Abstract
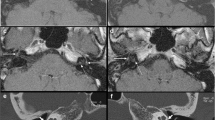
Our aim was to determine whether MRI reliably shows pathology in patients with active otosclerosis (otospongiosis). We studied five patients with clinical and audiometric signs of this disorder and positive findings on high-resolution CT and tympanocochlear scintigraphy. Contrast enhancement of otospongiotic lesions was found in all affected ears, and could be topographically related to demineralised otospongiotic foci on CT. In lesions in the lateral wall of the labyrinth MRI sometimes showed the pathology better than CT, where partial-volume effects could be troublesome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 April 1996 Accepted: 30 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziyeh, S., Berlis, A., Ross, U. et al. MRI of active otosclerosis. Neuroradiology 39, 453–457 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050445
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050445