Abstract
Introduction
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has become a reference MRI technique for the evaluation of neurological disorders. Few publications have investigated the application of DWI for inflammatory demyelinating lesions. The purpose of the study was to describe diffusion-weighted imaging characteristics of acute, spinal demyelinating lesions.
Methods
Six consecutive patients (two males, four females; aged 28–64 years) with acute spinal cord demyelinating lesions were studied in a prospective case series design from June 2009 to October 2010. We performed magnetic resonance imaging studies from 2 to 14 days from symptom onset on the patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (n = 3) or clinically isolated syndrome (n = 3). Main outcome measures were diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient pattern (ADC) of acute spinal cord demyelinating lesions.
Results
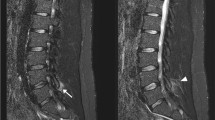
All spinal lesions showed a restricted diffusion pattern (DWI+/ADC−) with a 24% median ADC signal decrease. A good correlation between clinical presentation and lesion site was observed.
Conclusion
Acute demyelinating spinal cord lesions show a uniform restricted diffusion pattern. Clinicians and neuro-radiologists should be aware that this pattern is not necessarily confirmatory for an ischaemic aetiology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kloska SP, Wintermark M, Engelhorn T, Fiebach JB (2010) Acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging: current status and future perspective. Neuroradiol 52:189–201
Rizzo L, Crasto SG, Moruno PG, Cassoni P, Ruda R, Boccaletti R, Brosio M, De Lucchi R, Fava C (2009) Role of diffusion- and perfusion-weighted MR imaging for brain tumour characterisation. Radiol Med 114:645–659
Matsusue E, Fink JR, Rockhill JK, Ogawa T, Maravilla KR (2010) Distinction between glioma progression and post-radiation change by combined physiologic MR imaging. Neuroradiology 52:297–306
Kastrup O, Wanke I, Maschke M (2008) Neuroimaging of infections of the central nervous system. Semin Neurol 28:511–522
Milligan TA, Zamani A, Bromfield E (2009) Frequency and patterns of MRI abnormalities due to status epilepticus. Seizure 18:104–108
Enzinger C, Thimary F, Kapeller P, Ropele S, Schmidt R, Ebner F, Fazekas F (2008) Transient global amnesia: diffusion-weighted imaging lesions and cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 39:2219–2225
Belvis R, Ramos R, Villa C, Segura C, Pagonabarraga J, Ormazabal I, Kulisevsky J (2010) Brain apparent water diffusion coefficient magnetic resonance image during a prolonged visual aura. Headache 50:1045–1049
Tievsky AL, Ptak T, Farkas J (1999) Investigation of apparent diffusion coefficient and diffusion tensor anisotrophy in acute and chronic multiple sclerosis lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1491–1499
Rocca MA, Cercignani M, Iannucci G, Comi G, Filippi M (2000) Weekly diffusion-weighted imaging of normal-appearing white matter in MS. Neurology 55:882–884
Werring DJ, Brassat D, Droogan AG, Clark CA, Symms MR, Barker GJ, MacManus DG, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2000) The pathogenesis of lesions and normal-appearing white matter changes in multiple sclerosis: a serial diffusion MRI study. Brain 123(Pt 8):1667–1676
Rovira A, Pericot I, Alonso J, Rio J, Grive E, Montalban X (2002) Serial diffusion-weighted MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopy of acute large demyelinating brain lesions: case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:989–994
Wuerfel J, Bellmann-Strobl J, Brunecker P, Aktas O, McFarland H, Villringer A, Zipp F (2004) Changes in cerebral perfusion precede plaque formation in multiple sclerosis: a longitudinal perfusion MRI study. Brain 127:111–119
Rosso C, Remy P, Creange A, Brugieres P, Cesaro P, Hosseini H (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging characteristics of an acute strokelike form of multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1006–1008
Horsfield MA, Larsson HB, Jones DK, Gass A (1998) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64(Suppl 1):S80–S84
Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG (2000) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 217:331–345
