Abstract
Purpose
Infarct growth and final infarct volume are established outcome modifiers following endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) for patients with large vessel occlusion stroke (LVO). Simple techniques for final infarct volume measurement are lacking, and therefore, we tested whether post-EVT ASPECTS can be used for prognostic evaluation after EVT.
Methods
Infarct size at baseline was measured in a prospective cohort of patients with LVO that underwent EVT with the ASPECTS score on admission non-contrast CT. Final infarct size was assessed with a post-EVT ASPECTS (ASPECTS-POST) obtained from a follow-up CT 24–72 h post-EVT. The best performing ASPECTS-POST was chosen based on comparisons of different thresholds. Outcome measures included survival rates and modified Rankin Score at 90 days.
Results
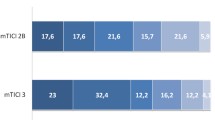
A total of 272 patients were included and 166 of them had an ASPECTS-POST ≥ 7. ASPECTS-POST ≥ 7 was associated with increased likelihood of favorable outcome at 90 days (67% vs. 21%, p < 0.001) with sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values of 86%, 58%, 61%, and 85%, respectively. On multivariate analysis, ASPECTS-POST ≥ 7 was found to be a significant modifier of favorable outcome (Odds Ratio [OR] 6.2, 95% confidence intervals [CI] 3.1–12.4) and survival (OR 5.8 95% CI 2.4–14.3).
Conclusion
ASPECTS can be rapidly and easily obtained from the post-EVT NCCT and ASPECTS-POST ≥ 7 correlates with good outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goyal M, Menon BK, van Zwam WH, Dippel DW, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, Davalos A, Majoie CB, van der Lugt A, de Miquel MA, Donnan GA, Roos YB, Bonafe A, Jahan R, Diener HC, van den Berg LA, Levy EI, Berkhemer OA, Pereira VM, Rempel J, Millan M, Davis SM, Roy D, Thornton J, Roman LS, Ribo M, Beumer D, Stouch B, Brown S, Campbell BC, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Saver JL, Hill MD, Jovin TG, collaborators H (2016) Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet. 387:1723–1731. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00163-X
Albers GW, Goyal M, Jahan R, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, Cognard C, Yavagal DR, Saver JL (2015) Relationships between imaging assessments and outcomes in solitaire with the intention for thrombectomy as primary endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 46(10):2786–2794. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.010710
Man S, Aoki J, Hussain MS, Wisco D, Tateishi Y, Toth G, Hui FK, Uchino K (2015) Predictors of infarct growth after endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 24(2):401–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.09.004
Marks MP, Lansberg MG, Mlynash M, Kemp S, McTaggart R, Zaharchuk G, Bammer R, Albers GW, Investigators D (2014) Correlation of AOL recanalization, TIMI reperfusion and TICI reperfusion with infarct growth and clinical outcome. J Neurointerv Surg 6(10):724–728. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010973
Al-Ajlan FS, Al Sultan AS, Minhas P, Assis Z, de Miquel MA, Millan M, San Roman L, Tomassello A, Demchuk AM, Jovin TG, Cuadras P, Davalos A, Goyal M, Menon BK, Investigators R (2018) Posttreatment infarct volumes when compared with 24-hour and 90-day clinical outcomes: insights from the REVASCAT randomized controlled trial. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 39(1):107–110. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5463
Al-Ajlan FS, Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Minhas P, Sabiq F, Assis Z, Willinsky R, Montanera WJ, Rempel JL, Shuaib A, Thornton J, Williams D, Roy D, Poppe AY, Jovin TG, Sapkota BL, Baxter BW, Krings T, Silver FL, Frei DF, Fanale C, Tampieri D, Teitelbaum J, Lum C, Dowlatshahi D, Shankar JJ, Barber PA, Hill MD, Menon BK, Investigators ET (2016) Intra-arterial therapy and post-treatment infarct volumes: insights from the ESCAPE randomized controlled trial. Stroke 47(3):777–781. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.012424
