Abstract
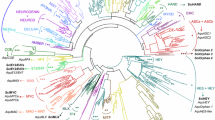
A survey across the most basal animal phylum, the Porifera, for the presence of homeobox-containing genes led to the isolation of 24 partial or complete homeobox sequences from 21 sponge species distributed in 15 families and 6 orders of Demospongiae. All the new sequences shared a high identity/similarity with EmH-3 (Ephydatia muelleri), a non-Hox gene from the Antp class. The Demox sequences, EmH-3, and related homeodomains formed a well-supported clade with no true affinity with any known bilaterian family, including the Tlx/Hox11 family, suggesting that the EmH-3 family of genes, comprising 31 members, represents a novel family of non-Hox genes, called the Demox family, widespread among Demospongiae. The presence of the Tlx/Hox11 specific signature in the Demox family and common regulatory elements suggested that the Demox and Tlx/Hox11 families are closely related. In the phylogenetic analyses, freshwater Haplosclerida appeared as monophyletic, and Haplosclerida and Halichondrida as polyphyletic, with a clade comprising Agelas species and Axinella corrugata. As for their expression, high levels of Demox transcripts were found in adult tissues. Our data add to the number of published poriferan homeobox sequences and provide independent confirmation of the current Demospongiae phylogenies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae Y-K, Shimizu T, Yabe T, Kim C-H, Tsutomu H, Nojima H, Muraoka M, Hiramo T, Hibi M (2003) A homeobox gene, pnx, is involved in the formation of posterior neurons in zebrafish. Development 130:1853–1865
Borchiellini C, Chombard C, Manuel M, Alivon E, Vacelet J, Boury-Esnault N (2004) Molecular phylogeny of Demospongiae: implications for classification and scenarios of character evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol 32:823–837
Coutinho CC, Vissers S, Van de Vyver G (1994) Evidence of homeobox genes in the freshwater sponge Ephydatia fluviatilis. In: van Soest RWM, van Kempen ThMG, Braekman JC (eds) Sponge in time and space; Biology, chemistry, paleontology. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 385–388
Coutinho CC, Seack J, Van de Vyver G, Borojevic R, Müller WEG (1998) Origin of the metazoan bodyplan: characterization and functional testing of the promoter of the homeobox gene EmH-3 from the freshwater sponge Ephydatia muelleri in mouse 3T3 cells. Biol Chem 379:1243–1251
Coutinho CC, Fonseca RN, Mansure JJ, Borojevic R (2003) Early steps in the evolution of multicellularity: deep structural and functional homologies among homeobox genes in sponges and higher metazoans. Mech Dev 120:429–440
Degnan BM, Degnan SM, Giusti A, Morse DE (1995) A hox/hom homeobox gene in sponges. Gene 155:175–177
Erpenbeck D, McCormack GP, Breeuwer JAJ, Soest RWM van (2004) Order level differences in the structure of partial LSU across demosponges (Porifera): new insights into an old taxon. Mol Phylogenet Evol 32:388–395
Erpenbeck D, van Soest RWM (2005a) A survey for biochemical synapomorphies to reveal phylogenetic relationships of halichondrid demosponges (Metazoa: Porifera). Biochem Syst Ecol 31:583–616
Erpenbeck D, Breeuwer JAJ, van Soest RWM (2005b) Implications from a 28S rRNA gene fragment for the phylogenetic relationships of halichondrid sponges (Porifera:Demospongiae). J Zool Soc 43:93–99
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Galliot B (2000) Conserved and divergent genes in apex and axis development of cnidarians. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:629–637
Gauchat D, Mazet F, Berney C, Schummer M, Kreger S, Pawlowski J, Galliot B (2000) Evolution of the Antp-class genes differential expression of Hydra Hox/paraHox genes in anterior patterning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4493–4498
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Hill A, Tetrault J, Hill M (2004) Isolation and expression analysis of a posterior Antp-class Bar-/Bsh-like homeobox gene. Dev Genes Evol 214:515–523
Hooper JNA, Soest RWM van (2002) Systema Porifera: A guide to the classification of sponges. In: Hooper JNA, Soest RWM van (eds) Systema Porifera: A guide to the classification of sponges, Vol 1. Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New York, pp 1–3
Hoshiyama D, Suga H, Iwabe N, Koyanagi M, Nikoh N, Kuma K, Matsuda F, Honjo T, Miyata T (1998) Sponge pax cDNA related to pax-2/5/8 and ancient gene duplication in the pax family. J Mol Evol 47:640–648
Itskovich VB, Belikov SI, Efremova SM, Masuda Y (1999) Phylogenetic relationships between Lubomirskiidae, Spongillidae and some marine sponges according partial sequences of 18S rDNA. Mem Queensl Mus 44:275–280
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci 8(3):275–282
