Abstract
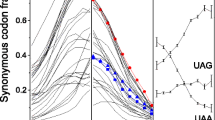
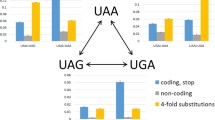
It is well known that stop codons play a critical role in the process of protein synthesis. However, little effort has been made to investigate whether stop codon usage exhibits biases, such as widely seen for synonymous codon usage. Here we systematically investigate stop codon usage bias in various eukaryotes as well as its relationships with its context, GC3 content, gene expression level, and secondary structure. The results show that there is a strong bias for stop codon usage in different eukaryotes, i.e., UAA is overrepresented in the lower eukaryotes, UGA is overrepresented in the higher eukaryotes, and UAG is least used in all eukaryotes. Different conserved patterns for each stop codon in different eukaryotic classes are found based on information content and logo analysis. GC3 contents increase with increasing complexity of organisms. Secondary structure prediction revealed that UAA is generally associated with loop structures, whereas UGA is more uniformly present in loop and stem structures, i.e., UGA is less biased toward having a particular structure. The stop codon usage bias, however, shows no significant relationship with GC3 content and gene expression level in individual eukaryotes. The results indicate that genomic complexity and GC3 content might contribute to stop codon usage bias in different eukaryotes. Our results indicate that stop codons, like synonymous codons, exhibit biases in usage. Additional work will be needed to understand the causes of these biases and their relationship to the mechanism of protein termination.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
H Akashi (1994) ArticleTitleSynonymous codon usage in Drosophila melanogaster: Natural selection and translational accuracy Genetics 136 927–935 Occurrence Handle8005445
S Arhondakis F Auletta G Torelli G D’Onofrio (2004) ArticleTitleBase composition and expression level of human genes Gene 325 165–169 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.gene.2003.10.009 Occurrence Handle14697521
B Bonetti L Fu J Moon DM Bedwell (1995) ArticleTitleThe efficiency of translation termination is determined by a synergistic interplay between upstream and downstream sequences insaccharomyces cerevisiae J Mol Biol 251 334–345 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jmbi.1995.0438 Occurrence Handle7650736
C Brown P Stockwell C Trotman W Tate (1990) ArticleTitleSequence analysis suggests that tetra-nucleotides signal the termination of protein synthesis in eukaryotes Nucleic Acids Res 18 6339–6345 Occurrence Handle2123028
M Cassan JP Rousset (2001) ArticleTitleUAG readthrough in mammalian cells: Effect of upstream and downstream stop codon contexts reveal different signals BMC Mol Biol 2 3 Occurrence Handle10.1186/1471-2199-2-3 Occurrence Handle11242562
A Coghlan KH Wolfe (2000) ArticleTitleRelationship of codon bias to mRNA concentration and protein length in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Yeast 16 1131–1145 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1097-0061(20000915)16:12<1131::AID-YEA609>3.0.CO;2-F Occurrence Handle10953085
GE Crooks G Hon J-M Chandonia SE Brenner (2004) ArticleTitleWebLogo: A sequence logo Generator Genome Res 14 1188–1190 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gr.849004 Occurrence Handle15173120
J Duan MA Antezana (2003) ArticleTitleMammalian mutation pressure, synonymous codon choice, and mRNA degradation J Mol Evol 57 694–701 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00239-003-2519-1 Occurrence Handle14745538
L Duret (2002) ArticleTitleEvolution of synonymous codon usage in metazoans Curr Opin Genet Dev 12 640–649 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0959-437X(02)00353-2 Occurrence Handle12433576
L Duret D Mouchiroud (2002) ArticleTitleExpression pattern and, surprisingly, gene length shape codon usage in Caenorhabditis, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96 4482–4487 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.96.8.4482
JH Gillespie (2000) ArticleTitleGenetic drift in an infinite population. The pseudohitchhiking Model Genetics 155 909–919 Occurrence Handle10835409
JT Herbeck DP Wall JJ Wernegreen (2003) ArticleTitleGene expression level influences amino acid usage, but not codon usage, in the tsetse fly endosymbiont Wigglesworthia Microbiology 149 2585–2596 Occurrence Handle10.1099/mic.0.26381-0 Occurrence Handle12949182
IL Hofacker (2003) ArticleTitleVienna RNA secondary structure server Nucleic Acids Res 31 3429–3431 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/gkg599 Occurrence Handle12824340
S Karlin J Mrazek AM Campbell (1998) ArticleTitleCodon usages in different gene classes of the Escherichia coli genome Mol Microbiol 29 1341–1355 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.01008.x Occurrence Handle9781873
S Karlin J Mrazek A Campbell D Kaiser (2001) ArticleTitleCharacterizations of highly expressed genes of four fast-growing bacteria J Bacteriol 183 5025–5040 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JB.183.17.5025-5040.2001 Occurrence Handle11489855
L Kisselev M Ehrenberg L Frolova (2003) ArticleTitleNew EMBO member’s review: Termination of translation: Interplay of mRNA, rRNAs and release factors? EMBO J 22 175–182 Occurrence Handle10.1093/emboj/cdg017 Occurrence Handle12514123
RM Kliman J Hey (1994) ArticleTitleThe effects of mutation and natural selection on codon bias in the genes of Drosophila Genetics 137 1049–1056 Occurrence Handle7982559
RM Kliman N Irving M Santiago (2003) ArticleTitleSelection conflicts, gene expression, and codon usage trends in yeast J Mol Evol 57 98–109 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00239-003-2459-9 Occurrence Handle12962310
Knight RD, Freeland SJ, Landweber LF (2001) A simple model based on mutation and selection explains trends in codon and amino-acid usage and GC composition within and across genomes. Genome Biol 2: research 0010.1-10.13.