Albers GW, Goyal M, Jahan R, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, Cognard C, Cohen DJ, Hacke W, Jansen O, Jovin TG, Mattle HP, Nogueira RG, Siddiqui AH, Yavagal DR, Baxter BW, Devlin TG, Lopes DK, Reddy VK, de Rochemont RM, Singer OC, Bammer R, Saver JL (2016) Ischemic core and hypoperfusion volumes predict infarct size in SWIFT PRIME. Ann Neurol 79(1):76–89. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24543
Boers AMM, Jansen IGH, Brown S, Lingsma HF, Beenen LFM, Devlin TG, Roman LS, Heo JH, Ribo M, Almekhlafi MA, Liebeskind DS, Teitelbaum J, Cuadras P, du Mesnil de Rochemont R, Beaumont M, Brown MM, Yoo AJ, Donnan GA, Mas JL, Oppenheim C, Dowling RJ, Moulin T, Agrinier N, Lopes DK, Aja Rodriguez L, Compagne KCJ, Al-Ajlan FS, Madigan J, Albers GW, Soize S, Blasco J, Davis SM, Nogueira RG, Davalos A, Menon BK, van der Lugt A, Muir KW, Roos Y, White P, Mitchell PJ, Demchuk AM, van Zwam WH, Jovin TG, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Dippel DWJ, Campbell BCV, Guillemin F, Bracard S, Hill MD, Goyal M, Marquering HA, Majoie C (2019) Mediation of the relationship between endovascular therapy and functional outcome by follow-up infarct volume in patients with acute ischemic stroke. JAMA Neurol 76(2):194–202. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.3661
Zaidi SF, Aghaebrahim A, Urra X, Jumaa MA, Jankowitz B, Hammer M, Nogueira R, Horowitz M, Reddy V, Jovin TG (2012) Final infarct volume is a stronger predictor of outcome than recanalization in patients with proximal middle cerebral artery occlusion treated with endovascular therapy. Stroke 43(12):3238–3244. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.671594
Boers AM, Marquering HA, Jochem JJ, Besselink NJ, Berkhemer OA, van der Lugt A, Beenen LF, Majoie CB, Investigators MC (2013) Automated cerebral infarct volume measurement in follow-up noncontrast CT scans of patients with acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34(8):1522–1527. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3463
Krongold M, Almekhlafi MA, Demchuk AM, Coutts SB, Frayne R, Eilaghi A (2015) Final infarct volume estimation on 1-week follow-up MR imaging is feasible and is dependent on recanalization status. Neuroimage Clin 7:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2014.10.010
Yoo AJ, Chaudhry ZA, Nogueira RG, Lev MH, Schaefer PW, Schwamm LH, Hirsch JA, Gonzalez RG (2012) Infarct volume is a pivotal biomarker after intra-arterial stroke therapy. Stroke 43(5):1323–1330. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.639401
Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Zhang J, Buchan AM (2000) Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. ASPECTS Study Group. Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score. Lancet 355(9216):1670–1674
Bhuva P, Yoo AJ, Jadhav AP, Jovin TG, Haussen DC, Bonafe A, Budzik RJ, Yavagal DR, Hanel RA, Hassan AE, Ribo M, Cognard C, Sila CA, Morgan PM, Zhang Y, Shields R, Smith W, Saver JL, Liebeskind DS, Nogueira RG, Investigators DT (2019) Noncontrast computed tomography Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score may modify intra-arterial treatment effect in DAWN. Stroke:STROKEAHA118024583. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.024583
Broocks G, Rajput F, Hanning U, Faizy TD, Leischner H, Schon G, Gellissen S, Sporns P, Deb-Chatterji M, Thomalla G, Kemmling A, Fiehler J, Flottmann F (2018) Highest lesion growth rates in patients with hyperacute stroke. Stroke:STROKEAHA118023457. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023457
Hill MD, Demchuk AM, Goyal M, Jovin TG, Foster LD, Tomsick TA, von Kummer R, Yeatts SD, Palesch YY, Broderick JP, Investigators IMS (2014) Alberta Stroke Program early computed tomography score to select patients for endovascular treatment: Interventional Management of Stroke (IMS)-III Trial. Stroke 45(2):444–449. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003580
Park JS, Lee JM, Kwak HS, Chung GH (2019) Predictive value of CT angiography source image ASPECTS in patients with anterior circulation acute ischemic stroke after endovascular treatment: ultimate infarct size and clinical outcome. J Neurointerv Surg 11(4):342–346. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2018-014359