Kurata T, Ueno N (2003) Xenopus Nbx, a novel NK-1 related gene essential for neural crest formation. Dev Biol 257:30–40
Logan C, Wingate RJT, McKay IJ, Lumsden A (1998) Tlx-1 and Tlx-3 homeobox gene expression in cranial sensory ganglia and hindbrain of the chick embryo: markers of patterned connectivity. J Neurosci 18:5389–5402
Manuel M, Le Parco Y (2000) Homeobox gene diversification in the calcareous sponge Sycon raphanus. Mol Phylogenet Evol 17:97–107
Martinelli C, Spring J (2005) T-box and homeobox genes from the ctenophore Pleurobrachia pileus: comparison of brachyury, Tlbx2/3 and Tlx in basal metazoans and bilaterians. FEBS Lett 579(22):5024–5028
Nichols SA (2005) An evaluation of support for order-level monophyly and interrelationships within the class Demospongiae using partial data from the large subunit rDNA and cytochrome oxidase subunit I. Mol Phylogenet Evol 34:81–96
Nikko E, Van de Vyver G, Richelle-Maurer E (2001) Retinoic acid down-regulates the expression of EmH-3 homeobox-containing gene in the freshwater sponge Ephydatia muelleri. Mech Age Dev 122:779–794
Perovic S, Schröder HC, Sudek S, Grebenjuk VA, Batel R, Stifanic M, Müller IM, Müller WEG (2003) Expression of one sponge Iroquois homeobox gene in primmorphs from Suberites domuncula during canal formation. Evol Dev 5:240–250
Richelle-Maurer E, Van de Vyver G (1999a) Expression of homeobox-containing genes in freshwater sponges. Mem Queensl Mus 44:509–514
Richelle-Maurer E, Van de Vyver G (1999b) Temporal and spatial expression of EmH-3, a homeobox-containing gene isolated from the freshwater sponge Ephydatia muelleri. Mech Age Dev 109:203–219
Richelle-Maurer E, Van de Vyver G, Vissers S, Coutinho CC (1998) Homeobox-containing genes in freshwater sponges: characterization, expression, and phylogeny. In: Müller WEG (ed) Molecular evolution: Evidence for monophyly of Metazoa, Vol 19. Springer, Berlin, pp 157–175
Richelle-Maurer E, Braekman J-C, De Kluijver MJ, Gomez R, Van de Vyver G, van Soest RWM, Devijver C (2001) Cellular location of (2R, 3R, 7Z)-2-aminotetradec-7-ene-1, 3-diol, a potent antimicrobial metabolite produced by the Caribbean sponge Haliclona vansoesti. Cell Tissue Res 306:157–165
Richelle-Maurer E, Sonet G, Van de Vyver G (2004) Identification of homologies of the EmH-3 homeobox-containing gene in demosponges. Boll Mus Ist Biol Univ Genova 68:565–577
Schröder HC, Efremova SM, Itskovich VB, Belikov SI, Masuda Y, Krasko A, Müller IM, Müller WEG (2003) Molecular phylogeny of the freshwater sponges in Lake Baikal. J Zool Syst Evol Res 41:81–86
Seimiya M, Ishiguro H, Miura K, Watanabe Y, Kurosawa Y (1994) Homeobox-containing genes in the most primitive metazoa, the sponges. Eur J Biochem 221:219–225
Seimiya M, Watanabe Y, Kurosawa YAD (1997) Identification of POU-class homeobox genes in a freshwater sponge and the specific expression of these genes during differentiation. Eur J Biochem 243:27–31
Smith ST, Jaynes JB (1996) A conserved region of Engrailed, shared among all en-, gsc-, Nk1-, Nk2- and msh class homeoproteins, mediates active transcriptional repression in vivo. Development 122:3141–3150
Swofford DL (2000) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Wiens M, Mangoni A, D’Esposito M, Fattorusso E, Korchagina N, Schröder HC, Grebenjuk VA, Krasko A, Batel R, Müller IM, Müller WEG (2003) The molecular basis for the evolution of the metazoan bodyplan: extracellular matrix-mediated morphogenesis in marine Demosponges. J Mol Evol 57:S60–S75
Yasuo H, Lemaire P (2001) Role of Goosecoid, Xnot and Wnt antagonists in the maintenance of the notochord genetic programme in Xenopus gastrulae. Development 128:3783–3793
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Amy Wright for her invitation to work in her laboratory and participate in the Bahamas Research cruise sponsored by the Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institution (HBOI), Division of Biomedical Marine Research; John K. Reed and the crew of the R/V Seward Johnson for their assistance in the collection of sponges; and Jane Thompson, Jose Lopez, and Laurent Gatto for their valuable advice and helpful discussions. This research was supported by an FNRS grant (Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique, Belgium; No. 1.5.082.03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Reviewing Editor: Dr. Nicolas Galtier]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richelle-Maurer, E., Boury-Esnault, N., Itskovich, V.B. et al. Conservation and Phylogeny of a Novel Family of Non-Hox Genes of the Antp Class in Demospongiae (Porifera). J Mol Evol 63, 222–230 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0294-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0294-x