Abstract
Introduction
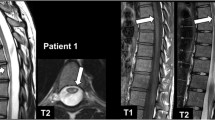
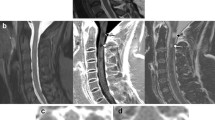
In multiple sclerosis (MS), spinal cord imaging can help in diagnosis and follow-up evaluation. However, spinal cord magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is technically challenging, and image quality, particularly in the axial plane, is typically poor compared to brain MRI. Because gradient-recalled echo (GRE) images might offer improved contrast resolution within the spinal cord at high magnetic field strength, both without and with a magnetization transfer prepulse, we compared them to T2-weighted fast-spin-echo (T2-FSE) images for the detection of MS lesions in the cervical cord at 3T.
Methods
On a clinical 3T MRI scanner, we studied 62 MS cases and 19 healthy volunteers. Axial 3D GRE sequences were performed without and with off-resonance radiofrequency irradiation. To mimic clinical practice, all images were evaluated in conjunction with linked images from a sagittal short tau inversion recovery scan, which is considered the gold standard for lesion detection in MS. Two experienced observers recorded image quality, location and size of focal lesions, atrophy, swelling, and diffuse signal abnormality independently at first and then in consensus.
Results
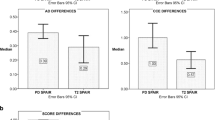
The number and volume of lesions detected with high confidence was more than three times as high on both GRE sequences compared to T2-FSE (p < 0.0001). Approximately 5 % of GRE scans were affected by artifacts that interfered with image interpretation, not significantly different from T2W-FSE.
Conclusions
Axial 3D GRE sequences are useful for MS lesion detection when compared to 2D T2-FSE sequences in the cervical spinal cord at 3T and should be considered when examining intramedullary spinal cord lesions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, Fujihara K, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Montalban X, O'Connor P, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Thompson AJ, Waubant E, Weinshenker B, Wolinsky JS (2011) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 69(2):292–302. doi:10.1002/ana.22366
Barkhof F (2002) The clinico-radiological paradox in multiple sclerosis revisited. Curr Opin Neurol 15(3):239–245
Poonawalla AH, Hou P, Nelson FA, Wolinsky JS, Narayana PA (2008) Cervical spinal cord lesions in multiple sclerosis: T1-weighted inversion-recovery MR imaging with phase-sensitive reconstruction. Radiology 246(1):258–264. doi:10.1148/radiol.2463061900
Vaithianathar L, Tench CR, Morgan PS, Constantinescu CS (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spinal cord in multiple sclerosis—a quantitative T1 relaxation time mapping approach. J Neurol 250(3):307–315. doi:10.1007/s00415-003-1001-8
Bot JC, Barkhof F, Lycklama a Nijeholt G, van Schaardenburg D, Voskuyl AE, Ader HJ, Pijnenburg JA, Polman CH, Uitdehaag BM, Vermeulen EG, Castelijns JA (2002) Differentiation of multiple sclerosis from other inflammatory disorders and cerebrovascular disease: value of spinal MR imaging. Radiology 223(1):46–56
Lycklama G, Thompson A, Filippi M, Miller D, Polman C, Fazekas F, Barkhof F (2003) Spinal-cord MRI in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 2(9):555–562
Weier K, Mazraeh J, Naegelin Y, Thoeni A, Hirsch JG, Fabbro T, Bruni N, Duyar H, Bendfeldt K, Radue EW, Kappos L, Gass A (2012) Biplanar MRI for the assessment of the spinal cord in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. doi:10.1177/1352458512442754
Thorpe JW, Kidd D, Moseley IF, Thompson AJ, MacManus DG, Compston DA, McDonald WI, Miller DH (1996) Spinal MRI in patients with suspected multiple sclerosis and negative brain MRI. Brain 119(Pt 3):709–714
Lycklama a Nijeholt GJ, Barkhof F, Scheltens P, Castelijns JA, Ader H, van Waesberghe JH, Polman C, Jongen SJ, Valk J (1997) MR of the spinal cord in multiple sclerosis: relation to clinical subtype and disability. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18(6):1041–1048
Kidd D, Thorpe JW, Kendall BE, Barker GJ, Miller DH, McDonald WI, Thompson AJ (1996) MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 60(1):15–19
Grossman RI, McGowan JC (1998) Perspectives on multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19(7):1251–1265
Brex PA, Miszkiel KA, O'Riordan JI, Plant GT, Moseley IF, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2001) Assessing the risk of early multiple sclerosis in patients with clinically isolated syndromes: the role of a follow up MRI. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70(3):390–393
