Abstract
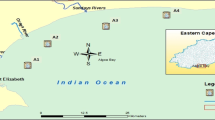
The Mediterranean region includes many small coastal rivers about which little is known concerning organic contaminant loads in their sediment. This study was designed to assess organic contamination in one of these small coastal rivers (Lez River) and associated coastal sediments. Levels of alkylphenols (APs), polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) were measured in sediments of the Lez River and two coastal lagoons impacted by wastewater discharges. In parallel, sediment surrounding a recently built submarine outfall that discharges treated wastewater, from an area encompassing some 450,000 inhabitants, into the sea was monitored a year after the beginning of emission via the outfall. Finally, these sediments were characterized by screening estrogenic, PAH-like and dioxin-like activities using in vitro bioassays. Both chemical analyses and bioassays revealed that wastewater inputs were a source of organic contamination of sediments from the Lez and lagoons, which still persisted 2 years after the discharges were stopped. APs could explain a small proportion of the overall estrogenic activities (up to 31%), suggesting that other estrogenic compounds were also present in the sediments. PAHs explained a great share (83% on average) of the EROD induction potency of the extracts. This survey should be the first step in the long-term monitoring of these sites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balaguer P, François F, Communal F, Fenet H, Boussioux A-M, Pons M, Nicolas JC, Casellas C (1999) Reporter cell lines to study the estrogenic effects of xenoestrogens. Sci Total Environ 233:47–56
Baumard P, Budzinski H, Garrigues P (1998) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments and mussels of the Western Mediterranean sea. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:765–776
Benlahcen KT, Chaoui A, Budzinski H, Bellocq J, Garrigues P (1997) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in some Mediterranean coastal sediments. Marine Pollut Bull 34:298–305
Blanchard M, Teil MJ, Ollivon D, Legenti L, Chevreuil M (2004) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorobiphenyls in wastewaters and sewage sludges from the Paris area (France). Environ Res 95:184–197
Braga O, Smythe GA, Schäfer AI, Feitz AJ (2005) Steroid estrogens in ocean sediments. Chemosphere 61:827–833
Budzinski H, Jones I, Bellocq J, Piérard C, Garrigues P (1997) Evaluation of sediment contamination by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Gironde estuary. Marine Chem 58:85–97
Busetti F, Heitz A, Cuomo M, Badoer S, Traverso P (2006) Determination of sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous and solid samples from an Italian wastewater treatment plant. J Chromatogr A 1102:104–115
David A, Fenet H, Gomez E (2009) Alkylphenols in marine environments: distribution monitoring strategies and detection considerations. Marine Pollut Bull 58:953–960
Directive 2000/60/EC (2000) Establishment and framework for community action in the field of water policy. European Parliament and the Council of the European Union, Luxembourg
Directive 2003/53/EC (2003) Amending for the 26th time the Council directive 76/769/EEC relating to restrictions on the marketing and use of certain dangerous substances and preparations (nonylphenol, nonylphenol ethoxylate and cement). European Parliament and the Council of the European Union, Luxembourg
Eljarrat E, Caixach J, Rivera J, de Torres M, Ginebreda A (2001) Toxic potency assessment of non- and mono-ortho PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs, and PAHs in northwest Mediterranean sediments (Catalonia, Spain). Environ Sci Technol 35:3589–3594
Fenet H, Gomez E, Pillon A, Rosain D, Nicolas JC, Casellas C, Balaguer P (2003) Estrogenic activity in water and sediments of a French river: contribution of alkylphenols. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44:1–6
Gomez-Gutierrez A, Garnacho E, Bayona JM, Albaiges J (2007) Assessment of the Mediterranean sediments contamination by persistent organic pollutants. Environ Pollut 148:396–408
Gonzalez S, Petrovic M, Barcelo D (2004) Simultaneous extraction and fate of linear alkylbenzene sulfonates, coconut diethanol amides, nonylphenol ethoxylates and their degradation products in wastewater treatment plants, receiving coastal waters and sediments in the Catalonian area (NE Spain). J Chromatogr A 1052:111–120
Guo W, He M, Yang Z, Lin C, Quan X, Men B (2009) Distribution, partitioning and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Daliao River water system in dry season, China. J Hazard Mater 164:1379–1385
Hilscherova K, Kannan K, Kang Y-S, Holoubek I, Machala M, Masunaga S, Nakanishi J, Giesy JP (2001) Characterisation of dioxin-like activity of sediments from a Czech river basin. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2768–2777
Houtman CJ, Booij P, Jover E, Del Rio DP, Swart K, Van Velzen M, Vreuls R, Legler J, Brouwer A, Lamoree MH (2006) Estrogenic and dioxin-like compounds in sediment from Zierikzee harbour identified with CALUX assay-directed fractionation combined with one and two dimensional gas chromatography analyses. Chemosphere 65:2244–2252
