Abstract
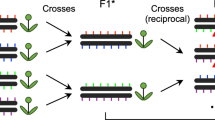
Broad-scale differences in crossover rate across the genome have been characterized in most genomes studied. Fine-scale differences, however, have only been examined in a few taxa, such as Arabidopsis, yeast, humans, and mice. No prior studies have directly looked for fine-scale recombination rate heterogeneity in Drosophila. We produced 370 Drosophila pseudoobscura containing a crossover event within the 2-megabase (MB) region between the genes yellow and white. We then examined 19 intervals within this region and determined where the crossovers occurred. We found that recombination events occur nonrandomly on a small scale and that mild “hotspots“ of a few kilobases exist in Drosophila. Among the regions studied, recombination rates varied from 1.4 to 52 cM/MB. We also observed a trend toward high codon bias in regions of high recombination. Finally, we identified a significantly positive correlation between recombination rate and simple repeats, as well as the motif CACAC. These sequence features may contribute to broad-scale variation in crossover rate and, thus, shed light on features associated with crossover rate heterogeneity at a genome-wide scale.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton NH, Charlesworth B (1998) Why sex and recombination? Science 281:1986–1990
Butlin RK (2005) Recombination and speciation. Mol Ecol 14:2621–2635
Charlesworth D, Charlesworth B, Marais G (2005) Steps in the evolution of heteromorphic sex chromosomes. Heredity 95:118–128
Comeron JM, Kreitman M, Aguade M (1999) Natural selection on synonymous sites is correlated with gene length and recombination in Drosophila. Genetics 151:239–249
Curtis D, Clark SH, Chovnick A, Bender W (1989) Molecular analysis of recombination events in Drosophila. Genetics 122:653–661
de Massy B (2003) Distribution of meiotic recombination sites. Trends Genet 19:514–522
Drouaud J, Camilleri C, Bourguignon PY, Canaguier A, Berard A, et al. (2006) Variation in crossing-over rates across chromosome 4 of Arabidopsis thaliana reveals the presence of meiotic recombination “hot spots.“ Genome Res 16:106–114
Felsenstein J (1974) The evolutionary advantage of recombination. Genetics 78:737–756
Foss E, Lande R, Stahl FW, Steinberg CM (1993) Chiasma interference as a function of genetic distance. Genetics 133:681–691
Gloor GB, Engels WR (1992) Single-fly DNA preps for PCR. Drosoph Info Serv 71:148–149
Guillon H, de Massy B (2002) An initiation site for meiotic crossing-over and gene conversion in the mouse. Nat Genet 32:296–299
Hey J (2004) What‘s so hot about recombination hotspots? PLoS Biol 2:e190
Hey J, Kliman RM (2002) Interactions between natural selection, recombination and gene density in the genes of Drosophila. Genetics 160:595–608
Hill WG, Robertson A (1966) The effect of linkage on the limits to artificial selection. Genet Res 8:269–294
Hillier LW, Miller W, Birney E, Warren W, Hardison RC, et al. (2004) Sequence and comparative analysis of the chicken genome provide unique perspectives on vertebrate evolution. Nature 432:695–716
Hilliker AJ, Clark SH, Chovnick A (1991) The effect of DNA sequence polymorphisms on intragenic recombination in the rosy locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 129:779–781
Isobe T, Yoshino M, Mizuno K, Lindahl KF, Koide T, et al. (2002) Molecular characterization of the Pb recombination hotspot in the mouse major histocompatibility complex class II region. Genomics 80:229–235
Jensen-Seaman MI, Furey TS, Payseur BA, Lu Y, Roskin KM, et al. (2004) Comparative recombination rates in the rat, mouse, and human genomes. Genome Res 14:528–538
Jones GH (1984) The control of chiasma distribution. Symp Soc Exp Biol 38:293–320
Kliman RM, Hey J (1993) Reduced natural selection associated with low recombination in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 10:1239–1258
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lynn A, Ashley T, Hassold T (2004) Variation in human meiotic recombination. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 5:317–349
Marais G, Mouchiroud D, Duret L (2001) Does recombination improve selection on codon usage? Lessons from nematode and fly complete genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:5688–5692
Muller HJ (1916) The mechanism of crossing-over. Am Nat 50:193–221
Myers S, Bottolo L, Freeman C, McVean G, Donnelly P (2005a) A fine-scale map of recombination rates and hotspots across the human genome. Science 310:321–324
Nachman MW (2002) Variation in recombination rate across the genome: evidence and implications. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:657–663
Orr HA (1995) A new linkage map of the D. pseudoobscura X chromosome. Drosoph Info Serv 76:127–128
Ortiz-Barrientos D, Reiland J, Hey J, Noor MAF (2002) Recombination and the divergence of hybridizing species. Genetica 116:167–178
Ortiz-Barrientos D, Chang AS, Noor MAF (2006) A recombinational portrait of the Drosophila pseudoobscura genome. Genet Res Cambr 87:23–31
Otto SP, Barton NH (1997) The evolution of recombination: removing the limits to natural selection. Genetics 147:879–906
Palsson A, Rouse A, Riley-Berger R, Dworkin I, Gibson G (2004) Nucleotide variation in the Egfr locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 167:1199–1212
Palumbi SR (1996) Nucleic acids II: the polymerase chain reaction. In: Hillis DM, Moritz C, Mable BK (eds) Molecular systematics. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, pp 205–247
Petes TD (2001) Meiotic recombination hot spots and cold spots. Nat Rev Genet 2:360–369
Reed FA, Tishkoff SA (2006) Positive selection can create false hotspots of recombination. Genetics 172:2011–2014
Richards S, Liu Y, Bettencourt BR, et al. (2005) Comparative genome sequencing of Drosophila pseudoobscura: chromosomal, gene, and cis-element evolution. Genome Res 15:1–18
Singh ND, Arndt PF, Petrov DA (2005) Genomic heterogeneity of background substitutional patterns in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 169:709–722
Sturtevant AH (1915) The behavior of the chromosomes as studied through linkage. Z Indukt Abstammungs-Vererbungsl 13:234–287
Takano-Shimizu T (1999) Local recombination and mutation effects on molecular evolution in Drosophila. Genetics 153:1285–1296
Takano-Shimizu T (2001) Local changes in GC/AT substitution biases and in crossover frequencies on Drosophila chromosomes. Mol Biol Evol 18:606–619
True JR, Mercer JM, Laurie CC (1996) Differences in crossover frequency and distribution among three sibling species of Drosophila. Genetics 142:507–523
Weinstein A (1958) The geometry and mechanics of crossing over. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 23:177–196
Acknowledgments
We thank N. Johnson, D. Petrov, N. Walley, and an anonymous reviewer for helpful comments on the manuscript and E. Gragg for technical assistance. Funding for this research was provided by NSF Grants 0509780 and 0549893 to M.A.F.N. and NIH Grant HG02456 to R.M.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Reviewing Editor: Dr. Dmitri Petrov]
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cirulli, E.T., Kliman, R. & Noor, M.A.F. Fine-Scale Crossover Rate Heterogeneity in Drosophila pseudoobscura . J Mol Evol 64, 129–135 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-006-0142-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-006-0142-7