Abstract
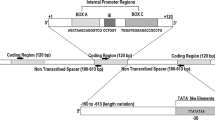
The genomic and gene organisation of 5S rDNA clusters have been extensively characterized in bony fish and eukaryotes, providing general issues for understanding the molecular evolution of this multigene DNA family. By contrast, the 5S rDNA features have been rarely investigated in cartilaginous fish (only three species). Here, we provide evidence for a dual 5S rDNA gene system in the Rajidae by sequence analysis of the coding region (5S) and adjacent nontranscribed spacer (NTS) in five Mediterranean species of rays (Rajidae), and in a large number of piscine taxa including lampreys and bony fish. As documented in several bony fish, two functional 5S rDNA types were found here also in the rajid genome: a short one (I) and a long one (II), distinguished by distinct 5S and NTS sequences. That the ancestral piscine genome had these two 5S rDNA loci might be argued from the occurrence of homologous dual gene systems that exist in several fish taxa and from 5S phylogenetic relationships. An extensive analysis of NTS-II sequences of Rajidae and Dasyatidae revealed the occurrence of large simple sequence repeat (SSR) regions that are formed by microsatellite arrays. The localization and organization of SSR within the NTS-II are conserved in Rajiformes since the Upper Cretaceous. The direct correlation between the SSRs extension and the NTS length indicated that they might play a role in the maintenance of the larger 5S rDNA clusters in rays. The phylogenetic analysis indicated that NTS-II is a valuable systematic tool limited to distantly related taxa of Rajiformes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Bogenhagen DF, Brown DD (1981) Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription terminator. Cell 14:261–270
Cappetta H, Duffin C, Zidek J (1993) Chondrichthyes. In: Benton MJ (eds). The fossil record. 2. Chapman & Hall, London, pp. 593–610
Catasti P, Chen X, Mariappan SV, Bradbury EM, Gupta G (1999) DNA repeats in the human genome. Genetica 106:15–36
Céspedes A, García T, Carrera E, González I, Fernández A, Hernández PE, Martín R (1999) Identification of sole (Solea solea) and Greenland halibut (Reinhardtius hippoglossoides) by PCR amplification of the 5S rDNA gene. J Agr Food Chem 47:1046–1050
Chamberlain NL, Driver ED, Miesfeld RL (1994) The length and location of CAG trinucleotide repeats in the androgen receptor N-terminal domain affect transactivation function. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3181–3186
Deiana AM, Cau A, Salvadori S, Coluccia E, Cannas R, Milia A, Tagliavini J (2000) Major and 5S ribosomal sequences of the largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides (Perciformes, Centrachidae) are localized in GC-rich regions of the genome. Chromosome Res 8:213–218
Denis H, Wegnez M (1977) Biochemical research oogenesis: oocytes and liver cells of the teleost fish Tinca tinca contain different kinds of 5S RNA. Dev Biol 59:228–236
Dover GA (1982) Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature 299:111–117
Drouin G, Moniz de Sà M (1995) The concerted evolution of 5S ribosomal genes linked to the repeat units of other multigene families. Mol Biol Evol 12:481–493
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Gebhardt F, Zanker KS, Brandt B (1999) Modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor gene transcription by a polymorphic dinucleotide repeat in intron 1. J Biol Chem 274:13176–13180
Gerbi SA (1985) Evolution of ribosomal DNA. In: MacIntyre RJ (eds). Molecular evolutionary genetics. Plenum Press, New York, p. 419
Gornung E, De Innocentiis S, Annesi F, Sola L (2000) Zebrafish 5S rRNA genes map to the long arms of chromosome 3. Chromosome Res 8:362
Inafuku J, Nabeyama M, Kikuma Y, Saitoh J, Kubota S, Kohono S (2000) Chromosomal location and nucleotide sequences of 5S ribosomal DNA of two cyprinid species (Osteichthyes, Pisces). Chromosome Res 8:193199
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitution through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Komiya H, Hasegawa M, Takemura S (1986) Differentiation of oocyte and somatic-type 5S rRNAs in animals. J Biochem 100:369–374
Komiya H, Takemura S (1979) Nucleotide sequence of 5S ribosomal RNA from rainbow trout (Salmo gairdnerii) liver. J Biochem 86:1067–1080
