Abstract
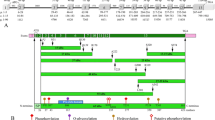
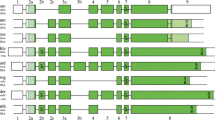
An evolutionary analysis of mammalian amelogenin, the major protein of forming enamel, was conducted by comparison of 26 sequences (including 14 new ones) representative of the main mammalian lineages. Amelogenin shows highly conserved residues in the hydrophilic N- and C-terminal regions. The central hydrophobic region (most of exon 6) is more variable, but it has conserved a high amount of proline and glutamine located in triplets, PXQ, indicating that these residues play an important role. This region evolves more rapidly, and is less constrained, than the other well-conserved regions, which are subjected to strong constraints. The comparison of the substitution rates in relation to the CpG richness confirmed that the highly conserved regions are subjected to strong selective pressures. The amino acids located at important sites and the residues known to lead to amelogenesis imperfecta when substituted were present in all sequences examined. Evolutionary analysis of the variable region of exon 6 points to a particular zone, rich in either amino acid insertion or deletion. We consider this region a hot spot of mutation for the mammalian amelogenin. In this region, numerous triplet repeats (PXQ) have been inserted recently and independently in five lineages, while most of the hydrophobic exon 6 region probably had its origin in several rounds of triplet insertions, early in vertebrate evolution. The putative ancestral DNA sequence of the mammalian amelogenin was calculated using a maximum likelihood approach. The putative ancestral protein was composed of 177 residues. It already contained all important amino acid positions known to date, its hydrophobic variable region was rich in proline and glutamine, and it contained triplet repeats PXQ as in the modern sequences.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
MJ Aldred PJ Crawford E Roberts NS Thomas (1992) ArticleTitleIdentification of a nonsense mutation in the amelogenin gene (AMELX) in a family with X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta (AIH1) Hum Genet 96 413–416
T Aoba (1996) ArticleTitleRecent observations on enamel crystal formation during mammalian amelogenesis Anat Rec 245 208–218
T Aoba EC Moreno M Kresak T Tanabe (1989) ArticleTitlePossible roles of partial sequences at N- and C-termini of amelogenin in protein-enamel mineral interaction J Dent Res 68 1331–1336
O Baba N Takahashi T Terashima W Li PK DenBesten Y Takano (2002) ArticleTitleExpression of alternatively spliced RNA transcripts of amelogenin gene exons 8 and 9 and its end products in the rat incisor J Histochem Cytochem 50 1229–1236
WA Bonass J Kirkham SJ Brookes RC Shore C Robinson (1994) ArticleTitleIsolation and characterisation of an alternatively-spliced rat amelogenin cDNA: LRAP—A highly conserved, functional alternatively-spliced amelogenin? Biochim Biophys Acta 1219 690–692
M Bulmer KH Wolfe PM Sharp (1991) ArticleTitleSynonymous nucleotide substitution rates in mammalian genes: Implications for the molecular clock and the relationship of mammalian orders Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88 5974–5978
B Charlesworth (1991) ArticleTitleThe evolution of sex chromosomes Science 251 IssueID4997 1030–1033
PM Collier JJ Sauk SJ Rosenbloom ZA Yuan CW Gibson (1997) ArticleTitleAn amelogenin gene defect associated with human X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta Arch Oral Biol 42 IssueID3 235–242
RI Couwenhoven ML Snead (1994) ArticleTitleEarly determination and permissive expression of amelogenin transcription during mouse mandibular first molar development Dev Biol 164 290–299
S Delgado (2002) L’amélogénine, protéine majeure de l’émail dentaire. Origine, analyses évolutive et phylogénétique chez les amniotes et recherche de son expression lors de la formation des dents de Chalcides viridanus (Squamate, Scincidé). PhD thesis University Paris VII Paris