Nijeholt GJ, Bergers E, Kamphorst W, Bot J, Nicolay K, Castelijns JA, van Waesberghe JH, Ravid R, Polman CH, Barkhof F (2001) Post-mortem high-resolution MRI of the spinal cord in multiple sclerosis: a correlative study with conventional MRI, histopathology and clinical phenotype. Brain 124(Pt 1):154–166
Lycklama a Nijeholt GJ, Castelijns JA, Weerts J, Ader H, van Waesberghe JH, Polman C, Barkhof F (1998) Sagittal MR of multiple sclerosis in the spinal cord: fast versus conventional spin-echo imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19(2):355–360
Bot JC, Blezer EL, Kamphorst W, Lycklama ANGJ, Ader HJ, Castelijns JA, Ig KN, Bergers E, Ravid R, Polman C, Barkhof F (2004) The spinal cord in multiple sclerosis: relationship of high-spatial-resolution quantitative MR imaging findings to histopathologic results. Radiology 233(2):531–540. doi:10.1148/radiol.2332031572
Tartaglino LM, Friedman DP, Flanders AE, Lublin FD, Knobler RL, Liem M (1995) Multiple sclerosis in the spinal cord: MR appearance and correlation with clinical parameters. Radiology 195(3):725–732
Simon JH, Li D, Traboulsee A, Coyle PK, Arnold DL, Barkhof F, Frank JA, Grossman R, Paty DW, Radue EW, Wolinsky JS (2006) Standardized MR imaging protocol for multiple sclerosis: consortium of MS centers consensus guidelines. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27(2):455–461
Bronskill MJ, McVeigh ER, Kucharczyk W, Henkelman RM (1988) Syrinx-like artifacts on MR images of the spinal cord. Radiology 166(2):485–488
Curtin AJ, Chakeres DW, Bulas R, Boesel CP, Finneran M, Flint E (1989) MR imaging artifacts of the axial internal anatomy of the cervical spinal cord. AJR Am J Roentgenol 152(4):835–842
Czervionke LF, Daniels DL, Ho PS, Yu SW, Pech P, Strandt JA, Williams AL, Haughton VM (1988) The MR appearance of gray and white matter in the cervical spinal cord. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 9(3):557–562
Hinks RS, Quencer RM (1988) Motion artifacts in brain and spine MR. Radiol Clin N Am 26(4):737–753
Levy LM, Di Chiro G, Brooks RA, Dwyer AJ, Wener L, Frank J (1988) Spinal cord artifacts from truncation errors during MR imaging. Radiology 166(2):479–483
Mikulis DJ, Wood ML, Zerdoner OA, Poncelet BP (1994) Oscillatory motion of the normal cervical spinal cord. Radiology 192(1):117–121
Roemer PB, Edelstein WA, Hayes CE, Souza SP, Mueller OM (1990) The NMR phased array. Magn Reson Med 16(2):192–225
Tench CR, Morgan PS, Jaspan T, Auer DP, Constantinescu CS (2005) Spinal cord imaging in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimaging 15(4 Suppl):94S–102S. doi:10.1177/1051228405283292
Smith SA, Jones CK, Gifford A, Belegu V, Chodkowski B, Farrell JA, Landman BA, Reich DS, Calabresi PA, McDonald JW, van Zijl PC (2010) Reproducibility of tract-specific magnetization transfer and diffusion tensor imaging in the cervical spinal cord at 3 tesla. NMR Biomed 23(2):207–217. doi:10.1002/nbm.1447
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33(11):1444–1452
Martin N, Malfair D, Zhao Y, Li D, Traboulsee A, Lang D, Vertinsky AT (2012) Comparison of MERGE and axial T2-weighted fast spin-echo sequences for detection of multiple sclerosis lesions in the cervical spinal cord. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199(1):157–162. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7039
White ML, Zhang Y, Healey K (2011) Cervical spinal cord multiple sclerosis: evaluation with 2D multi-echo recombined gradient echo MR imaging. J Spinal Cord Med 34(1):93–98
Hittmair K, Mallek R, Prayer D, Schindler EG, Kollegger H (1996) Spinal cord lesions in patients with multiple sclerosis: comparison of MR pulse sequences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17(8):1555–1565
Hackney DB (1999) MR studies of the spinal cord in patients with multiple sclerosis: what should we do? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20(9):1581–1583
Zackowski KM, Smith SA, Reich DS, Gordon-Lipkin E, Chodkowski BA, Sambandan DR, Shteyman M, Bastian AJ, van Zijl PC, Calabresi PA (2009) Sensorimotor dysfunction in multiple sclerosis and column-specific magnetization transfer-imaging abnormalities in the spinal cord. Brain 132(Pt 5):1200–1209. doi:10.1093/brain/awp032
Oh J, Chen M, Zackowski KM, Newsome SD, Smith SA, Prince JL, Calabresi PA, Reich DS (2012) Diffusion tensor and magnetization transfer imaging correlates of motor dysfunction in the spinal cord in multiple sclerosis. Paper presented at the American Academy of Neurology, New Orleans