Hurst MR, Balaam J, Chan-Man YL, Thain JE, Thomas KV (2004) Determination of dioxin and dioxin-like compounds in sediments from UK estuaries using a bio-analytical approach: chemical-activated luciferase expression (CALUX) assay. Marine Pollut Bull 49:648–658
Huuskonen SE, Tuvikene A, Trapido M, Fent K, Hahn ME (2000) Cytochrome P4501A induction and porphyrin accumulation in PLHC-1 fish cells exposed to sediment and oil shale extracts. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 38:59–69
Isobe T, Serizawa S, Horiguchi T, Shibata Y, Managaki S, Takada H, Morita M, Shiraishi H (2006) Horizontal distribution of steroid estrogens in surface sediments in Tokyo Bay. Environ Pollut 144:632–638
Johnson AC, Larsen PF, Gadbois DF, Humason AW (1985) The distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surficial sediments of Phenobscot Bay (Maine, USA) in relation to possible sources and to other sites worldwide. Marine Environ Res 15:1–16
Keiter S, Grund S, van Bavel B, Hagberg J, Engwall M, Kammann U, Klempt M, Manz W, Olsman H, Braunbeck T, Hollert H (2008) Activities and identification of aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists in sediments from the Danube river. Anal Bioanal Chem 390:2009–2019
Kinani S, Bouchonnet S, Creusot N, Bourcier S, Balaguer P, Porcher JM, Aït-Aïssa S (2010) Bioanalytical characterisation of multiple endocrine- and dioxin-like activities in sediments from reference and impacted small rivers. Environ Pollut 158:74–83. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.07.041
Koh C-H, Khim JS, Villeneuve DL, Kannan K, Johnson BG, Giesy JP (2005) Instrumental and bioanalytical measures of dioxin-like and estrogenic compounds and activities associated with sediment from the Korean coast. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 61:366–379
Koh CH, Khim JS, Villeneuve DL, Kannan K, Giesy JP (2006) Characterization of trace organic contaminants in marine sediment from Yeongil Bay, Korea: 2. Dioxin-like and estrogenic activities. Environ Pollut 142:48–57
Lacorte S, Raldúa D, Martínez E, Navarro A, Diez S, Bayona JM, Barceló M (2006) Pilot survey of a broad range of priority pollutants in sediment and fish from the Ebro river basin (NE Spain). Environ Pollut 40(3):471–482
Laville N, Ait-Aissa S, Gomez E, Casellas C, Porcher JM (2004) Effects of human pharmaceuticals on cytotoxicity, EROD activity and ROS production in fish hepatocytes. Toxicology 196:41–55
Li D, Dong M, Shim WJ, Yim UH, Hong SH, Kannan N (2008) Distribution characteristics of nonylphenolic chemicals in Masan Bay environments, Korea. Chemosphere 71:1162–1172
Louiz I, Kinani S, Gouze ME, Ben-Attia M, Menif D, Bouchonnet S, Porcher JM, Ben-Hassinea OK, Aït-Aïssa S (2008) Monitoring of dioxin-like, estrogenic and anti-androgenic activities in sediments of the Bizerta lagoon (Tunisia) by means of in vitro cell-based bioassays: contribution of low concentrations of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Sci Total Environ 402:318–329
Maldonado C, Venkatesan MI, Phillips CR, Bayona JM (2000) Distribution of trialkylamines and coprostanol in San Pedro shelf sediments adjacent to a sewage outfall. Marine Pollut Bull 2000(40):680–687
Michallet-Ferrier P, Aït-Aïssa S, Balaguer P, Dominik J, Haffner GD, Pardos M (2004) Assessment of estrogen receptor (ER) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) mediated activities in organic sediment extracts of the Detroit river, using in vitro bioassays based on human MELN and teleost PLHC-1 cell lines. J Great Lakes Res 30:82–92
Moon HB, Choi M, Choi HG, Ok G, Kannan K (2009) Historical trends of PCDDs, PCDFs, dioxin-like PCBs and nonylphenols in dated sediment cores from a semi-enclosed bay in Korea: tracking the sources. Chemosphere 75:565–571
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Notar M, Leskovsek H, Faganeli J (2001) Composition, distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of the Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea. Marine Pollut Bull 42:36–44
Oh JR, Ikonomou MG, Fernandez MP, Hong S-H (2003) PCB and PCDD/F totals, TEQs, and congener patterns in Korean coastal marine environments 1987, 1988, 1990, 1996 and 1999. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44:224–236
Peck M, Gibson RW, Kortenkamp A, Hill EM (2004) Sediments are major sinks of steroidal estrogens in two United Kingdom rivers. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:945–952
Peng X, Wang Z, Mai B, Chen F, Chen S, Tan J, Yu Y, Tang C, Li K, Zhang G, Yang C (2007) Temporal trends of nonylphenol and bisphenol A contamination in the Pearl River Estuary and the adjacent South China Sea recorded by dated sedimentary cores. Sci Total Environ 384:393–400
Pham TT, Proulx S (1997) PCBs and PAHs in the Montreal Urban Community (Quebec, Canada) wastewater treatment plant and in the effluent plume in the St Lawrence River. Water Res 31:1887–1896
Pillon A, Boussioux AM, Escande A, Ait-Aissa S, Gomez E, Fenet H, Ruff M, Moras D, Vignon F, Duchesne M-J, Casellas C, Nicolas J-C, Balaguer P (2005) Binding of estrogenic compounds to recombinant estrogen receptor-alpha: application to environmental analysis. Environ Health Perspect 113:278–284
