Abstract
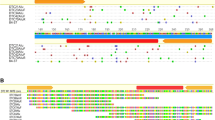
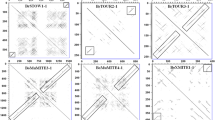
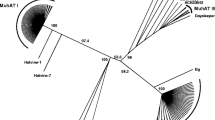
Transposable elements (TEs) are mobile DNA regions that alter host genome structure and gene expression. A novel 588 bp non-autonomous high copy number TE in the Ostrinia nubilalis genome has features in common with miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs): high A + T content (62.3%), lack of internal protein coding sequence, and secondary structure consisting of subterminal inverted repeats (SIRs). The O. nubilalis TE has inserted at (GAAA)n microsatellite loci, and was named the microsatellite-associated interspersed nuclear element (MINE-1). Non-autonomous MINE-1 superfamily members also were identified downstream of (GAAA)n microsatellites within Bombyx mori and Pectinophora gossypiella genomes. Of 316 (GAAA)n microsatellites from the B. mori whole genome sequence, 201 (63.6%) have associated autonomous or non-autonomous MINE-1 elements. Autonomous B. mori MINE-1s a encode a helicase and endonuclease domain RepHel-like protein (BMHELp1) indicating their classification as Helitron-like transposons and were renamed Helitron1_BM. Transposition of MINE-1 members in Lepidoptera has resulted in the disruption of (GAAA)n microsatellite loci, has impacted the application of microsatellite-based genetic markers, and suggests genome sequence that flanks TT/AA dinucleotides may be required for target site recognition by RepHel endonuclease domains.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi H, Yokozeki Y, Inagaki A, Mori K, Fujimura T (2001) Micron, a microsatellite-targeting transposable element in the rice genome. Mol Genet Genomics 266:471–480
Anderson SJ, Gould P, Freeland JR (2007) Repetitive flanking sequences (ReFS): novel molecular markers from microsatellite families. Mol Ecol Notes 7:374–376
Anthony N, Gelembiuk G, Raterman D, Nice C, Ffrench-Constant R (2001) Brief report: isolation and characterization of microsatellite markers from the endangered Karner blue butterfly Lycaeides melissa samuelis (Lepidoptera). Hereditas 134:271–273
Arcot SS, Wang Z, Weber JL, Deininger PL, Batzer MA (1995) Alu repeats: a source for the genesis of primate microsatellites. Genomics 29:136–144
Bergman CM, Quesneville H (2007) Discovering and detecting transposable elements in genome sequences. Brief Bioinform 8:382–392
Bidichandani SI, Ashizawa T, Patel PI (1998) The GAA triplet-repeat expansion in Friedrich ataxia interferes with transcription and may be associated with an unusual DNA structure. Am J Hum Genet 62:111–121
Bork P, Koonin EV (1993) An expanding family of helicase within the ‘DEAD/H’ superfamily. Nucleic Acids Res 11:751–752
Brunner S, Fengler K, Morgante M, Tingey S, Rafalski A (2005) Evolution of DNA sequence nonhomologies among maize inbreds. Plant Cell 17:343–360
Bureau TE, Wessler SR (1994a) Mobile inverted-repeat elements of the Tourist family are associated with the genes of many cereal grasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:1411–1415
Bureau TE, Wessler SR (1994b) Stowaway: a new family of inverted repeat elements associated with the genes of both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants. Plant Cell 6:907–916
Casacuberta E, Casacuberta JM, Puigdomenech P, Monfort A (1998) Presence of miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) in the genome of Arabidopsis thaliana: characterisation of the Emigrant family of elements. Plant J 16:79–85
Chen S, Li X (2007) Transposable elements are enriched within or in close proximity to xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome P450 genes. BMC Evol Biol 7:46
Coates BS, Sumerford DS, Hellmich RL, Lewis LC (2009) Repetitive genome elements in a European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis, bacterial artificial chromosome library was indicated by (BAC) end sequencing and development of sequence tag site (STS) markers: Implications for lepidopteran genomic research. Genome (in press)
Craig NL (1995) Unity in transposition reactions. Science 270:253–254
