Abstract
Introduction
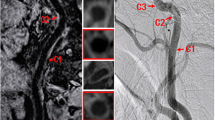
Prospective studies have shown that an increased thickness of the carotid wall is a significant predictor of coronary and cerebrovascular complications. Our purpose was to assess the agreement between multi-detector row computed tomography (CT) angiography (MDCTA) and colour Doppler ultrasound (CD-US) in measuring carotid artery wall thickness (CAWT) and the intima–media thickness (IMT).
Methods
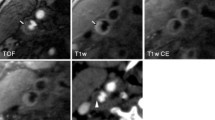
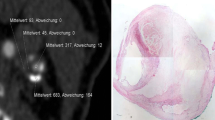
Altogether, 97 subjects (age range 64–84 years) were prospectively analysed using a four-detector row CT and a sonographic scanner. In total, 46 subjects had shown cerebral ischaemic symptoms. CAWT and IMT were measured in each patient using MDCTA and CD-US (by applying a digital calliper), respectively. Continuous data were described as the mean value ± standard deviation and were compared using the Mann–Whitney U test. A p value <0.05 was considered significant. Bland–Altman statistics was employed to measure the agreement between MDCTA and CD-US.
Results
CAWT ranged from 0.5 to 1.53 mm, with a mean value of 0.9072 mm. IMT ranged from 0.46 to 1.5 mm, with a mean value of 0.8839 mm. By analysing the Bland–Altman plot, we observed an excellent agreement between CD-US and MDCTA with a bias between methods of 0.023 ± 0.0424 mm. A limit of agreement from −0.06 to 0.106 was recorded. Correlation coefficient r was 0.9855 (95% confidence interval 0.9808–0.989). Mann–Whitney U test indicated a p value of 0.377.
Conclusions
Obtained results indicated a significant agreement between MDCTA and CD-US in the measurement of CAWT and IMT.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zureik M, Ducimetiere P, Touboul PJ, Courbon D, Bonithon-Kopp C, Berr C, Magne C (2000) Common carotid intima–media thickness predicts occurrence of carotid atherosclerotic plaques: longitudinal results from the Aging Vascular Study (EVA) study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1622–1629
Simon A, Gariepy J, Chironi G, Megnien JL, Levenson J (2002) Intima–media thickness: a new tool for diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular risk. J Hypertens 20:159–169
Lorenz MW, von Kegler S, Steinmetz H, Markus HS, Sitzer M (2006) Carotid intima–media thickening indicates a higher vascular risk across a wide age range prospective data from the Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study (CAPS). Stroke 37:87–92
Ebrahim S, Papacosta O, Whincup P, Wannamethee G, Walker M, Nicolaides AN, Dhanjil S, Griffin M, Belcaro G, Rumley A, Lowe GDO (1999) Carotid plaque, intima media thickness, cardiovascular risk factors, and prevalent cardiovascular disease in men and women the British Regional Heart Study. Stroke 30:841–850
Kitamura A, Iso H, Imano H, Ohira T, Okada T, Sato S, Kiyama M, Tanigawa T, Yamagishi K, Shimamoto T (2004) Carotid intima–media thickness and plaque characteristics as a risk factor for stroke in Japanese elderly men. Stroke 35:2788–2794
Iglesias del Sol A, Bots ML, Grobbee DE, Hofman A, Witteman JC (2002) Carotid intima–media thickness at different sites: relation to incident myocardial infarction; The Rotterdam Study. Eur Heart J 23:934–940
Salonen JT, Salonen R (1991) Ultrasonographically assessed carotid morbidity and the risk of coronary heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb 11:1245–1249
Bonithon-Kopp C, Touboul PJ, Berr C, Leroux C, Mainard F, Courbon D, Ducimetière P (1996) Relation of intima–media thickness to atherosclerotic plaques in the carotid arteries: the EVA study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16:310–316
Suurkula M, Agewall S, Fagerberg B, Wendelhag I, Widgren B, Wikstrand J (1994) Ultrasound evaluation of atherosclerotic manifestations in the carotid artery in high-risk patients. Arterioscler Thromb 14:1297–1304
Li R, Duncan BB, Metcalf PA, Crouse JR, Sharrett AR, Tyroler HA, Barnes R, Heiss G, for the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study Investigator (1994) B-mode-detected carotid artery plaque in a general population. Stroke 25:2377–2383
Rosfors S, Hallerstam S, Jensen-Urstad K, Zetterling M, Carlstrom C (1998) Relationship between intima–media thickness in the common carotid artery and atherosclerosis in the carotid bifurcation. Stroke 29:1378–1382
Eliasziw M, Rankin RN, Fox AJ et al (1995) Accuracy and prognostic consequences of ultrasonography in identifying severe carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 26:1747–1752
Saba L, Caddeo G, Sanfilippo R, Montisci R, Mallarini G (2007) CT and US in the study of ulcerated carotid plaque compared with surgical results. Advantages of multi-detector-row CT angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 28:1061–1066