Castriota-Scanderbeg A, Sabatini U, Fasano F, Floris R, Fraracci L, Mario MD, Nocentini U, Caltagirone C (2002) Diffusion of water in large demyelinating lesions: a follow-up study. Neuroradiology 44:764–767
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452
Gass A, Back T, Behrens S, Maras A (2000) MRI of spinal cord infarction. Neurology 54:2195
Gass A, Moeckel R, Hirsch J, Hennerici M, Schwartz A (1999) Diffusion MRI characterisation of MS lesion evolution. Mult Scler 5(Suppl 1):S21
Balashov KE, Aung LL, Dhib-Jalbut S, Keller IA (2011) Acute multiple sclerosis lesion: conversion of restricted diffusion due to vasogenic edema. J Neuroimaging 21:202–204
Schlaug G, Siewert B, Benfield A, Edelman RR, Warach S (1997) Time course of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) abnormality in human stroke. Neurology 49:113–119
Tien RD, Felsberg GJ, Friedman H, Brown M, MacFall J (1994) MR imaging of high-grade cerebral gliomas: value of diffusion-weighted echoplanar pulse sequences. AJR Am J Roentgenol 162:671–677
Brunberg JA, Chenevert TL, McKeever PE, Ross DA, Junck LR, Muraszko KM, Dauser R, Pipe JG, Betley AT (1995) In vivo MR determination of water diffusion coefficients and diffusion anisotropy: correlation with structural alteration in gliomas of the cerebral hemispheres. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:361–371
Els T, Eis M, Hoehn-Berlage M, Hossmann KA (1995) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of experimental brain tumors in rats. MAGMA 3:13–20
Gass A, Niendorf T, Hirsch JG (2001) Acute and chronic changes of the apparent diffusion coefficient in neurological disorders—biophysical mechanisms and possible underlying histopathology. J Neur Sci 186(Suppl 1):S15–S23
Loher TJ, Bassetti CL, Lovblad KO, Stepper FP, Sturzenegger M, Kiefer C, Nedeltchev K, Arnold M, Remonda L, Schroth G (2003) Diffusion-weighted MRI in acute spinal cord ischaemia. Neuroradiology 45:557–561
Kuker W, Weller M, Klose U, Krapf H, Dichgans J, Nagele T (2004) Diffusion-weighted MRI of spinal cord infarction–high resolution imaging and time course of diffusion abnormality. J Neurol 251:818–824
Thurnher MM, Bammer R (2006) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and spinal cord. Semin Roentgenol 41:294–311
Cortes Nino Mdel P, Tampieri D, Melancon D (2010) Endovascular venous procedures for multiple sclerosis? Mult Scler 16:771–772
Compston A, Coles A (2008) Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 372:1502–1517
Pichiecchio A, Tavazzi E, Maccabelli G, Precupanu CM, Romani A, Roccatagliata L, Luccichenti G, Bergamaschi R, Bastianello S (2009) What insights have new imaging techniques given into aggressive forms of MS–different forms of MS or different from MS? Mult Scler 15:285–293
Bugnicourt JM, Garcia PY, Monet P, Bonnaire B, Al Khedr A, Godefroy O (2010) Teaching NeuroImages: marked reduced apparent diffusion coefficient in acute multiple sclerosis lesion. Neurology 74:e87
Frohman EM, Wingerchuk DM (2010) Clinical practice. Transverse myelitis. N Engl J Med 363:564–572
Inglese M, Bester M (2010) Diffusion imaging in multiple sclerosis: research and clinical implications. NMR Biomed 23:865–872
Losseff NA, Webb SL, O'Riordan JI, Page R, Wang L, Barker GJ, Tofts PS, McDonald WI, Miller DH, Thompson AJ (1996) Spinal cord atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. A new reproducible and sensitive MRI method with potential to monitor disease progression. Brain 119(Pt 3):701–708
Vos SB, Jones DK, Viergever MA, Leemans A (2011) Partial volume effect as a hidden covariate in DTI analyses. Neuroimage 55:1566–1576
Mamata H, Jolesz FA, Maier SE (2005) Apparent diffusion coefficient and fractional anisotropy in spinal cord: age and cervical spondylosis-related changes. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:38–43
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Liliane Petrini (Ph.D.) for her help in finalizing the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zecca, C., Cereda, C., Wetzel, S. et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in acute demyelinating myelopathy. Neuroradiology 54, 573–578 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0907-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0907-6