S Delgado D Casane L Bonnaud M Laurin JY Sire M Girondot (2001) ArticleTitleMolecular evidence for Precambrian origin of amelogenin, the major protein of vertebrate enamel Mol Biol Evol 18 2146–2153
F Delsuc M Scally O Madsen MJ Stanhope WW Jong Particlede (2002) ArticleTitleMolecular phylogeny of living xenarthrans and the impact of characters and taxon sampling on the placental tree rooting Mol Biol Evol 19 1656–1671 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnvFSluro%3D Occurrence Handle12270893
D Deutsch (1989) ArticleTitleStructure and function of enamel gene products Anat Rec 224 189–210
D Deutsch J Catalano-Sherman L Dafni S David A Palmon (1995) ArticleTitleEnamel matrix proteins and ameloblast biology Connect Tissue Res 32 97–107
T Diekwisch S David P Bringas V Santos HC Slavkin (1993) ArticleTitleAntisense inhibition of AMEL translation demonstrates supramolecular control for enamel HAP crystal growth during embryonic mouse molar development Development 117 471–482
S Easteal (1999) ArticleTitleMolecular evidence for the early divergence of placental mammals Bioessays 21 1052–1058
JF Elder BJ Turner (1995) ArticleTitleConcerted evolution of repetitive DNA—sequences in eukaryotes Q Rev Biol 70 297–320 Occurrence Handle10.1086/419073 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXksFGrurY%3D Occurrence Handle7568673
AG Fincham J Moradian-Oldak (1993) ArticleTitleAmelogenin post-translational modifications: Carboxy-terminal processing and the phosphorylation of bovine and porcine “TRAP” and “LRAP” amelogenins Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197 248–255
AG Fincham J Moradian-Oldak (1995) ArticleTitleRecent advances in amelogenin biochemistry Connect Tissue Res 32 119–124
AG Fincham AB Belcourt JD Termine WT Butler WC Cothran (1983) ArticleTitleAmelogenins. Sequence homologies in enamel-matrix proteins from three mammalian species Biochem J 211 149–154
AG Fincham Y Hu EC Lau HC Slavkin ML Snead (1991) ArticleTitleAmelogenin post-secretory processing during biomineralization in the postnatal mouse molar tooth Arch Oral Biol 36 305–317
AG Fincham J Moradian-Oldak JP Simmer P Sarte EC Lau T Diekwisch HC Slavkin (1994) ArticleTitleSelf-assembly of a recombinant amelogenin protein generates supramolecular structures J Struct Biol 112 103–109
M George OA Ryder (1986) ArticleTitleMitochondrial DNA evolution in the genus Equus Mol Biol Evol 3 IssueID6 535–546
C Gibson E Golub R Herold M Risser W Ding H Shimokawa M Young J Termine J Rosenbloom (1991) ArticleTitleStructure and expression of the bovine amelogenin gene Biochemistry 30 1075–1079
CW Gibson U Kucich P Collier G Shen S Decker M Bashir J Rosenbloom (1994) ArticleTitleAnalysis of amelogenin proteins using monospecific antibodies to defined sequences Connect Tissue Res 32 109–114
M Girondot J-Y Sire (1998) ArticleTitleEvolution of the amelogenin gene in toothed and tooth-less vertebrates Eur J Oral Sci 106 IssueIDSuppl 1 501–508
SR Greene ZA Yuan JT Wright H Amjad WR Abrams JA Buchanan DI Trachtenberg CW Gibson (2002) ArticleTitleA new frameshift mutation encoding a truncated amelogenin leads to X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta Arch Oral Biol 47 211–217
PS Hart MJ Aldred PJM Crawford NJ Wright TC Hart JT Wright (2002a) ArticleTitleAmelogenesis imperfecta phenotype-genotype correlations with two amelogenin gene mutations Arch Oral Biol 47 261–265
PS Hart TC Hart JP Simmer JT Wright (2002b) ArticleTitleA nomenclature for X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta Arch Oral Biol 47 255–260
AM Hoang RJ Klebe B Steffensen OH Ryu JP Simmer DL Cochran (2002) ArticleTitleAmelogenin is a cell adhesion protein J Dent Res 81 497–500
