Abstract
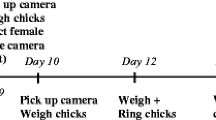
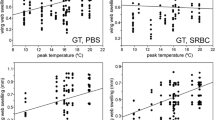
Although many studies have investigated possible effects of heavy metal contamination on components of the immune system in captive birds, studies on the effects of chronic exposure to heavy metals on the immune system of free-living birds are rare. Therefore we studied the effect of heavy metal exposure on the humoral immune responsiveness in free-living great tit (Parus major) populations from four study sites along a pollution gradient near a metallurgic smelter. Although there were no differences in body condition or hematocrit values among great tits from the four study sites, the heavy metal exposure appeared to affect an individual’s humoral immune responsiveness, as measured by antibody titers to sheep red blood cells. Great tits from the study site farthest away from the smelter complex had a significantly higher immune responsiveness than birds from the two areas closest to the metallurgic smelter. Further work is now necessary to establish a causal association between heavy metal contamination and immunosuppression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snoeijs, T., Dauwe, T., Pinxten, R. et al. Heavy Metal Exposure Affects the Humoral Immune Response in a Free-Living Small Songbird, the Great Tit (Parus major). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46, 399–404 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-003-2195-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-003-2195-6