Pojana G, Gomiero A, Jonkers N, Marcomini A (2007) Natural and synthetic endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in water, sediment and biota of a coastal lagoon. Environ Int 33:929–936
Reddy S, Brownawell BJ (2005) Analysis of estrogens in sediment from a sewage-impacted urban estuary using high-performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:1041–1047
Safe S (1994) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): environmental impact, biochemical and toxic responses, and implicationsfor risk assessment. Crit Rev Toxicol 24:87–149
Sánchez-Avila J, Bonet J, Velasco G, Lacorte S (2009) Determination and occurrence of phthalates, alkylphenols, bisphenol A, PBDEs, PCBs and PAHs in an industrial sewage grid discharging to a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Sci Total Environ 407:4157–4167
Sicre MA, Fernandes MB, Pont D (2008) Poly-aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) inputs from the Rhone River to the Mediterranean Sea in relation with the hydrological cycle: impact of floods. Marine Pollut Bull 56:1935–1942
Soares A, Guieysse B, Jefferson B, Cartmell E, Lester JN (2008) Nonylphenol in the environment: a critical review on occurrence, fate, toxicity and treatment in wastewaters. Environ Int 34:1033–1049
Song M, Xu Y, Jiang Q, Lam PK, O’Toole DK, Giesy JP, Guibin J (2006) Measurement of estrogenic activity in sediments from Haihe and Dagu River, China. Environ Int 32:676–681
Soto AM, Justicia H, Wray JW, Sonnenschein C (1991) p-Nonyl-phenol: an estrogenic xenobiotic released from “modified” polystyrene. Environ Health Perspect 92:167–173
Thomas KV, Balaam J, Hurst M, Nedyalkova Z, Mekenyan O (2004) Potency and characterization of estrogen-receptor agonist in United Kingdom estuarine sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:471–479
Trabelsi S, Driss MR (2005) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in superficial coastal sediments from Bizerte Lagoon, Tunisia. Marine Pollut Bull 50:344–358
Traven L, Zaja R, Loncar J, Smital T, Micovic V (2008) CYP1A induction potential and the concentration of priority pollutants in marine sediment samples—in vitro evaluation using the PLHC-1 fish hepatoma cell line. Toxicol In Vitro 22:1648–1656
UNEP (2004) Municipal wastewater treatment plants in Mediterranean coastal cities (II). MAP Tech. Rep. No. 157. UNEP, Athens
UNEP (2008) Municipal wastewater treatment plants in Mediterranean coastal cities: inventory of treatment plants in cities of between 2,000 and 10,000 inhabitants. MAP Tech. Rep. No. 169. UNEP, Athens
Vigano L, Benfenati E, van Cauwenberge A, Eidem JK, Erratico C, Goksoyr A, Kloasf W, Maggionib S, Mandichh A, Urbatzka R (2008) Estrogenicity profile and estrogenic compounds determined in river sediments by chemical analysis, ELISA and yeast assays. Chemosphere 73:1078–1089
Villeneuve DL, Blankenship AL, Giesy JP (2000) Derivation and application of relative potency estimates based on in vitro bioassay results. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2835–2843
Vindimian E, Robaut C, Fillion G (1983) A method for cooperative or noncooperative binding studies using nonlinear regression analysis on a microcomputer. J Appl Biochem 5:261–278
Vondrácek J, Machala M, Minksová K, Bláha L, Murk AJ, Kozubık A, Hofmanová J, Hilscherová K, Ulrich R, Ciganek M, Neča J, Švrčková D, Holoubek I (2001) Monitoring river sediments contaminated predominantly with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by chemical and in vitro bioassay techniques. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1499–1506
Windal I, Denison MS, Birnbaum LS, Van Wouwe N, Baeyens W, Goeyens L (2005) Chemically activated luciferase gene expression (CALUX) cell bioassay analysis for the estimation of dioxin-like activity: critical parameters of the CALUX procedure that impact assay results. Environ Sci Technol 39:7357–7364
Ying GG, Kookana RS, Dillon P (2003) Sorption and degradation of selected five endocrine disrupting chemicals in aquifer material. Water Res 37:3785–3791
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank E. Maillot-Marechal and A. Znidah who contributed to the experimental work. They would also like to thank the staff of Ifremer coastal laboratories in Sete (France) for sediment samplings. A. David was supported by a doctoral fellowship from the French Research Ministry. This work was funded by PNRPE (French Endocrine Disrupter Research Programme), ERICHE (Evaluate and Reduce the Impact of Chemistry on the Environment) network, and the French Ministry of Ecology and Sustainable Development (grant P189-AP08 to S.A.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
David, A., Gomez, E., Aït-Aïssa, S. et al. Impact of Urban Wastewater Discharges on the Sediments of a Small Mediterranean River and Associated Coastal Environment: Assessment of Estrogenic and Dioxin-like Activities. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58, 562–575 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9475-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-010-9475-8