Du C, Fefelova N, Caronna J, He L, Dooner HK (2009) The polychromatic Helitron landscape of the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19916–19921
Dufresne M, Hua-Van A, El Wahab HA, Ben M’Barek S, Vasnier C, Teysset L, Kema GHJ, Daboussi MJ (2006) Transposition of a fungal MITE through the action of a Tc1-like transposase. Genetics 175:441–452
Economou EP, Bergen AW, Warren AC, Antonarakis SE (1990) The poly(A) tract of Alu repetitive elements is polymorphic in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2951–2954
Fauvelot C, Cleary DFR, Menen SBJ (2006) Short-term impact of 1997/1998 ENSO-induced disturbance on abundance and genetic variation in a tropical butterfly. J Heredity 97:367–380
Feschotte CM, Mouchès C (2000) Evidence that a family of miniature inverted repeat transposable elements (MITEs) from the Arabidopsis thaliana genome has arisen from a pogo-like DNA transpsoson. Mol Biol Evol 17:730–737
Galagan JE, Calvo SE, Cuomo C, Ma LJ, Wortman JR, Batzaglou S, Lee SI, Basturkmen M, Spevak CC, Clutterbuck J, Kapitonov V, Jurka J, Scazzocchio C, Farman M, Butler J, Purcell S, Harris S et al (2005) Sequencing of Aspergillus nidulans and comparative analysis with A. fumigatus and A. oryzae. Nature 438:1105–1115
Gupta S, Gallavotti A, Stryker GA, Lai SK (2005) A novel class of Helitron-related transposable elements in maize contain portions of multiple pseudogenes. Plant Mol Biol 57:115–127
Hutchison C III, Hardies S, Loeb D, Shehee W, Edgell M (1989) LINEs and related retroposons: long interspersed repeated sequences in the eucaryotic genome. In: Berg DE, Howe MM (eds) Mobile DNA. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 593–617
Jelinek WR, Toomey TP, Leinwand L, Duncan CH, Biro PA, Choudary PV, Weissman SM, Rubin CM, Houck CM, Denlinger PL, Schmid CW (1980) Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1398–1402
Jurka J, Pethiyagoda C (1995) Sequences from primates: compilation and analysis. J Mol Evol 40:120–126
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2001) Rolling-circle transposons in eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:8714–8719
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2007a) Helitrons in fruit flies. Rephase reports 7:132–271
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2007b) Helitrons on a roll: eukaryotic rolling-circle transposons. Trend Genet 23:521–529
Kofler R, Schlotterer C, Lelley T (2007) SciRoKo: a new tool for whole genome microsatellite search and investigation. Bioinformatics 23:1683–1685
Kudo Y, Okazaki S, Anzai T, Fujiwara H (2001) Structural and phylogenetic analysis of TRAS, telomeric repeat-specific non-LTR retrotransposon families in Lepidopteran insects. Mol Biol Evol 18:848–857
Lai J, Li Y, Messing J, Dooner H (2005) Gene movement by Helitron transposons contributes to the haplotype variability in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9068–9073
Lal SK, Hannah L (2005) Helitrons contribute to the lack of gene colinearity observed in modern maize inbreds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9993–9994
Lerat E, Sémon M (2007) Influence of the transposable element neighborhood on human gene expression in normal and tumor tissues. Gene 396:303–311
Levinson G, Gutman GA (1987) Slipped strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol Biol Evol 4:203–221
Livak KL, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Locke J, Howard LT, Aippersbach N, Podemski L, Hodgetts RB (1999) The characterization of DINE-1, a short, interspersed repetitive element present on chromosome and in the centric heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 108:356–366
López-Giráldez F, Andres O, Domingo-Roura X, Bosch M (2006) Análisis of carnivore microsatellites and their intimate association with tRNA-derived SINEs. BMC Genomics 7:269
Malausa T, Dalecky A, Ponsard S, Audiot P, Streiff R, Chaval Y, Bourguet D (2007) Genetic structure and gene flow in French populations of two Ostrinia taxa: host races or sibling species? Mol Ecol 16:4210–4222
