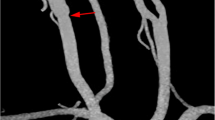
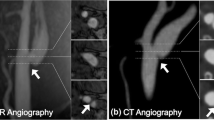
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to retrospectively analyze the ultrasonographic images of 46 cases of carotid web (CW) and summarize their manifestations to reduce the rate of misdiagnosis.
Methods
For the analysis of ultrasonic manifestations, 46 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of CW by digital subtraction angiography (DSA) and CT angiography (CTA) in our hospital from January 2015 to October 2020 were collected. The location and the morphology of CW, the presence of a plaque at the base and thrombus at the surrounding of the CW, and whether they resulted in arteriostenosis were discussed.
Results
The average age of 46 patients was 43.23 ± 4.89 years old and there were 18 males and 28 females. Fifteen patients were admitted with cerebral infarction. The CW was located at the initial segment of the internal carotid artery in 22 cases, the bifurcation of the carotid artery in 20 cases, and the common carotid artery in 4 cases. CW in 5 patients was longer than half of the artery diameter, two patients with “cliff-like” arteriostenosis, 29 patients with plaques, and 16 patients with thrombi. The CW grew in the direction of the blood flow without obvious fluttering. The CW has a higher display rate on the ultrasound longitudinal section than the transverse section.
Conclusion
We identified some typical ultrasound characteristics of CW. Recognizing them will improve diagnostic accuracy of CW by ultrasonography.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wirth FP, Miller WA, Russell AP (1981) Atypical fibromusclar hyperplasia Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 54:685–689
Kim SJ, Allen JW, Bouslama M et al (2019) Carotid webs in cryptogenic ischemic strokes: a matched case-control study. Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 28:104402
Joux J, Boulanger M, Jeannin S et al (2016) Association between carotid bulb diaphragm and ischemic stroke in young Afro-Caribbean patients: a population-based case-control study. Stroke 47:2641–2644
Lenck S, Labeyrie MA, Saint-Maurice JP et al (2014) Diaphragms of the carotid and vertebral arteries: an under-diagnosed cause of ischaemic stroke. Eur J Neurol 21:586–593
Joux J, Boulanger M, Jeannin S et al (2016) Association between carotid bulb diaphragm and ischemic stroke in young Afro-Caribbean patients: a population-based case-control study. Stroke 47:2641–2644
Haussen DC, Grossberg JA, Bouslama M et al (2017) Carotid web (intimal fibromuscular dysplasia) has high stroke recurrence risk and is amenable to stenting. Stroke 48:3134–3137
Pacei F, Quilici L, Mullin S et al (2018) Web of the carotid artery: an under-recognized cause of ischemic stroke. J Clin Neurosci 50:122–123
Grant EG, Benson CB, Moneta GL et al (2003) Carotid artery stenosis: gray-scale and Doppler US diagnosis—Society of Radiologists in Ultrasound Consensus Conference. Radiology 229:340–346
Connett MC, Lansche JM (1965) Fibromuscular hyperplasia of the internal carotid artery: report of a case. Ann Surg 162:59–62
Coutinho JM, Derkatch S, Potvin AR et al (2017) Carotid artery web and ischemic stroke: A case-control study. Neurology 88:65–69
Marc-Antoine L, Fabiola S, Vittorio C et al (2020) Carotid artery webs in embolic stroke of undetermined source with large intracranial vessel occlusion. Int J Stroke 0:1–4
Dan O, Toshiki E, Hiroyoshi S et al (2020) Carotid web leads to new thrombus formation: computational fluid dynamic analysis coupled with histological evidence. Acta Neurochirurgica 162:2583–2588
Compagne KCJ, Dilba K, Postema XEJ et al (2019) Flow patterns in carotid webs: a patient-based computational fluid dynamics study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 40:703–708
Yang J, Hua Y, Zhou FB et al (2020) Ultrasonographic features of carotid web. Chin J Med Ultrasound (Electronic Edition) 17:679–683
Luo XH, Li ZJ (2019) Ultrasonic risk stratification of carotid web. Echocardiography 36:2103–2107
Zhu CT, Li ZX, Ju Y et al (2020) Detection of carotid webs by CT Angiography, high-resolution MRI, and ultrasound. J Neuroimaging 00:1–5
Ning B, Zhang D, Sui BB et al (2020) Ultrasound imaging of carotid web with atherosclerosis plaque: a case report. J Med Case Rep 14:145
Labeyrie MA, Serrano F, Civelli V et al (2020) Carotid artery webs in embolic stroke of undetermined source with large intracranial vessel occlusion. Int J Stroke 0(0):1–4
Funding
This work was supported by the grants from Zhejiang Medicine and Health Sciences Research Fund (NO.2019RC077), Clinical Research Fund Project of Zhejiang Medical Association (NO.2019ZYC-A110) and Ningbo Natural Science Foundation (NO.202003N4225).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhifei Ben: Design, implementation and the writing of papers
Jue Wang: Implementation and data collection
Jingyong Zhan: Implementation and data collection
Saijun Chen: Design, implementation and paper revision
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared they do not have anything to disclose regarding conflict of interest with respect to this manuscript.
Ethical approval
The study was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben, Z., Wang, J., Zhan, J. et al. Ultrasonic characteristics of carotid webs. Neuroradiology 64, 95–98 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02757-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02757-0