Keiper MD, Grossman RI, Hirsch JA, Bolinger L, Ott IL, Mannon LJ, Langlotz CP, Kolson DL (1998) MR identification of white matter abnormalities in multiple sclerosis: a comparison between 1.5T and 4T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19(8):1489–1493
Gauthier SA, Glanz BI, Mandel M, Tsagkaropoulos A, Neema M, Stankiewicz J, Arora A, Duan Y, Liptak Z, Egorova S, Buckle GJ, Bakshi R, Guttmann CR, Khoury SJ, Weiner HL (2009) Incidence and factors associated with treatment failure in the CLIMB multiple sclerosis cohort study. J Neurol Sci 284(1–2):116–119. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2009.04.020
Stankiewicz JM, Neema M, Alsop DC, Healy BC, Arora A, Buckle GJ, Chitnis T, Guttmann CR, Hackney D, Bakshi R (2009) Spinal cord lesions and clinical status in multiple sclerosis: A 1.5T and 3T MRI study. J Neurol Sci 279(1–2):99–105. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2008.11.009
Ge Y (2006) Multiple sclerosis: the role of MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27(6):1165–1176
Kidd D, Thorpe JW, Thompson AJ, Kendall BE, Moseley IF, MacManus DG, McDonald WI, Miller DH (1993) Spinal cord MRI using multi-array coils and fast spin echo II. Findings in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 43(12):2632–2637
Lycklama a Nijeholt GJ, Barkhof F, Castelijns JA, van Waesberghe JH, Valk J, Jongen PJ, Hommes OR (1996) Comparison of two MR sequences for the detection of multiple sclerosis lesions in the spinal cord. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17(8):1533–1538
Bot JC, Barkhof F (2009) Spinal-cord MRI in multiple sclerosis: conventional and nonconventional MR techniques. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 19(1):81–99. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2008.09.005
Sze G, Merriam M, Oshio K, Jolesz FA (1992) Fast spin-echo imaging in the evaluation of intradural disease of the spine. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 13(5):1383–1392
Keiper MD, Grossman RI, Brunson JC, Schnall MD (1997) The low sensitivity of fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery MR in the detection of multiple sclerosis of the spinal cord. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18(6):1035–1039
Stevenson VL, Gawne-Cain ML, Barker GJ, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (1997) Imaging of the spinal cord and brain in multiple sclerosis: a comparative study between fast FLAIR and fast spin echo. J Neurol 244(2):119–124
Thorpe JW, Kidd D, Kendall BE, Tofts PS, Barker GJ, Thompson AJ, MacManus DG, McDonald WI, Miller DH (1993) Spinal cord MRI using multi-array coils and fast spin echo I. Technical aspects and findings in healthy adults. Neurology 43(12):2625–2631
Sze G, Kawamura Y, Negishi C, Constable RT, Merriam M, Oshio K, Jolesz F (1993) Fast spin-echo MR imaging of the cervical spine: influence of echo train length and echo spacing on image contrast and quality. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14(5):1203–1213
Enzmann DR, Rubin JB (1988) Cervical spine: MR imaging with a partial flip angle, gradient-refocused pulse sequence Part II. Spinal cord disease. Radiology 166(2):473–478
Dale RC, de Sousa C, Chong WK, Cox TC, Harding B, Neville BG (2000) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, multiphasic disseminated encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis in children. Brain 123(Pt 12):2407–2422
Finelli DA, Hurst GC, Karaman BA, Simon JE, Duerk JL, Bellon EM (1994) Use of magnetization transfer for improved contrast on gradient-echo MR images of the cervical spine. Radiology 193(1):165–171
Acknowledgments
We thank Terri Brawner, Jonathan Farrell, Eliza Gordon-Lipkin, Kathleen Kahl, Ivana Kusevic, and Peter van Zijl for assistance with data collection, and Govind Nair and Jiwon Oh for critical comments on the manuscript. Funding sources include NIH grants P41RR015241 and K99NS064098; National Multiple Sclerosis Society grants CA1029A2 and TR3760A3; and the Nancy Davis Center without Walls. Dr. Reich is supported by the Intramural Research Program of NINDS.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk, A., Aygun, N., Smith, S.A. et al. Axial 3D gradient-echo imaging for improved multiple sclerosis lesion detection in the cervical spinal cord at 3T. Neuroradiology 55, 431–439 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1118-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1118-5