Abstract
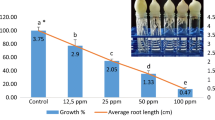
Saturated water solutions of calcium chloride, calcium bromide (densities 1.30 kg dm−3 and 1.61 kg dm−3, respectively) and their 1:1 mixture have been commonly used as oil industry “high-density brines.” In our experiment they were added to tap water in amounts appropriate to achieve concentrations of 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, and 0.1 mol dm−3 to study their cytotoxic effect on the root tip cells of shallot (Allium cepa L. var. ascalonicum). All tested solutions in concentrations of 0.075 and 0.1 mol dm−3 caused significant inhibition of shallot root growth. CaBr2 showed this effect in concentration 0.05 mol dm−3. The investigated solutions in all concentrations applied decreased mitotic activity in root tip cells. The most of mitotic abnormalities were the consequence of spindle failure and chromosome stickiness. Furthermore, the cell microtubules were investigated by indirect immunofluorescence to confirm that most abnormalities observed were the consequence of spindle failure. The present study, as well as previously done Lemna tests and Chlorella tests showed that investigated samples have certain effects on plants, so constant control of their presence in the environment is needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 3 November 2001/Accepted: 5 April 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vidaković-Cifrek, .., Pavlica, M., Regula, I. et al. Cytogenetic Damage in Shallot (Allium cepa) Root Meristems Induced by Oil Industry “High-Density Brines”. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 43, 0284–0291 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-1223-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-1223-2