Abstract
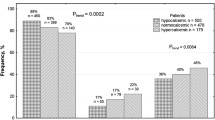
Environmental and genetic factors are important in development of nephrolithiasis. In a recent study, it has been demonstrated that hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) has an anti-apoptotic effect and thus can reduce the adhesion of calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals to renal epithelial cells. The aim of this study was to evaluate the HGF serum levels and its two gene polymorphisms and possible association of the two in patients with nephrolithiasis. One hundred and five patients with nephrolithiasis and 70 healthy volunteers with similar demographic features were included in this study. Serum HGF levels were measured, and HGF intron 13 C>A (in 102 stone patients and 68 healthy subjects) and intron 14 T>C (in 99 stone patients and 56 healthy subjects) polymorphisms were determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction with TaqMan allelic discrimination method. There were no statistically significant differences in HGF intron 13 C>A and intron 14 T>C polymorphisms between the control and patient groups (X 2 = 1.72 df = 2; p = 0.42, and X 2 = 0.68 df = 2; p = 0.71, respectively). Mean serum HGF concentration was significantly lower in the stone disease patients than in the control subjects (1.05 ± 0.63 pg/mL and 1.35 ± 0.58 ng/mL respectively, p = 0.0001). When allele distribution frequency between stone patients and healthy subjects was compared, there were no significant differences in intron 13 and intron 14 allele distributions between two groups (p = 0.43 and p = 0.44, respectively). It may be concluded from the findings that decrease in HGF levels may play a role in renal stone formation, independent from gene polymorphisms.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- COM:
-
Calcium oxalate monohydrate
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
References
Tiselius HG (2003) Epidemiology and medical management of stone disease. BJU Int 91(8):758–767
Stechman MJ, Loh NY, Thakker RV (2009) Genetic causes of hypercalciuric nephrolithiasis. Pediatr Nephrol 24(12):2321–2332
Worcester EM, Coe FL (2010) Clinical Practice Calcium Kidney Stones. N Engl J Med 363(10):954–963
Favus MJ (2011) The risk of kidney stone formation: the form of calcium matters. Am J Clin Nutr 94(1):5–6
Tei N, Tsujihata M, Tsujikawa K, Yoshimura K, Nonomura N, Okuyama A (2006) Hepatocyte growth factor has protective effects on crystal-cell interaction and crystal deposits. Urology 67(4):864–869
Khan SR, Byer KJ, Thamilselvan S, Hackett RL, McCormack WT, Benson NA, Vaughn KL, Erdos GW (1999) Crystal-cell interaction and apoptosis in oxalate-associated injury of renal epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. Suppl 14:457–463
Jonassen JA, Kohjimoto Y, Scheid CR, Schmidt M (2005) Oxalate toxicity in renal cells. Urol Res 33(5):329–339
Madonna R, Cevik C, Nasser M, De Caterina R (2012) Hepatocyte growth factor: molecular biomarker and player in cardioprotection and cardiovascular regeneration. Thromb Haemost 107(4):656–661
Nakamura T, Nawa K, Ichihara A (1984) Partial purification and characterization of hepatocyte growth factor from serum of hepatectomized rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 122(3):1450–1459
Aoki S, Takahashi K, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T (1996) Molecular cloning of the Xenopus c-met/hepatocyte growth factor receptor and its regional expression during early development. J Biochem 120(5):961–968
Boros P, Miller CM (1995) Hepatocyte growth factor: a multifunctional cytokine. Lancet 345(8945):293–295
Nakamura T, Sakai K, Nakamura T, Matsumoto K (2011) Hepatocyte growth factor twenty years on: much more than a growth factor. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26(suppl 1):188–202
Matsumoto K, Nakamura T (2001) Hepatocyte growth factor: renotropic role and potential therapeutics for renal diseases. Kidney Int 59(6):2023–2038
Gao B, Yasui T, Okada A, Tozawa K, Hayashi Y, Kohri K (2005) A polymorphism of the osteopontin gene is related to urinary calcium stones. J Urol. 174(4Pt 1):1472–1476
Aksoy H, Aksoy Y, Ozturk N, Aydin HR, Yildirim AK, Akçay F (2010) Fetuin-A gene polymorphism in patients with calcium oxalate stone disease. Urology 75(4):928–932
Gao B, Yasui T, Itoh Y, Tozawa K, Hayashi Y, Kohri K (2007) A polymorphism of matrix Gla protein gene is associated with kidney stones. J Urol 177(6):2361–2365
Ozturk M, Kordan Y, Cangul H, Dogan HS, Kilicarslan H, Vuruskan H, Oktay B (2008) Association of urokinase gene 3′-UTR T/C polymorphism with calcium oxalate urolithiasis in children. Int Urol Nephrol 40(3):563–568
