase I enzymes). In: Varanasi U (ed) Metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the aquatic environment. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 151–184
Collier TK, Varanasi U (1991) Hepatic activities of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes and biliary levels of xenobiotics in English sole (Parophrys vetulus) exposed to environmental contaminants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20:462–473
De’Ath G, Fabricius KE (2000) Classification and regression trees: a powerful yet simple technique for ecological data analysis. Ecology 81:3178–3192
Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. (1994) 32645, Nachweis-, Erfassungs- und Bestimmungsgrenze. Beuth Verlag, Berlin
Di Giulio RT, Benson WH, Sanders BM, van Veld PA (1995) Biochemical mechanisms: metabolism, adaptation, and toxicity. In: Rand GM (ed) Fundamentals of aquatic toxicology. Taylor & Francis, Washington, DC, pp 523–561
Durif C, Dufour S, Elie P (2005) The silvering process of Anguilla anguilla: a new classification from yellow resident to silver migrating stage. J Fish Biol 66:1025–1043
Eggens ML, Opperhuizen A, Boon JP (1996) Temporal variation of CYP1A indices, PCB and 1-OH pyrene concentration in flounder, Platichthys flesus, from the Dutch Wadden Sea. Chemosphere 33:1579–1596
Escartin E, Porte C (1999) Assessment of PAH pollution in coastal areas from the NW Mediterranean through the analysis of fish bile. Mar Pollut Bull 38:1200–1206
European Union Council Regulation (EC) No. 1100 (2007) Establishing measures for the recovery of the stock of European eel. Official Journal of the European Union, L 248/17
Fenet H, Gomez E, Rosain D, Casellas C (2006) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites and 7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase activity in caged European eels. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:232–236
Gorbi S, Baldini C, Regoli F (2005) Seasonal variability of metallothioneins, cytochrome P450, bile metabolites and oxyradical metabolism in the European eel Anguilla anguilla L. (Anguillidae) and striped mullet Mugil cephalus L. (Mugilidae). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 49:62–70
Grossbard ML, Boyer JL, Gorden ER (1987) The excretion pattern of biliverdin and bilirubin in bile of the small skate (Raja erinacea). J Comp Physiol B 157:61–66
International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (2009) Report of the ICES Advisory Committee 2009. ICES Advice 2009, Book 9. http://www.ices.dk/products/icesadvice.asp. Accessed 21 June 2011
International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (2010a) Report of the ICES Advisory Committee 2010, ICES Advice 2010. Book 9, pp 115–123. http://www.ices.dk/products/icesadvice.asp. Accessed 21 June 2011
International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (2010b) Advice 1.5.5.1. Further development of guidance on integrated monitoring and assessment of chemicals and biological effects, p 57. http://www.ices.dk/committe/acom/comwork/report/2010/Special%20Requests/OSPAR%20Guidance%20on%20integrated%20monitoring%20and%20assessment.pdf. Accessed 21 June 2011
James MO, Kleinow KM (1993) Trophic transfer of chemicals in the aquatic environment. In: Malins DC, Ostrander GK (eds) Aquatic toxicology: molecular, biochemical and cellular perspectives. Lewis, London, pp 69–92
Kammann U (2007) PAH metabolites in bile fluids of dab (Limanda limanda) and flounder (Platichthys flesus)―spatial distribution and seasonal changes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 14:102–108
Kammann U, Gercken J (2010) PAK-Metaboliten in Aalmuttern (Zoarces viviparus) aus der Wismar-Bucht. Umweltwiss Schadst Forsch 22:541–546
Krahn MM, Myers MS, Burrows DG, Malins DC (1984) Determination of metabolites of xenobiotics in the bile of fish from polluted waterways. Xenobiotica 14:633–646
Limburg KE, Wickström H, Svedäng H, Elfman M, Kristiansson P (2003) Do stocked freshwater eels migrate? Evidence from the Baltic suggests “Yes”. Am Fish Soc Symp 33:275–284
Lin ELC, Cormier SM, Racine RN (1994) Synchronous fluorometric measurement of metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the bile of brown bullhead. Environ Toxicol Chem 13:707–715
Luthe G, Stroomberg GJ, Ariese F, Brinkman UAT, van Straalen NM (2002) Metabolism of 1-fluoropyrene and pyrene in marine flatfish and terrestrial isopods. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 12:221–229
Meador J, Stein J, Reichert W, Varanasi U (1995) Bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by marine organisms. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 143:79–165
Myers MS, Johnson LL, Collier TK (2003) Establishing the causal relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) exposure and hepatic neoplasms and neoplasia-related liver lesions in English sole (Pleuronectes vetulus). Hum Ecol Risk Assess 9:67–94
Notar M, Leskosek H, Faganeli J (2001) Composition, distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 42:36–44
O’Malley VP, Abrajano TA, Hellou J (1996) Stable carbon isotopic apportionment of individual polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in St. John’s Harbour, Newfoundland. Environ Sci Technol 30:634–639
