Abstract
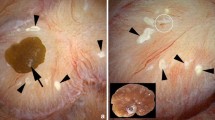
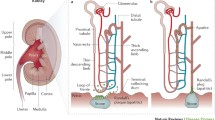
Data concerning nine forms of human stone disease, along with observations on normal people give new insights into formation of interstitial apatite plaque and intra-tubular crystal deposits. In general, across multiple disease states, one can reproduce the same relationships between plaque abundance as is seen among patients within individual disease states, so that the link between plaque and high urine calcium excretion, and low urine volume and pH seems increasingly secure. From this, one can propose a specific model of plaque formation, susceptible to experimental test. In many diseases, formation of inner medullary collecting duct and Bellini duct deposits is compatible with simple crystallization driven by urine supersaturations; this is expected in that these segments contain tubule fluid quite close in composition to final urine. But in ileostomy, small bowel disease and obesity bypass patients, crystals found in deposits are not those expected: apatite and urates in deposits, despite formation of highly acidic urine. Also, this discrepancy suggests the possibility of divergence between bulk urine pH and pH of focal collecting ducts, a new kind of possibility that is susceptible to experimental test.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evan AP, Lingeman JE, Coe FL et al (2003) Randall’s plaque of patients with nephrolithiasis begins in basement membranes of thin loops of Henle. J Clin Invest 111:607–616
Evan AP, Coe FL, Lingeman JE et al (2007) Mechanism of formation of human calcium oxalate renal stones on Randall’s plaque. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 290:1315–1323
Kuo RL, Lingeman JE, Evan AP et al (2003) Urine calcium and volume predict coverage of renal papilla by Randall’s plaque. Kidney Int 64:2150–2154
Evan AP, Lingeman JE, Coe FL et al (2009) Intra-tubular deposits, urine and stone composition are divergent in patients with ileostomy. Kidney Int 76:1081–1088
Evan AP, Coe FL, Lingeman JE et al (2006) Renal crystal deposits and histopathology in patients with cystine stones. Kidney Int 69:2227–2235
Evan AE, Lingeman JE, Coe FL et al (2008) Histopathology and surgical anatomy of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism and calcium phosphate stones. Kidney Int 74:223–229
Evan AP, Lingeman JE, Coe FL et al (2005) Crystal-associated nephropathy in patients with brushite nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int 67:576–591
Asplin JR, Mandel NS, Coe FL (1996) Evidence of calcium phosphate supersaturation in the loop of Henle. Am J Physiol 270:F604–F613
Worcester EM, Coe FL, Evan AP et al (2008) Evidence for increased postprandial distal nephron calcium delivery in hypercalciuric stone-forming patients. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 295:F1286–F1294
Finlayson B, Reid F (1978) The expectation of free and fixed particles in urinary stone disease. Invest Urol 15:442
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by PO1 DK56788.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Proceedings paper from the 3rd International Urolithiasis Research Symposium, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 3–4 December 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coe, F.L., Evan, A.P., Lingeman, J.E. et al. Plaque and deposits in nine human stone diseases. Urol Res 38, 239–247 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-010-0296-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-010-0296-z