D Konuo M Li (2002) ArticleTitleCorrelations between mRNA expression levels and GC contents of coding and untranslated regions of genes in rodents J Mol Evol 54 35–41 Occurrence Handle11734896
X Maside AW Lee B Charlesworth (2004) ArticleTitleSelection on codon usage in Drosophila Americana Curr Biol 20 150–154 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.cub.2003.12.055
K McCaughan C Brown M Dalphin M Berry W Tate (1995) ArticleTitleTranslational termination efficiency in mammals is influenced by the base following the stop codon Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 6 5431–5435
S Mottagui-Tabar LA Isaksson (1997) ArticleTitleOnly the last amino acids in the nascent peptide influence translation termination in Escherichia coli genes FEBS Lett 414 165–170 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-5793(97)00978-2 Occurrence Handle9305752
S Mottagui-Tabar MF Tuite LA Isaksson (1998) ArticleTitleThe influence of 5′ codon context on translation termination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Eur J Biochem 257 249–254 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2570249.x Occurrence Handle9799126
O Namy I Hatin J-P Rousset (2001) ArticleTitleImpact of the six nucleotides downstream of the stop codon on translation termination EMBO Rep 2 787–793 Occurrence Handle10.1093/embo-reports/kve176 Occurrence Handle11520858
G Pesole S Liuni G Grillo F Licciulli F Mignone C Gissi C Saccone (2002) ArticleTitleUTRdb and UTRsite: specialized databases of sequences and functional elements of 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions of eukaryotic mRNAs. Update 2002 Nucleic Acids Res 30 335–340 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/30.1.335 Occurrence Handle11752330
P Rice I Longden A Bleasby (2000) ArticleTitleEMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite Trends Genet 16 276–277 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-9525(00)02024-2 Occurrence Handle10827456
TD Schneider GD Stormo L Gold A Ehrenfeuch (1986) ArticleTitleThe information content of binding sites on nucleotide sequences J Mol Biol 188 415–431 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-2836(86)90165-8 Occurrence Handle3525846
P Sharp W Li (1987) ArticleTitleThe codon adaptation index—a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications Nucleic Acids Res 15 1281–1295 Occurrence Handle3547335
P Sharp T Tuohy K Mosurski (1986) ArticleTitleCodon usage in yeast: cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes Nucleic Acids Res 14 5125–5143 Occurrence Handle3526280
PM Sharp M Bulmer (1988) ArticleTitleSelective differences among translation termination codons Gene 63 141–145 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-1119(88)90553-7 Occurrence Handle3133285
G Stoesser W Baker A Broek Particlevan den M Garcia-Pastor C Kanz T Kulikova R Leinonen Q Lin V Lombard R Lopez R Mancuso F Nardone P Stoehr MA Tuli K Tzouvara R Vaughan (2003) ArticleTitleThe EMBL Nucleotide Sequence Database: major new developments Nucleic Acids Res 31 17–22 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/gkg021 Occurrence Handle12519939
AI Su MP Cooke KA Ching Y Hakak JR Walker T Wiltshire AP Orth RG Vega LM Sapinoso A Moqrich A Patapoutian GM Hampton PG Schultz JB Hogenesch (2002) ArticleTitleLarge-scale analysis of the human and mouse transcriptomes Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99 4465–4470 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.012025199 Occurrence Handle11904358
N Sueoka Y Kawanishi (2000) ArticleTitleDNA G+C content of the third codon position and codon usage biases of human genes Gene 261 53–62 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00480-7 Occurrence Handle11164037
WP Tate ES Poole ME Dalphin LL Major DJG Crawford SA Mannering (1996) ArticleTitleThe translational stop signal: Codon with a context, or extended factor recognition element? Biochimie 78 945–952 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0300-9084(97)86716-8 Occurrence Handle9150871
AE Vinogradov (2003) ArticleTitleIsochores and tissue-specificity Nucleic Acids Res 31 5212–5220 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/gkg699 Occurrence Handle12930973
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 863 Hi-Tech Program of China (Grant 2002AA234021), the State Key Program of Basic Research of China (Grant 2002CB512800), and the Sci & Tech Committee of Shanghai (Grant K02D 105501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Reviewing Editor: Dr. Manyuan Long]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Chen, M., Xu, J. et al. Relationships Among Stop Codon Usage Bias, Its Context, Isochores, and Gene Expression Level in Various Eukaryotes. J Mol Evol 61, 437–444 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-004-0277-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-004-0277-3