Marchler-Bauer A, Anderson JB, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, DeWeese-Scott C, Fong JH, Geer LY, Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, He S, Hurwitz DI, Jackson JD, Ke Z, Lanczycki CJ, Liebert CA, Liu C, Lu F, Lu S, Marchler GH, Mullokandov M, Song JS, Tasneem A, Thanki N, Yamashita RA, Zhang D, Zhang N, Bryant SH (2009) CDD: Specific functional annotation with the conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D205–D210
Meglécz E, Pétenian F, Danchin E, D’Acier AC, Rasplus JY, Faure E (2004) High similarity between flanking regions of different microsatellites detected within each of two species of Lepidoptera: Parnassius apollo and Euphydryas aurinia. Mol Ecol 13:1693–1700
Meglécz E, Anderson SJ, Bourguet D, Butcher R, Caldas A, Cassel-Lundhagen A, d’Acier AC, Dawson DA, Faure N, Fauvelot C, Franck P, Harper G, Keyghobadi N, Kluetsch C, Muthulakshmi M, Nagaraju J, Patt A, Péténian F, Silvain JF, Wilcock HR (2007) Microsatellite flanking region similarities among different loci within insect species. Insect Mol Biol 16:175–185
Miao XX, Xub SJ, Ming JL, Li MW, Huang JH, Dai FY, Marino SW, Mills DR, Zeng P, Mita K, Jia SH, Zhang Y, Liu WB, Xiang H, Guo QH, Xu AY, Kong XY, Lin HX, Shi YZ, Lu G, Zhang X, Huang W, Yasukochi Y, Sugasaki T, Shimada T, Nagaraju J, Xiang ZH, Wang SY, Goldsmith MR, Lu C, Zhao GP, Huang YP (2005) Simple sequence repeat-based consensus linkage map of Bombyx mori. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 45:16303–16308
Miller WJ, Nagel A, Bachmann J, Bachmann L (2000) Evolutionary dynamics of the SGM transposon family in the Drosophila obscura species group. Mol Biol Evol 17:1597–1609
Mita K, Kasahara M, Sasaki S, Nagayasu Y, Yamada T, Kanamori H, Namiki N, Kitagawa M, Yamashita H, Yasukochi Y, Kadono-Okuda K, Yamamoto K, Ajimuar M, Ravikumar G, Shimomura M, Nagamura Y, Shin-I T, Abe H, Shimada T, Morishita S, Sasaki T (2004) The genome sequence of silkworm, Bombyx mori. DNA Res 11:27–36
Pemberton JM, Slate J, Bancroft DR, Barrett JA (1995) Nonamplifying alleles at microsatellite loci—a caution for parentage and population studies. Mol Ecol 4:249–252
Petersen G, Seberg O (2000) Phylogenetic evidence of excision of stowaway miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements in Triticeae (Poaceae). Mol Biol Evol 17:1589–1596
Posey JE, Pytlos MJ, Sinden RR, Roth DB (2006) Target DNA structure plays a crucial role in RAG transposition. PLoS Biol 4:E350
Poulter RT (2003) Vertebrate Helitrons and other novel Helitrons. Gene 313:201–212
Prasad MD, Muthulakshmi M, Madju M, Archak S, Mita K, Nagaraju J (2005) Survey analysis of microsatellites in the Silkworm, Bombyx mori: freqeuncy distribution, mutations, marker potential and their conservation in heterologous species. Genetics 169:197–214
Quesneville H, Nouaud D, Anxolabéhère D (2006) P elements and MITE relative in the whole genome sequence of Anopheles gambiae. BMC Genomics 7:214
Ramsey L, Macaulay M, Cardle L, Morgante M, degli Ivanissevich S, Maestri E, Powell W, Waugh R (1999) Intimate association of microsatellite repeats with retroelements and other dispersed repetitive elements in barley. Plant J 17:415–425
Reddy KD, Abraham EG, Nagaraju J (1999) Microsatellites in the silkworm, Bombyx mori: abundance, polymorphism, and strain characterization. Genome 42:1057–1065
Roeder GS, Rose AB, Pearlman RE (1985) Transposable element sequences involved in the enhancement of yeast gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:5428–5432
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 365–386
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetic analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tautz D (1989) Hypervariability of simple sequences as a general source for polymorphic DNA markers. Nucleic Acids Res 17:6463–6471
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
The International Silkworm Genome Consortium (2008) The genome of a lepidopteran model insect, the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:1036–1045
Tu Z (1997) Three novel families of miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements are associated with genes of the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7475–7480