CC Hu C Zhang Q Qian OH Ryu J Moradian-Oldak AG Fincham JP Simmer (1996a) ArticleTitleCloning, DNA sequence, and alternative splicing of opossum amelogenin mRNAs J Dent Res 75 1728–1734
CC Hu JD Bartlett CH Zhang Q Qian OH Ryu JP Simmer (1996b) ArticleTitleCloning, cDNA sequence, and alternative splicing of porcine amelogenin mRNAs J Dent Res 75 1735–1741
CC Hu JP Simmer JD Bartlett Q Qian C Zhang OH Ryu J Xue M Fukae T Uchida M Mac Dougall (1998) ArticleTitleMurine enamelin: cDNA and derived protein sequences Connect Tissue Res 39 47–61
K Ishibashi T Iino F Sekiguchi (1990) ArticleTitleAmelogenesis imperfecta, a new dental mutation in rats Lab Anim Sci 40 16–20
M Ishiyama M Mikami H Shimokawa S Oida (1998) ArticleTitleAmelogenin protein in tooth germs of the snake Elaphe quadrivirgata, immunohistochemistry, cloning and cDNA sequence Arch Histol Cytol 61 467–474
M Iwase Y Satta N Takahata (2001) ArticleTitleSex-chromosomal differentiation and amelogenin genes in mammals Mol Biol Evol 18 1601–1603
M Iwase Y Satta Y Hirai H Hirai H Imai N Takahata (2003) ArticleTitleThe amelogenin loci span an ancient pseudoautosomal boundary in diverse mammalian species Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100 5258–5263
S Jamain M Girondot P Leroy M Clergue H Quach M Fellous T Bourgeron (2002) ArticleTitleTransduction of the human gene AHCP by endogenous retrovirus during primate evolution Genomics 78 38–45
A Janke O Magnell G Wieczorek M Westerman U Arnason (2002) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic analysis of 18S rRNA and the mitochondrial genomes of the wombat, Vombatus ursinus, and the spiny anteater, Tachyglossus aculeatus: Increased support for the Marsupionta hypothesis J Mol Evol 54 71–80
M Lagerstrom N Dahl Y Nakahori Y Nakagome B Backman U Landegren U Pettersson (1991) ArticleTitleA deletion in the amelogenin gene (AMG) causes X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta (AIH1) Genomics 10 971–975 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0888-7543(91)90187-J
BT Lahn NM Pearson K Jegalian (2001) ArticleTitleThe human Y chromosome, in the light of evolution Nat Rev Genet 2 207–216
NJ Lench GB Winter (1995) ArticleTitleCharacterisation of molecular defects in X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta (AIH1) Hum Mut 5 251–259
NJ Lench AH Brook GB Winter (1994) ArticleTitleSSCP detection of a nonsense mutation in exon 5 of the amelogenin gene (AMGX) causing X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta (AIH1) Hum Mol Genet 3 827–828
G Levinson GA Gutman (1987) ArticleTitleSlipped-strandmispairing: A major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution Mol Biol Evol 4 203–221 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXksFejsLw%3D Occurrence Handle3328815
R Li W Li PK DenBesten (1995) ArticleTitleAlternative splicing of amelogenin mRNA from rat incisor ameloblasts J Dent Res 74 1880–1885
W Li C Mathews C Gao PK DenBesten (1998) ArticleTitleIdentification of two additional exons at the 3′ end of the amelogenin gene Arch Oral Biol 43 497–504
DQ Liao (1999) ArticleTitleConcerted evolution: Molecular mechanism and biological implications Am J Hum Genet 64 24–30
O Madsen M Scally CJ Douady DJ Kao RW DeBry R Adkins HM Amrine MJ Stanhope WW de Jong MS Springer (2001) ArticleTitleParallel adaptive radiations in two major clades of placental mammals Nature 409 610–614 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35054544 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhtVygur4%3D Occurrence Handle11214318
AK Mathur PD Polly (2000) ArticleTitleThe evolution of enamel microstructure: How important is amelogenin? J Hum Evol 7 23–42
T Miyata H Hayashida K Kuma K Mitsuyasu T Yasunaga (1987) ArticleTitleMale-driven molecular evolution: A model and nucleotide sequence analysis Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 52 863–867