Lanz RB, Wieland S, Hug M, Rusconi S (1995) A transcriptional repressor obtained by alternative translation of a trinucleotide repeat. Nucleic Acids Res 23:138–145
Li YC, Korol AB, Fahima T, Beiles A, Nevo E (2002) Microsatellites: genomic distribution, putative functions and mutational mechanisms: A review. Mol Ecol 11:2453–2465
Martins C, Wasko AP, Oliveira C, Wright JM (2000) Nucleotide sequence of 5S rDNA and localization of the ribosomal RNA genes to metaphase chromosomes of the tilapiine cichlid fish, Oreochromis niloticus. Hereditas 133:39–46
Martins C, Galetti PM (2001a) Organisation of 5S rDNA in Leporinus fish species: two different genomic locations are characterized by distinct nontranscribed spacers. Genome 44:903–910
Martins C, Galetti PM (2001b) Two 5S rDNA arrays in neotropical fish species: is it a general rule for fishes? Genetica 111:439–446
Martins C, Wasko AP, Oliveira C, Porto-Foresti F, Parise-Maltempi PP, Wright JM, Foresti F (2002) Dynamics of 5S rDNA in the tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) genome: repeat units, inverted sequences, pseudogenes and chromosome loci. Cytogenet Gen Res 98:78–85
Marukami M, Fujitani H (1998) Characterization of repetitive DNA sequences carriyng 5S rDNA of the triploid ginbuna (Japanese silver crucian carp, Carassius auratus langsdorfi) Genes Gen Syst 73:9–20
Mashkova TD, Serenkova TI, Mazo AM, Avdonina TA, Timofeyeva MY, Kisselev LL (1981) The primary structure of oocyte and somatic 5S rRNAs from the loach Misgurnus fossilis. Nucleic Acids Res 9:2141–2151
Meloni R, Albanese V, Ravassard P, Treilhou F, Mallet J (1998) A tetranucleotide polymorphic microsatellite, located in the first intron of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene, acts as a transcription regulatory element in vitro. Human Mol Genet 7:423–428
Messias LH, Ferreira DC, Wasko AP, Oliveira C, Foresti F, Martins C (2003) 5S rDNA organization in the fish Synbranchus marmoratus (Synbranchidae, Synbranchiformes). Hereditas 139:228–231
Moran P, Martinez JL, Garcia-Vasquez E, Pendas AM (1996) Sex linkage of 5S rDNA in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Cytogenet Cell Genet 75:145–150
Nederby-Nielsen J, Hallenberg G, Frederiksen S, Sorensen PD, Lomholt B (1993) Transcription of human 5S rRNA genes is influenced by an upstream DNA sequence. Nucleic Acid Res 26:3631–3636
Nelson JS (1994) Fishes of the world. 3rd ed. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Ota K, Tateno Y, Gojobori T (2003) Highly differentiated and conserved sex chromosome in fish species (Aulopus japonicus: Teleostei, Aulopidae). Gene 317:187–193
Okladnova O, Syagailo YV, Tranitz M, Stöber G, Riederer P, Mössner R, Lesch KP (1998) A promoter-associated polymorphic repeat modulates PAX-6 expression in human brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 248:402–405
Pearson CE, Sinden RR (1996) Alternative structures in duplex DNA formed within the trinucleotide repeats of the myotonic dystrophy and fragile X loci. Biochemistry 35:5041–5053
Pendas AM, Moran P, Freije JP, Garcia-Vasquez E (1994) Chromosomal mapping and nucleotide sequence of two tandem repeats of Atlantic salmon 5S rDNA. Cytogenet Cell Genet 67:31–36
Pieler T, Hamm J, Roeder RG (1987) The 5S gene internal control region is composed of three distinct sequence elements, organized as two functional domains with variable spacing. Cell 41:91–100
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:917–818
Qi GR, Cao GJ, Jiang P, Feng XL, Gu XR (1988) Studies on the sites expressing evolutionary changes in the structure of eukaryotic 5S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Evol 27:336–340
Robles F, de la Herran R, Ludwig A, Rejon CR, Rejon MR, Garrido-Ramos MA (2005) Genomic organization and evolution of the 5S ribosomal DNA in the ancient fish sturgeon. Genome 48:18–28
Rocco L, Russo C, Stingo V, Aprea G, Odierna G (1999) Characterisation of 5S rDNA in Gasterosteus aculeatus (Teleostei, Gasterosteidae). It J Zool 66:285–289
Rocco L, Costagliola D, Fiorillo M, Tinti F, Stingo V (2005) Molecular and chromosomal analysis of ribosomal cistrons in two cartilaginous fish, Taeniura lymma and Raja montagui (Chondrichthyes, Batoidea). Genetica 123:245–253
Roest Crollius H, Jaillon O, Bernot A, Dasilva C, Bouneau L, Fischer C, Fizames C, Wincker P, Brottier P, Quetier F, Saurin W, Weissenbach J (2000) Estimate of human gene number provided by genome-wide analysis using Tetraodon nigroviridis DNA sequence. Nature Genet 25:235–238