Organization for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the North-East Atlantic (1998) JAMP guidelines for contaminant-specific biological effects monitoring. Oslo and Paris Commission, London
Pikkarainen AL (2006) Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) activity and bile metabolites as contamination indicators in Baltic Sea perch: determination by HPLC. Chemosphere 65:1888–1897
Pointet K, Milliet A (2000) PAHs analysis of fish whole gall bladders and livers from the Natural Reserve of Camargue by GC/MS. Chemosphere 40:293–299
Reynolds WJ, Feist SW, Jones GJ, Lyons BP, Sheahan DA, Stentiford GD (2003) Comparison of biomarker and pathological responses in flounder (Platichthys flesus L.) induced by ingested polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) contamination. Chemosphere 52:1135–1145
Ribeiro CAO, Vollaire Y, Sanchez-Chardi A, Roche H (2005) Bioaccumulation and the effects of organochlorine pesticides, PAH and heavy metals in the eel (Anguilla anguilla) at the Camargue Natural Reserve, France. Aquat Toxicol 74:53–69
Richardson DM, Gubbins MJ, Davies IM, Moffat CF, Pollard PM (2004) Effects of feeding status on biliary PAH metabolite and biliverdin concentrations in plaice (Pleuronectes platessa). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 17:79–85
Roche H, Buet A, Ramade F (2002) Accumulation of lipophilic microcontaminants and biochemical responses in eels from the Biosphere Reserve of Carmargue. Ecotoxicology 11:9–18
Roy LA, Steinert S, Bay SM, Greenstein D, Sapozhnikova Y, Bawardi O et al (2003) Biochemical effects of petroleum exposure in hornyhead turbot (Pleuronichthys verticalis) exposed to a gradient of sediments collected from a natural petroleum seep in CA, USA. Aquat Toxicol 65:159–169
Ruddock PJ, Bird DJ, McCalley DV (2002) Bile metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in three species of fish from the Severn estuary. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 51:97–105
Ruddock PJ, Bird DJ, McEvoy J, Peters LD (2003) Bile metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in European eels Anguilla anguilla from United Kingdom estuaries. Sci Total Environ 301:105–117
Stein JE, Reichert WL, Nishimoto M, Varanasi U (1990) Overview of studies in liver carcinogenesis in English sole from Puget Sound: evidence for a xenobiotic chemical etiology II: biochemical studies. Sci Total Environ 94:51–69
Svedäng H, Wickström H (1997) Low fat content in female silver eels: indications of insufficient energetic stores for migration and gonadal development. J Fish Biol 50:475–486
Van der Oost R, Goksoyr A, Celander M, Heida H, Vermeulen NPE (1996) Biomonitoring of aquatic pollution with feral eel (Anguilla anguilla). 2. Biomarkers: pollution-induced biochemical responses. Aquat Toxicol 36(3–4):189–222
Van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Van Schanke A, Holtz F, van der Meer J, Boon JP, Ariese F, Stroomberg G et al (2001) Dose- and time dependent formation of biliary benzo[a]pyrene metabolites in the marine flatfish dab (Limanda limanda). Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1641–1647
Van Schooten FJ, Maas LM, Moonen EJC, Kleinjans JCS, van der Oost R (1995) DNA dosimetry in biological indicator species living on PAH-contaminated soils and sediments. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 30:171–179
Varanasi U, Stein JE (1991) Deposition of xenobiotic chemicals and metabolites in marine organisms. Environ Health Perspect 90:93–100
Varanasi U, Stein JE, Nishimoto M (1989) Biotransformation and disposition of PAH in fish. In: Varanisi U (ed) Metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the aquatic environment. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 93–150
Vuorinen PJ, Keinänen M, Vuontisjärvi H, Barsiene J, Broeg K, Förlin L et al (2006) Use of biliary PAH metabolites as a biomarker of pollution in fish from the Baltic Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 53:479–487
Westin L (2003) Migration failure in stocked eels Anguilla anguilla. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 254:307–311
Yuan SY, Chang JS, Yen JH, Chang BV (2001) Biodegradation of phenanthrene in river sediment. Chemosphere 43:273–278
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Alexander Schulz for skillful technical assistance and to Florian Sambraus for support with data evaluation. Furthermore, we thank our colleagues Klaus Wysujack, Thomas Lang, and Udo Koops, for many useful discussions. This study was partly financed by the EU-Data Collection Regulation (2008/949/EC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. Nagel and U. Kammann contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagel, F., Kammann, U., Wagner, C. et al. Metabolites of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Bile as Biomarkers of Pollution in European Eel (Anguilla anguilla) from German Rivers. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 62, 254–263 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-011-9693-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-011-9693-8