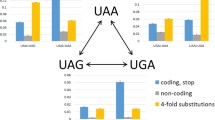
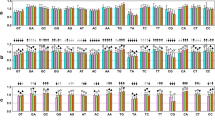
Abstract
De novo origin of coding sequence remains an obscure issue in molecular evolution. One of the possible paths for addition (subtraction) of DNA segments to (from) a gene is stop codon shift. Single nucleotide substitutions can destroy the existing stop codon, leading to uninterrupted translation up to the next stop codon in the gene’s reading frame, or create a premature stop codon via a nonsense mutation. Furthermore, short indels-caused frameshifts near gene’s end may lead to premature stop codons or to translation past the existing stop codon. Here, we describe the evolution of the length of coding sequence of prokaryotic genes by change of positions of stop codons. We observed cases of addition of regions of 3′UTR to genes due to mutations at the existing stop codon, and cases of subtraction of C-terminal coding segments due to nonsense mutations upstream of the stop codon. Many of the observed stop codon shifts cannot be attributed to sequencing errors or rare deleterious variants segregating within bacterial populations. The additions of regions of 3′UTR tend to occur in those genes in which they are facilitated by nearby downstream in-frame triplets which may serve as new stop codons. Conversely, subtractions of coding sequence often give rise to in-frame stop codons located nearby. The amino acid composition of the added region is significantly biased, compared to the overall amino acid composition of the genes. Our results show that in prokaryotes, shift of stop codon is an underappreciated contributor to functional evolution of gene length.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Artamonova II, Gelfand MS (2007) Comparative genomics and evolution of alternative splicing: the pessimists’ science. Chem Rev 107:3407–3430
Bazykin G, Kochetov A (2010) Alternative translation start sites are conserved in eukaryotic genomes. Nucl Acids Res. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq806
Bertram G, Innes S, Minella O, Richardson J, Stansfield I (2001) Endless possibilities: translation termination and stop codon recognition. Microbiology 147:255–269
Cai J, Zhao R, Jiang H, Wang W (2008) De novo origination of a new protein-coding gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 179:487–496
Dermitzakis ET, Bergman CM, Clark AG (2003) Tracing the evolutionary history of Drosophila regulatory regions with models that identify transcription factor binding sites. Mol Biol Evol 20:703–714
Doniger SW, Fay JC (2007) Frequent gain and loss of functional transcription factor binding sites. PLoS Comput Biol 3:e99
Echols N, Harrison P, Balasubramanian S, Luscombe NM, Bertone P, Zhang Z, Gerstein M (2002) Comprehensive analysis of amino acid and nucleotide composition in eukaryotic genomes, comparing genes and pseudogenes. Nucl Acids Res 30:2515–2523
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucl Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Engelberg-Kulka H, Dekel L, Israeli-Reches M (1977) Streptomycin-resistant Escherichia coli mutant temperature sensitive for the production of Qbeta-infective particles. J Virol 21:1–6
Frenkel FE and Korotkov EV (2009) Using triplet periodicity of nucleotide sequences for finding potential reading frame shifts in genes. DNA Res 16:105–114
Giacomelli MG, Hancock AS, Masel J (2007) The conversion of 3′UTR’s into coding regions. Mol Biol Evol 24:457–464
Jordan IK, Rogozin IB, Glazko GV, Koonin EV (2003) Origin of a substantial fraction of human regulatory sequences from transposable elements. Trends Genet 19:68–72
Jordan IK, Kondrashov FA, Adzhubei IA, Wolf YI, Koonin EV, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev S (2005) A universal trend of amino acid gain and loss in protein evolution. Nature 433:633–638
Kazanov MD (2008) Functional classification of genes from complete bacterial genomes, based on Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG) database. In: Proceedings of informational technologies and systems conference, Moscow, pp 104–109
Kondrashov FA, Koonin EV (2003) Evolution of alternative splicing: deletions, insertions and origin of functional parts of proteins from intron sequences. Trends Genet 19:115–119
Kramer EM, Su HJ, Wu CC, Hu JM (2006) A simplified explanation for the frameshift mutation that created a novel C-terminal motif in the APETALA3 gene lineage. BMC Evol Biol 6:30
Kreahling J, Graveley BR (2004) The origins and implications of aluternative splicing. Trends Genet 20:1–4
Krull M, Brosius J, Schmitz J (2005) Alu-SINE exonization: en route to protein-coding function. Mol Biol Evol 22:1702–1711
Kurmangaliyev YZ, Gelfand MS (2008) Computational analysis of splicing errors and mutations in human transcripts. BMC Genomic 9:13
Li CY, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Cao C, Zhang PW, Lu SJ, Li XM, Yu Q, Zheng X, Du Q, Uhl GR, Liu QR, Wei L (2010) A human-specific de novo protein-coding gene associated with human brain functions. PLoS Comput Biol 6:e1000734