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (1998) Primer 3. Code available at http://www.genome.wi.mit.edu/genome_software/other/primer3.html
Sajdak SL, Reed KM, Phillips RB (1998) Intraindividual and interspecies variation in the 5S rDNA of coregonid fish. J Mol Evol 46:680–688
Schlötter C, Tautz D (1992) Slippage synthesis of simple sequence DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 20:211–215
Sedman IE, Shostak NG, Kuprianova NS, Serenkova TI, Fel’gengauer PE, Gimalov F, Lind AI, Timofeyeva MY, Baev AA (1989) Intragenomic polymorphism of the primary structure of 5S rRNA gene variants of the loach (Misgurnus fossilis L.). Determination of the transcriptional activity Mol Biol (Mosk) 23:1295–1308
Sola L, Rossi AR, Annesi F, Gornung E (2003) Cytogenetic studies in Sparus auratus (Pisces, Perciformes): molecular organization of 5S rDNA and chromosomal mapping of 5S and 45S ribosomal genes and of telomeric repeats. Hereditas 139:232–236
Stehmann M, Burkel DL (1984) Rajidae. In: Whitehead PJP, Bauchot ML, Hureau JC, Nielsen J, Tortonese E (eds). Fishes of the North-eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean. Vol. 1. UNESCO, Paris, pp. 163–196
Strimmer K, Von Haesler A (1996) Quartet puzzling: a quarted maximum likelihood method for reconstructing tree topologies. Mol Biol Evol 13:964–969
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*: Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods), Version 4.0b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acid Res 24:4876–4882
Tigano C, Rocco L, Ferrito V, Costagliola D, Pappalardo AM, Stingo V (2004) Chromosomal mapping and molecular characterization of ribosomal RNA genes in Lebias fasciata (Teleostei, Cyprinodontidae). Genetica 121:95–100
Tinti F, Ungaro N, Pasolini P, De Panfilis M, Garoia F, Guarniero I, Sabelli B, Marano G, Piccinetti C (2003) Development of molecular and morphological markers to improve species-specific monitoring and systematics of North-East Atlantic and Mediterranean skates (Rajiformes). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 288:149–165
Valsecchi E, Pasolini P, Bertozzi M, Garoia F, Ungaro N, Vacchi M, Sabelli B, Tinti F (2005) Rapid Miocene-Pliocene dispersal and evolution of rajid fauna of the Mediterranean Sea as inferred by mitochondrial gene variation. J Evol Biol 18:436–446
Wasko AP, Martins C, Wright JM, Galetti PM (2001) Molecular organization of 5S rDNA in fishes of the genus Brycon. Genome 44:893–902
Wegnez M, Denis H, Mazabraud A, Clerot JC (1978) RNA accumulation during oogenesis of the dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula. Biochemical research on oogenesis. Dev Biol 62:99–111
Winnepennickx B, Backeljau T, De Wachter R (1993) Extraction of high molecular weight DNA from Mollusks. Trends Genet 9:407
Xu G, Goodridge AG (1998) A CT repeat in the promoter of the chicken malic enzyme gene is essential for function at an alternative transcription start site. Arch Biochem Biophys 358:83–91
Young ET, Sloan JS, van Riper K (2000) Trinucleotide repeats are clustered in regulatory genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 154:1053–1068
Zheng M, Huang X, Smith GK, Yang X, Gao X (1996) Genetically unstable CXG repeats are structurally dynamic and have a high propensity for folding. An NMR and UV spectroscopic study. J Mol Biol 264:323–336
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciated suggestions and criticisms of both anonymous reviewers, which effectively improved the claim and the quality of the manuscript. We also thank T. Labriola and M. Landi for the helpful assistance in editing the manuscript. This work was supported by grants “Canziani” and “Biodiversity” given by the University of Bologna to FT and PP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Reviewing Editor: Dr. Rafael Zardoya]
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pasolini, P., Costagliola, D., Rocco, L. et al. Molecular Organization of 5S rDNAs in Rajidae (Chondrichthyes): Structural Features and Evolution of Piscine 5S rRNA Genes and Nontranscribed Intergenic Spacers. J Mol Evol 62, 564–574 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0118-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0118-z