J Moradian-Oldak JP Simmer EC Lau PE Sarte HC Slavkin AG Fincham (1994a) ArticleTitleDetection of monodisperse aggregates of a recombinant amelogenin by dynamic light scattering Biopolymers 34 1339–1347
J Moradian-Oldak JP Simmer PE Sarte M Zeichner-David AG Fincham (1994b) ArticleTitleSpecific cleavage of a recombinant murine amelogenin at the carboxy-terminal region by a proteinase fraction isolated from developing bovine tooth enamel Arch Oral Biol 39 647–656
J Moradian-Oldak JP Simmer EC Lau T Diekwisch HC Slavkin AG Fincham (1995) ArticleTitleA review of the aggregation properties of a recombinant amelogenin Connect Tissue Res 32 125–130
J Moradian-Oldak M Iijima N Bouropoulos HB Wen (2003) ArticleTitleAssembly of amelogenin proteolytic products and control of octocalcium phosphate crystal morphology Connect Tissue Res 44 IssueIDSuppl 1 58–64
WJ Murphy E Elzirik WE Johnson YP Zhang OA Ryder SJ O’Brien (2001) ArticleTitleMolecular phylogenetics and the origin of placental mammals Nature 409 614–618 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35054550 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhtVylt7Y%3D Occurrence Handle11214319
T Ohta (2000) ArticleTitleEvolution of gene families Gene 259 45–52 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitV2msw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11163960
ML Paine DH Zhu W Luo P Bringas SuffixJr M Goldberg SN White YP Lei M Sarikaya HK Fong ML Snead (2000) ArticleTitleEnamel biomineralization defects result from alterations to amelogenin self-assembly J Struct Biol 132 191–200
ML Paine H-J Wang ML Snead (2003a) ArticleTitleAmelogenin self-assembly and the role of the proline located within the carboxyl-telopeptide Connect Tissue Res 44 IssueIDSuppl 1 52–57
ML Paine W Luo D-H Zhu P Bringas SuffixJr ML Snead (2003b) ArticleTitleFunctional domains for amelogenin revealed by compound genetic defects J Bone Min Res 18 466–472
L Quintana-Murci S Jamain M Fellous (2001) ArticleTitleOrigine et évolution des chromosomes sexuels des mammifères CR Acad Sci III 324 1–11
RM Ravindranath J Moradian-Oldak AG Fincham (1999) ArticleTitleTyrosyl motif in amelogenins binds N-acetyl-D-glucosamine J Biol Chem 274 2464–2471
RMH Ravindranath W Tam P Nguyen AG Fincham (2000) ArticleTitleThe enamel protein amelogenin binds to the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-mimicking peptide motif of cytokeratins J Biol Chem 275 39654–39661
RMH Ravindranath W Tam P Bringas V Santos AG Fincham (2001) ArticleTitleAmelogenin-cytokeratin 14 interaction in ameloblasts during enamel formation J Biol Chem 276 36586–36597
RMH Ravindranath RM Basilrose NH Ravindranath B Vaitheesvaran (2003) ArticleTitleAmelogenin interacts with cytokeratin-5 in ameloblasts during enamel growth J Biol Chem 278 20293–20302
T Rowe (1999) ArticleTitleAt the roots of the mammalian family tree Nature 398 283–284 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXitlCnt7w%3D Occurrence Handle10192326
EC Salido PH Yen K Koprivnikar LC Yu LJ Shapiro (1992) ArticleTitleThe human enamel protein gene amelogenin is expressed from both the X and the Y chromosomes [see comments] Am J Hum Genet 50 303–316 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXktVehu7o%3D Occurrence Handle1734713
S Sasaki H Shimokawa (1995) ArticleTitleThe amelogenin gene Int J Dev Biol 39 127–133
JP Simmer (1995) ArticleTitleAlternative splicing of amelogenins Connect Tissue Res 32 131–136
JP Simmer CC Hu EC Lau P Sarte HC Slavkin AG Fincham (1994) ArticleTitleAlternative splicing of the mouse amelogenin primary RNA transcript Calcif Tissue Int 55 302–310
W Stephan (1989) ArticleTitleTandem-repetitive noncoding DNA: Forms and forces Mol Biol Evol 6 198–212
F Tajima M Nei (1993) ArticleTitleUnbiased estimation of evolutionary distance between nucleotide sequences Mol Biol Evol 10 677–688