Thorleifsson G, Holm H, Edvardsson V, Walters GB, Styrkarsdottir U, Gudbjartsson DF et al (2009) Sequence variants in the CLDN14 gene associate with kidney stones and bone mineral density. Nat Genet 41(8):926–930. doi:10.1038/ng.404
Besiroglu H, Sahin S, Otunctemur A, Ozbek E (2014) Calcium-sensing receptor gene polymorphisms in patients with calcium urolithiasis: a systematic review. Ren Fail 36(8):1187–1192. doi:10.3109/0886022X.2014.937673
Liu W, Chen M, Li M, Ma H, Tong S, Lei Y, Qi L (2014) Vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) polymorphisms and the urolithiasis risk: an updated meta-analysis based on 20 case-control studies. Urolithiasis 42:45–52. doi:10.1007/s00240-013-0619-y
Motone M, Katsuya T, Ishikawa K, Iwashima Y, Sugimoto K, Yamamoto K, Fu Y, Matsuo A, Ohishi M, Rakugi H, Ogihara T (2004) Association between hepatocyte growth factor gene polymorphism and essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 27(4):247–251
Bell LN, Cai L, Johnstone BH, Traktuev DO, March KL, Considine RV (2008) A central role for hepatocyte growth factor in adipose tissue angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 294(2):336–344
Mizuno S, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T (2008) HGF as a renotrophic and anti-fibrotic regulator in chronic renal disease. Front Biosci 1(13):7072–7086
Zhou D, Tan RJ, Lin L, Zhou L, Liu Y (2013) Activation of hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-met, in renal tubules is required for renoprotection after acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 84(3):509–520
Han W, Yap MK, Wang J, Yip SP (2006) Family-based association analysis of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) gene polymorphisms in high myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47(6):2291–2299
Yanovitch T, Li YJ, Metlapally R, Abbott D, Viet KN, Young TL (2009) Hepatocyte growth factor and myopia: genetic association analyses in a Caucasian population. Mol Vis. 20(15):1028–1035
Toyoda T, Nakamura K, Yamada K, Thanseem I, Anitha A, Suda S, Tsujii M, Iwayama Y, Hattori E, Toyota T, Miyachi T, Iwata Y, Suzuki K, Matsuzaki H, Kawai M, Sekine Y, Tsuchiya K, Sugihara G, Ouchi Y, Sugiyama T, Takei N, Yoshikawa T, Mori N (2007) SNP analyses of growth factor genes EGF, TGFbeta-1, and HGF reveal haplotypic association of EGF with autism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 360(4):715–720
Kaya M, Çokakli M, Berk AT, Yaman A, Yesilirmak D, Kumral A, Atabey N (2013) Associations of VEGF/VEGF-receptor and HGF/c-Met promoter polymorphisms with progression/regression of retinopathy of prematurity. Curr Eye Res 38(1):137–142
Nakamura S, Moriguchi A, Morishita R, Aoki M, Yo Y, Hayashi S, Nakano N, Katsuya T, Nakata S, Takami S, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Higaki J, Ogihara T (1998) A novel vascular modulator, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), as a potential index of the severity of hypertension. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 242(1):238–243
Nakamura Y, Morishita R, Nakamura S, Aoki M, Moriguchi A, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Higaki J, Ogihara T (1996) A vascular modulator, hepatocyte growth factor, is associated with systolic pressure. Hypertension 28(3):409–413
Nakamura T, Mizuno S, Matsumoto K, Sawa Y, Matsuda H, Nakamura T (2000) Myocardial protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury by endogenous and exogenous HGF. J Clin Invest. 106(12):1511–1519
Matsumori A, Furukawa Y, Hashimoto T, Ono K, Shioi T, Okada M, Iwasaki A, Nishio R, Sasayama S (1996) Increased circulating hepatocyte growth factor in the early stage of acute myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 221(2):391–395
Chen XH, Minatoguchi S, Kosai K, Yuge K, Takahashi T, Arai M, Wang N, Misao Y, Lu C, Onogi H, Kobayashi H, Yasuda S, Ezaki M, Ushikoshi H, Takemura G, Fujiwara T, Fujiwara H (2007) In vivo hepatocyte growth factor gene transfer reduces myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through its multiple actions. J Card Fail 13(10):874–883
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by a research fund from the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) (Project number: 107S273). This study has been accepted as a poster presentation in the “American Association for Clinical Chemistry (AACC) Annual Meeting on July 25–29, 2010, California, USA”.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk, N., Aksoy, H., Aksoy, Y. et al. The low levels of circulating hepatocyte growth factor in nephrolithiasis cases: independent from gene polymorphism. Urolithiasis 43, 427–432 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-015-0793-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-015-0793-1