Abstract
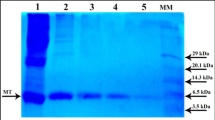
Metallothioneins (MTs) are cysteine-rich, metal-binding proteins that are useful biomarkers for monitoring pollution by heavy metals. In this report, a novel cadmium (Cd)-binding MT (CdMT) from Sinopotamon henanense was purified using acetone precipitation (50–80%), followed by gel-filtration chromatography and anion-exchange chromatography. Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis showed that S. henanense CdMT existed as monomer and dimmer forms, with a monomer molecular weight of 6890 Da and a dimmer molecular weight of 13,766 Da. In addition, the full-length cDNA sequence of S. henanense CdMT was prepared from the gill RNA using reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction and 3′ and 5′ rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) methods. Sequence analyses indicated that the isolated cDNA (633 bp) contains an open reading frame of 177 bp that encodes a protein with 59 amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence has 18 cysteine residues, implying that S. henanense CdMT binds six equivalents of bivalent metal ions (Cd) as opposed to the seven in its mammalian counterparts. The deduced molecular weight of MT without binding metals is 6218 Da. If six bound Cd atoms are counted, the deduced molecular weight of S. henanense CdMT would be 6892 Da, which is very similar to the molecular weight of the purified protein (6890 Da) determined by time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis. These confirmed our results of MT purification. These present studies will be helpful to increase the database information of heavy-metal-induced MT in terms of crustaceans.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway BJ (1990) Cadmium. Heavy metals in soils. Wiley, New York, pp 100–124
Banni M, Dondero F, Jebali J, Guerbej H, Boussetta H, Viarengo A (2007) Assessment of heavy metal contamination using real-time PCR analysis of mussel metallothionein mt10 and mt20 expression: a validation along the Tunisian coast. Biomarkers 12:369–83. doi:10.1080/13547500701217061
Brouwer M, Enghild J, Hoexum-Brouwer T (1995) Primary structure and tissue-specific expression of blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) metallothionein isoforms. Biochem J 311:617–622
Chowdhury MJ, Baldisserotto B, Wood CM (2005) Tissue-specific cadmium and metallothionein levels in rainbow trout chronically acclimated to waterborne or dietary cadmium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:381–390. doi:10.1007/s00244-004-0068-2
Dallinger R, Berger B, Gruber C, Hunziker P, Sturzenbaum S (2000) Metallothioneins in terrestrial invertebrates: structural aspects, biological significance and implications for their use as biomarkers. Cell Mol Biol 46:331–346
De Lafontaine Y, Gagne F, Blaise C, Costan G, Gagnon P, Chan HM (2000) Biomakers in zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) for the assessment and monitoring of water quality of the St. Lawrence River (Canada). Aquat Toxicol 50:51–71. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(99)00094-6
Dondero F, Piacentini L, Banni M, Rebelo M (2005) Quantitative PCR analysis of two molluscan metallothionein genes unveils differential expression and regulation. Gene 345:259–270. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2004.11.031
Fingerman M, Devi M, Reddy PS, Katyayani R (1996) Impact of heavy metal exposure on the nervous system and endocrine-mediated processes in Crustaceans. Zool Stud 35:1–8
Jiang SH, PSh Wang, Wu YB (2007) Survey of status of contamination of food with cadmium in Shantou City in 2004–2006. China Trop Med 7:1012–1014
Kagi JHR, Schaffer A (1988) Biochemistry of metallothionein. Biochemistry 27:8509–8515. doi:10.1021/bi00423a001
Lerch K, Ammer D, Olafson RW (1982) Crab metallothionein. Primary structures of metallothioneins 1 and 2. J Biol Chem 257:2420–2426
Li B, Fu X, Liu QC, Chen YY (2002) Cloning and comparison of four metallothionein cDNAs in crabs from different habitats. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 8:627–631
Li B, Savva D (2000) Cloning of metallotionein cDNAs and its gene in shore crab (Carcinus maenas). Acta Biochem Biophys Sin 32:640–644
Ma WL, Wang L, He YJ, Yan T (2008) Tissue-specific cadmium and metallothionein levels in freshwater crab Sinopotamon henanense during acute exposure to waterborne cadmium. Environ Toxicol 23(3):393–400. doi:10.1002/tox.20339
Mao XW, Li YY, Lin XH (2007) Investigation on pollutant of aquatic products in Guangzhou City. Chin J Health Lab Technol 17:2288–2290
Otvos JD, Olafson RW, Armitage IM (1982) Structure of an invertebrate metallothionein from Scylla serrata. J Biol Chem 257:2427–2431
ChCh Pat, Carmen KM, Felice WY (2004) Common carp metallothionein–1 gene: cDNA cloning, gene structure and expression studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1676:162–171
Pedersen SN, Lundebye AK, Depledge MH (1997) Field application of metallothionein and stress protein biomakers in the shore crab (Carcinus maenas) exposed to trace metals. Aquat Toxicol 37:183–200. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(96)00816-8
Pedersen KL, Pedersen SN, Hojrup P (1994) Purification and characterization of a cadmium-induced metallothionein from the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Biochem J 297:609–614
Pedersen SN, Pedersen KL, Hojrup PH, Michael HD (1996) Primary structures of decapod crustacean metallothioneins with special emphasis on freshwater and semi-terrestrial species. Biochem J 319:999–1003
Ponzano E, Dondero F, Bouquegneau JM (2001) Purification and biochemical characterization of a cadmium metallothionein from the digestive gland of the Antarctic scallop Adamussium colbecki (Smith, 1902). Polar Biol 24(3):147–153. doi:10.1007/s003000000186
Roesijadi G (1992) Metallothionein in metal regulation and toxicity in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 22:81–114. doi:10.1016/0166-445X(92)90026-J
Roesijadi G, Robinson WE (1994) Metal regulation in aquatic animals: mechanisms of uptake, accumulation, and release. Aquatic toxicology: molecular. biochemical and cellular perspective. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, pp 387–419
Savvau D, Li B (2000) Characterisation of two metallothionein cDNAs from the shore crab for use as biomarkers of heavy metal pollution. Ecotoxicology 8:485–493. doi:10.1023/A:1008920206323
Syring RA, Brouwer TH, Brouwer M (2000) Cloning and sequencing of cDNAs encoding for a novel copper-specific metallothionein and two cadmium-inducible metallothioneins from the blue crab Callinectes sapidus. Comp. Biochem Physiol C 125:325–332
Vasák M, Hasler DW (2000) Metallothioneins: new functional and structural insights. Curr Opin Chem Biol 4:177–183. doi:10.1016/S1367-5931(00)00082-X
ZhT Wang, Wang MQ, Han HW (2004) Survey on the cadmium levels in fish, crustaceans and bivalve mollusks in China of 2002. J Hygiene Res 33:473–474
Wu SM, Hwang PP (2003) Copper or cadmium pretreatment increases the protection against cadmium toxicity in tilapia larvae (Oreochromis mossambicus). Zool Stud 42:179–185
YZh Zhang, Wang GJ (2004) Evaluation of heavy metals in aquatic product in the market of major cities in Zhejiang province. Trace Elem Sci 11:58–61
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Natural Sciences Foundation of China (grant Nos. 30470254 and 30640051) and the Natural Sciences Foundation of Shanxi Province (grant No. 20041082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, WL., Yan, T., He, Y. et al. Purification and cDNA Cloning of a Cadmium-Binding Metallothionein from the Freshwater Crab Sinopotamon henanense . Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56, 747–753 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9224-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9224-4