Abstract
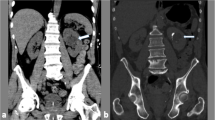
The objective of the study is to evaluate unenhanced CT following intravenous urography (IVU) for the detection of upper urinary tract (UUT) abnormalities, when IVU fails to provide the qualitative diagnosis. Helical CT scan was performed on patients with suspected disorders of UUT, after the completion of IVU for further diagnoses. In total, 124 cases of definite diagnosis and 71 cases of uncertain diagnosis via IVU were collected from 195 patients with suspected UUT disorders. Among the 71 uncertain cases, 65 patients were consent to undergo immediate or delayed CT scan. CT data were transferred to the workstation for postprocessing. Of all the 65 cases, the major CT diagnoses were the following: stone disease (n = 41), urinary tract infections (n = 4), UUT tumors (n = 7), neighboring invasion or metastasis (n = 2), congenital anomalies (n = 2), and compressed stenosis (n = 6). Among all the results, 62 cases were confirmed by surgery, pathology or clinical follow-up, while three cases (4.6%) left were still uncertain. The diagnose accordance rate of IVU + CT achieved to 95.4%. There was significant difference between IVU and IVU + CT in the determinate diagnosis of UUT diseases (χ 2 = 30.4, P < 0.05). In conclusion, IVU + CT provides more valuable information for the localization and qualitative diagnosis of UUT abnormalities. It is recommended as a cost-effective and time-saving complemental means for IVU.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim JK, Cho KS (2003) CT urography and virtual endoscopy: promising imaging modalities for urinary tract evaluation. Br J Radio 76:199–209
Heneghan JP, Kim DH, Leder RA, DeLong D, Nelson RC (2001) Compression CT urography: a comparison with IVU in the opacification of the collecting system and ureters. J Comp Assist Tomogr 25:343–347
Yilmaz S, Sindel T, Arslan G et al (1998) Renal colic: comparison of spiral CT, US and IVU in the detection of ureteral calculi. Eur Radiol 8:212–217
Worster A, Preyra I, Weaver B (2002) The accuracy of noncontrast helical computed tomography versus intravenous pyelography in the diagnosis of suspected acute urolithiasis: a meta-analysis. Ann Emerg Med 40:280–286
Caoili EM, Cohan RH, Korobkin M et al (2002) Urinary tract abnormalities: initial experience with multi-detector row CT urography. Radiology 222:353–360
Nawfel RD, Judy PF, Schleipman AR, Silverman SG (2004) Patient radiation dose at CT urography and conventional urography. Radiology 232:126–132
Nolte-Ernsting C, Cowan N (2006) Understanding multislice CT urography techniques: many roads lead to Rome. Eur Radiol 16:2670–2686
Dillman JR, Caoili EM, Cohan RH (2007) Multi-detector CT urography: a one-stop renal and urinary tract imaging modality. Abdom Imaging 32:519–529
Perlman ES, Rosenfield AT, Wexler JS, Glickman MG (1996) CT urography in the evaluation of urinary tract disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 20:620–626
McNicholas MM, Raptopoulos VD, Schwartz RK et al (1998) Excretory phase CT urography for opacification of the urinary collecting system. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170:1261–1267
Chow LC, Sommer FG (2001) Multidetector CT urography with abdominal compression and three-dimensional reconstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:849–855
Van Der Molen AJ, Cowan NC, Mueller-Lisse UG et al (2008) CT urography: definition, indications and techniques: a guideline for clinical practice. Eur Radiol 18:4–17
Catalano O, Nunziata A, Altei F, Siani A (2002) Suspected ureteral colic: primary helical CT versus selective helical CT after unenhanced radiography and sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178:379–387
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H., Hu, XY., Fang, XM. et al. Unenhanced helical CT following excretory urography in the diagnosis of upper urinary tract disease: a little more cost, a lot more value. Urol Res 38, 127–133 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-009-0237-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-009-0237-x