JD Termine AB Belcourt PJ Christner KM Conn MU Nylen (1980) ArticleTitleProperties of dissociatively extracted fetal tooth matrix proteins. I. Principal molecular species in developing bovine enamel J Biol Chem 255 9760–9768
S Toyosawa C O’HUigin F Figueroa H Tichy J Klein (1998) ArticleTitleIdentification and characterization of amelogenin genes in monotremes, reptiles, and amphibians Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95 13056–13061
A Veis (2003) ArticleTitleAmelogenin gene splice products: Potential signaling molecules Cell Mol Life Sci 60 38–55
A Veis K Tompkins K Alvares K Wei L Wang XS Wang AG Brownell SM Jengh KE Healy (2000) ArticleTitleSpecific amelogenin gene splice products have signaling effects on cells in culture and in implants in vivo J Biol Chem 275 41263–412672
C Vila P Savolainen JE Maldonado IR Amorin JE Rice RL Honeycutt KA Candall J Lundeberg RK Wayne (1997) ArticleTitleMultiple and ancient origins of the domestic dog Science 276 IssueID5319 1687–1689
RK Wayne B Valkenburgh ParticleVan SJ O’brien (1991) ArticleTitleMolecular distance and divergence time in carnivores and primates Mol Biol Evol 8 IssueID3 297–319
HB Wen AG Fincham J Moradian-Oldak (2001) ArticleTitleProgressive accretion of amelogenin molecules during nanospheres assembly revealed by atomic force microscopy Matrix Biol 20 387–395
MP Williamson (1994) ArticleTitleThe structure and function of proline-rich regions in proteins Biochem J 297 249–260
DE Wilson DM Reeder (1993) Mammal species of the world Smithsonian Institution Press Washington, DC
JT Wright PS Hart MJ Aldred K Seow PJM Crawford SP Hong CW Gibson TC Hart (2003) ArticleTitleRelationship of phenotype and genotype in X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta Connect Tissue Res 44 IssueIDSuppl 1 72–78
Y Yamakoshi T Tanabe M Fukae M Shimizu (1994) ArticleTitlePorcine amelogenins Calc Tissue Int 54 69–75
K Yamamoto T Tsubota T Komatsu A Katayama T Murase I Kita T Kudo (2002) ArticleTitleSex identification of Japanese black bear, Ursus thibetanus japonicus, by PCR based on amelogenin gene J Vet Med Sci 64 505–508
Z Yang R Nielsen (1998) ArticleTitleSynonymous and nonsynonymous rate variation in nuclear genes of mammals J Mol Evol 46 409–418
ZA Yuan PM Collier J Rosenbloom CW Gibson (1997) ArticleTitleAnalysis of amelogenin mRNA during bovine tooth development Arch Oral Biol 41 205–213
ZA Yuan E Chen CW Gibson (2001) ArticleTitleModel system for evaluation of alternative splicing: Exon skipping DNA Cell Biol 20 807–813
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Prof. Ann Huysseune (Ghent University, Belgium) and to Dr. Caroline Gibson (University of Pennsylvania, USA) for their helpful remarks and suggestions. We are greatly indebted to the following colleagues for providing the material: Dr. F. Catzeflis (UMR 5554, Université de Montpellier 2, France), gray seal and one tamandua; Drs. F. Ollivet and A. Lécu (Zoo de Vincennes, Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle, France), Asiatic elephant, fennec fox, cheetah, pygmy hippopotamus, and Grevy’s zebra; Dr. W. Dabin (Muséum de la Rochelle, France), bottle-nosed dolphin; and Dr. G. Véron (Laboratoire de Zoologie, mammifères et oiseaux, Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle, France), common tree shrew, short-nosed fruit bat, Malayan flying lemur, western European hedgehog, Malayan pangolin, one tamandua, and three-toed sloth. Part of this project has been financially supported by the “GIS-Institut des maladies rares”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Reviewing Editor: Dr. Cecilia Saccone
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delgado, S., Girondot, M. & Sire, JY. Molecular Evolution of Amelogenin in Mammals. J Mol Evol 60, 12–30 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-003-0070-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-003-0070-8