Tu Z (2000) Molecular and evolutionary analysis of two divergent subfamilies of a novel miniature inverted repeat transposable element in the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Mol Biol Evol 17:1313–1325
Van’t Hof AE, Brakefield PM, Saccheri IJ, Zwaan BJ (2007) Evolutionary dynamics of multilocus microsatellite arrangements in the genome of the butterfly Bicyclus anynana, with implications for other Lepidoptera. Heredity 98:320–328
Vivas MV, Garcia-Planells J, Ruiz C, Marfany G, Paricio N, Gonzalez-Duarte R, de Frutos R (1999) GEM, a cluster of repetitive sequences in the Drosophila subobscura genome. Gene 229:47–57
Wang J, Wong GK, Ni P, Han Y, Huang X, Zhang J, Ye C, Zhang Y, Hu J, Zhang K et al (2002) RePS: a sequence assembler that masks exact repeats identified from the shotgun data. Genome Res 12:824–831
Wang J, Xia Q, He X, Dai M, Ruan J, Chen J, Yu G, Yuan H, Hu Y, Li R, Feng T, Ye C, Lu C, Wang J, Li S, Wong GKS, Yang H, Wang J, Xiang Z, Zhou Z, Yu J (2005) SilkDB: a knowledgebase for silkworm biology and genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D399–D402
Weber JL, May PE (1989) Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet 44:388–396
Wessler SR, Bureau TE, White SE (1995) LTR-retrotransposons and MITEs: important players in the evolution of plant genomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 5:814–821
Wicker T, Guyot R, Yahiaoui N, Keller B (2003) CACTA transposons in Triticeae. A diverse family of high-copy repetitive elements. Plant Phys 132:52–63
Wilder J, Hollocher H (2001) Mobile elements and the genesis of microsatellites in dipterans. Mol Biol Evol 18:384–392
Witte CP, Le QH, Bureau T, Kumar A (2001) Terminal-repeat retrotransposons in miniature (TRIM) are involved in restructuring plant genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13779–13783
Xia Q, Zhou Z, Lu C, Cheng D, Dai F, Li B, Zhao P, Zha X, Cheng T, Chai C, Pan G, Xu J, Liu C, Lin Y et al (2004) A draft sequence for the genome of the domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori). Science 306:1937–1940
Yandava CN, Gastier JM, Pulido JC, Brody T, Sheffield V, Murray J, Buetow K, Duyk GM (1997) Characterization of Alu repeats that are associated with trinucleotide and tetranucleotide repeat microsatellites. Genome Res 7:716–724
Yang HP, Barbash DA (2008) Abundant and species-specific DINE-1 transposable elements in 12 Drosophila genomes. Genome Biol 9:R39
Yang HP, Hung TL, You TL, Yang TH (2006) Genome-wide comparative analysis of the highly abundant transposable element DINE-1 suggests a recent transpositional burst in Drosophila yakuba. Genetics 173:189–196
Zhang DX (2004) Lepidopteran microsatellite DNA: redundant but promising. Trends Ecol Evol 19:507–509
Zhou Q (2006) Helitron transposons on the sex chromosome of the platyfish Xiphphorus maculates and their evolution in animal genomes. Zebrafish 3:39–52
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3406–3415
Zuliani G, Hobbs H (1990) A high frequency of length polymorphisms in repeated sequences adjacent to Alu sequences. Am J Hum Genet 46:963–969
Acknowledgments
This research is a joint contribution from the United States Department of Agriculture Agriculture Research Service and the Iowa Agriculture and Home Economics Experiment Station, Ames (project 3543). Mention of proprietary products does not constitute an endorsement or a recommendation by USDA, or Iowa State University for its use.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
This file is unfortunately not in the Publisher's archive anymore: Supplementary material 3 (MAS 201 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coates, B.S., Sumerford, D.V., Hellmich, R.L. et al. A Helitron-Like Transposon Superfamily from Lepidoptera Disrupts (GAAA)n Microsatellites and is Responsible for Flanking Sequence Similarity within a Microsatellite Family. J Mol Evol 70, 275–288 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-010-9330-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-010-9330-6