Yoo AJ, Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, van den Berg LA, Beumer D, Lingsma HF, Schonewille WJ, Sprengers ME, van den Berg R, van Walderveen MA, Beenen LF, Wermer MJ, Nijeholt GJ, Boiten J, Jenniskens SF, Bot JC, Boers AM, Marquering HA, Roos YB, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Dippel DW, van der Lugt A, van Zwam WH, Majoie CB, Investigators MC (2016) Effect of baseline Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score on safety and efficacy of intra-arterial treatment: a subgroup analysis of a randomised phase 3 trial (MR CLEAN). Lancet Neurol 15(7):685–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00124-1
Brott T, Adams HP Jr, Olinger CP, Marler JR, Barsan WG, Biller J, Spilker J, Holleran R, Eberle R, Hertzberg V et al (1989) Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: a clinical examination scale. Stroke 20(7):864–870
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 24(1):35–41
Higashida RT, Furlan AJ, Roberts H, Tomsick T, Connors B, Barr J, Dillon W, Warach S, Broderick J, Tilley B, Sacks D (2003) Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 34(8):e109–e137
Rankin J (1957) Cerebral vascular accidents in patients over the age of 60. II. Prognosis. Scott Med J 2(5):200–215. https://doi.org/10.1177/003693305700200504
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Davalos A, Guidetti D, Larrue V, Lees KR, Medeghri Z, Machnig T, Schneider D, von Kummer R, Wahlgren N, Toni D, Investigators E (2008) Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 359(13):1317–1329. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0804656
Broocks G, Kniep H, Schramm P, Hanning U, Flottmann F, Faizy T, Schonfeld M, Meyer L, Schon G, Aulmann L, Machner B, Royl G, Fiehler J, Kemmling A (2019) Patients with low Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) but good collaterals benefit from endovascular recanalization. J Neurointerv Surg 12:747–752. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-015308
Baird AE, Lovblad KO, Dashe JF, Connor A, Burzynski C, Schlaug G, Straroselskaya I, Edelman RR, Warach S (2000) Clinical correlations of diffusion and perfusion lesion volumes in acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 10(6):441–448. https://doi.org/10.1159/000016105
Lovblad KO, Baird AE, Schlaug G, Benfield A, Siewert B, Voetsch B, Connor A, Burzynski C, Edelman RR, Warach S (1997) Ischemic lesion volumes in acute stroke by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging correlate with clinical outcome. Ann Neurol 42(2):164–170. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410420206
Albers GW, Wald MJ, Mlynash M, Endres J, Bammer R, Straka M, Maier A, Hinson HE, Sheth KN, Taylor Kimberly W, Molyneaux BJ (2019) Automated calculation of Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score: validation in patients with large hemispheric infarct. Stroke 50(11):3277–3279. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026430
Reznik ME, Yaghi S, Jayaraman MV, McTaggart RA, Hemendinger M, Mac Grory BC, Burton TM, Cutting SM, Siket MS, Madsen TE, Thompson BB, Wendell LC, Mahta A, Potter NS, Furie KL (2018) Baseline NIH Stroke Scale is an inferior predictor of functional outcome in the era of acute stroke intervention. Int J Stroke 13(8):806–810. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747493018783759
King S, Khatri P, Carrozella J, Spilker J, Broderick J, Hill M, Tomsick T (2007) Anterior cerebral artery emboli in combined intravenous and intra-arterial rtPA treatment of acute ischemic stroke in the IMS I and II trials. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28(10):1890–1894. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A0702
Funding
This study was supported in part by the Peritz and Chantal Scheinberg Cerebrovascular Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not obtained from all individual participants included in the study because the IRB approved a retrospective analysis of anonymized data without the need to obtain informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leker, R.R., Honig, A., Filioglo, A. et al. Post-stroke ASPECTS predicts outcome after thrombectomy. Neuroradiology 63, 769–775 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02576-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-020-02576-9