Liang H, Cavalcanti AR, Landweber L (2005) Conservation of tandem stop codons in yeasts. Genome Biol 6:R31
Lynch M (2007) The origins of genome architecture. Sinauer Assosiates, Sunderland
Lynch M, Conery JS (2000) The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science 290:1151–1155
Major LL, Edgar TD, Yee YP, Isaksson LA, Tate WP (2002) Tandem termination signals: myth or reality? FEBS Lett 514:84–89
Moses AM, Pollard DA, Nix DA, Iyer VN, Li XY, Biggin MD, Eisen MB (2006) Large-scale turnover of functional transcription factor binding sites in Drosophila. PLoS Comput Biol 2:e130
Mustonen V, Lassig M (2005) Evolutionary population genetics of promoters: Predicting binding sites and functional phylogenies. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:15936–15941
Nichols JL (1970) Nucleotide sequence from the polypeptide chain termination region of the coat protein cistron in bacteriophage R17 RNA. Nature 225:147–151
Novichkov PS, Ratnere I, Wolf YI, Koonin EV, Dubchak I (2009) ATGC: a database of orthologous genes from closely related prokaryotic genomes and a research platform for microevolution of prokaryotes. Nucl Acids Res 37:D448–D454
Nurtdinov RN, Neverov AD, Favorov AV, Mironov AA, Gelfand MS (2007) Conserved and species-specific alternative splicing in mammalian genomes. BMC Evol Biol 7:249
Ohno S (1970) Evolution by gene duplication. Springer-Verlag, New York
Okamura K, Feuk L, Marquès-Bonetc T, Navarroc A, Scherer SW (2006) Frequent appearance of novel protein-coding sequences by frameshift translation. Genomics 88:690–697
Piriyapongsa J, Polavarapu N, Borodovsky M, McDonald J (2007a) Exonization of the LTR transposable elements in human genome. BMC Genomics 8:291
Piriyapongsa J, Rutledge MT, Patel S, Borodovsky M, Jordan IK (2007b) Evaluating the protein coding potential of exonized transposable element sequences. Biol Direct 2:31
Radloff RJ, Kaesberg P (1973) Electrophoretic and other properties of bacteriophage Q: the effect of a variable number of read-through proteins. J Virol 11:116–128
Raes J, Van de Peer Y (2005) Functional divergence of proteins through frameshift mutations. Trends Genet 21:428–431
Ridout KE, Dixon CJ, Filatov DA (2010) Positive selection differs between protein secondary structure elements in Drosophila. Genome Biol Evol 2:166–179
Rocha EP, Danchin A, Viari A (1999) Translation in Bacillus subtilis: roles and trends of initiation and termination, insights from a genome analysis. Nucl Acids Res 27:3567–3576
Rodionov DA (2007) Comparative genomic reconstruction of transcriptional regulatory networks in bacteria. Chem Rev 107:3467–3497
Shabalina SA, Ogurtsov AY, Rogozin IB, Koonin EV, Lipman DJ (2004) Comparative analysis of orthologous eukaryotic mRNAs: potential hidden functional signals. Nucl Acids Res 32:1774–1782
Silva JC, Shabalina SA, Harris DG, Spouge JL, Kondrashov AS (2003) Conserved fragments of transposable elements in intergenic regions: evidence for widespread recruitment of MIR- and L2-derived sequences within the mouse and human genomes. Genet Res 82:1–18
Stephen S, Pheasant M, Makunin IV, Mattick JS (2008) Large-scale appearance of ultraconserved elements in tetrapod genomes and slowdown of the molecular clock. Mol Biol Evol 25:402–408
Tatusov RL, Natale DA, Garkavtsev IV, Tatusova TA, Shankavaram UT, Rao BS, Kiryutin B, Galperin MY, Fedorova ND, Koonin EV (2001) The COG database: new developments in phylogenetic classification of proteins from complete genomes. Nucl Acids Res 29:22–28
Vitreschak AG, Mironov AA, Lyubetsky VA, Gelfand MS (2008) Comparative genomic analysis of T-box regulatory systems in bacteria. RNA 14:717–735
Ward JH (1963) Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J Am Stat Assoc 58:236–244
Wernegreen JJ, Kauppinen SN, Degnan PH (2009) Slip into something more functional: selection maintains ancient frameshifts in homopolymeric sequences. Mol Biol Evol 27:833–839
Wilder JA, Hewett EK, Gansner ME (2009) Molecular evolution of GYPC: evidence for recent structural innovation and positive selection in humans. Mol Biol Evol 26:2679–2687
Zhou Q, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Xu S, Zhao R, Zhan Z, Li X, Ding Y, Yang S, Wang W (2008) On the origin of new genes in Drosophila. Genome Res 18:1446–1455
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grants from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research [08-04-01394-a], the Russian Ministry of Science and Education grant “Phylogenetic analysis of complex selection in molecular evolution” and contract P916, and the “Molecular and Cellular Biology” Program of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vakhrusheva, A.A., Kazanov, M.D., Mironov, A.A. et al. Evolution of Prokaryotic Genes by Shift of Stop Codons. J Mol Evol 72, 138–146 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-010-9408-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-010-9408-1