Abstract
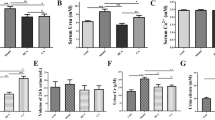
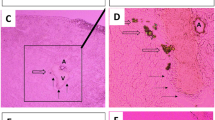
Previous studies have described the inhibitory effects of citrate on calcium oxalate crystallization in place of crystal growth, but the effects of citrate on matrix proteins of stones has not been studied in vivo. To examine the effect of citrate on the matrix, we investigated the effect of citrate on osteopontin (OPN) expression, which we had previously identified as an important stone matrix protein. Control rats were treated with saline while rats of the stone group were treated with ethylene glycol (EG) and vitamin D3, and the citrate groups (low-dose and high-dose groups) were treated with a citrate reagent compound of sodium citrate and potassium citrate, in addition to EG and vitamin D3. The rate of renal stone formation was lower in the citrate groups than in the stone group. This was associated with a low expression of OPN mRNA in citrate-treated rats relative to that in the stone group. Citrate was effective in preventing calcium oxalate stone formation and reduced OPN expression in rats. Our results suggest that citrate prevents renal stone formation by acting against not only the crystal aggregation and growth of calcium oxalate but also OPN expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 June 2000 / Accepted: 20 September 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasui, T., Sato, M., Fujita, K. et al. Effects of citrate on renal stone formation and osteopontin expression in a rat urolithiasis model. Urological Research 29, 50–56 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002400000152
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002400000152