MacMahon S, Sharpe N, Gamble G, Hart H, Scott J, Simes J, White H, on behalf of the LIPID Trial Research Group (1998) Effects of lowering average or below-average cholesterol levels on the progression of carotid atherosclerosis: results of the LIPID atherosclerosis substudy. Circulation 97:1784–1790
Mercuri M, Bond G, Sirtori CR, Veglia F, Crepaldi G, Feruglio S, Descovich RG, Rubba P, Mancini M, Gallus G, Bianchi G, D’Alò G, Ventura A (1996) Pravastatin reduces carotid intima–media thickness progression in an asymptomatic hypercholesterolemic Mediterranean population: the Carotid Atherosclerosis Italian Ultrasound Study. Am J Med 101:627–634
Salonen R, Nyyssonen K, Porkkala E, Rummukainen J, Belder R, Park JS, Kuopio SJT (1995) Atherosclerosis Prevention Study (KAPS): a population-based primary prevention trial of the effect of LDL lowering on atherosclerotic progression in carotid and femoral arteries. Circulation 92:1758–1764
De Groot E, Jukema JW, Montauban van Swijndregt AD, Zwinderman AH, Ackerstaff RG, van der Steen AF, Bom N, Lie KI, Bruschke AV (1998) B-mode ultrasound assessment of pravastatin treatment effect on carotid and femoral artery walls and its correlations with coronary arteriographic findings: a report of the Regression Growth Evaluation Statin Study (REGRESS). J Am Coll Cardiol 31:1561–1567
Wendelhag I, Wiklund O, Wikstrand J (1992) Arterial wall thickness in familial hypercholesterolemia: ultrasound measurement of intima–media thickness in the common carotid artery. Arterioscler Thromb 12:70–77
Wendelhag I, Wiklund O, Wikstrand J (1993) Atherosclerotic changes in the femoral and carotid arteries in familial hypercholesterolemia: ultrasonographic assessment of intima–media thickness and plaque occurrence. Arterioscler Thromb 13:1404–1411
Riley WA, Barnes RW, Applegate WB, Dempsey R, Hartwell T, Davis VG, Bond MG, Furberg CD (1992) Reproducibility of non-invasive ultrasonic measurement of carotid atherosclerosis: the Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Plaque Study. Stroke 23:1062–1068
Veller MG, Fisher CM, Nicolaides AN, Renton S, Geroulakos G, Stafford NJ, Sarker A, Szendro G, Belcaro G (1993) Measurement of the ultrasonic intima–media complex thickness in normal subjects. J Vasc Surg 17:719–725
Saba L, Sanfilippo R, Pirisi R, Pascalis L, Montisci R, Mallarini G (2007) Multidetector row CT in the study of atherosclerotic carotid artery. Neuroradiology 49:623–637
Saba L, Caddeo G, Sanfilippo R, Montisci R, Mallarini G (2007) Efficacy and sensitivity of axial scans and different reconstruction methods in the study of the ulcerated carotid plaque by using multi-detector-row CT angiography. Comparison with surgical results. Am J Neuroradiol AJNR 28:716–723
Rydberg J, Buckwalter KA, Caldemeyer KS (2000) Multisection CT: scanning techniques and clinical applications. RadioGraphics 20:1787–1806
Robinson ML, Sacks D, Perlmutter GS, Marinelli DL (1988) Diagnostic criteria for carotid duplex sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 155:1045–1049
Wendelhag I, Gustavsson T, Suurkula M, Berglund G, Wikstrand J (1991) Ultrasound measurement of wall thickness in the carotid artery: fundamental principles and description of a computerized analysing system. Clin Physiol 11:565–577
Ebrahim S, Papacosta O, Whincup P, Wannamethee G, Walker M, Nicolaides AN, Dhanjil S, Griffin M, Belcaro G, Rumley A, Rowe GD (1999) Carotid plaque, intima media thickness, cardiovascular risk factors, and prevalent cardiovascular disease in men and women: the British Regional Heart Study. Stroke 30:841–850
Lemne C, Jogestrand T, de Faire U (1995) Carotid intima–media thickness and plaque in borderline hypertension. Stroke 26:34–39
Baldassarre D, Werba JP, Tremoli E, Poli A, Pazzucconi F, Sirtori CR (1994) Common carotid intima–media thickness measurement: a method to improve accuracy and precision. Stroke 25:1588–1592
Baldassarre D, Amato M, Bondioli A, Sirtori CR, Tremoli E (2000) Carotid artery intima–media thickness measured by ultrasonography in normal clinical practice correlates well with atherosclerotic risk factors. Stroke 31:2426–2430
Frauchiger B, Schmid HP, Roedel C, Moosmann P, Staub D (2001) Comparison of carotid arterial resistive indices with intima-media thickness as sonographic markers of atherosclerosis. Stroke 32:836–841
Davis PH, Dawson JD, Riley WA, Lauer RM (2001) Carotid intimal–medial thickness is related to cardiovascular risk factors measured from childhood through middle age: the Muscatine study. Circulation 104:2815–2819
Saba L, Sanfilippo R, Pascalis G, Montisci R, Caddeo G, Mallarini G (2008) Carotid artery wall thickness and ischemic symptoms: evaluation using multi-detector-row CT Angiography. Eur Radiology 18:1962–1971
Puchner S, Reiter M, Baros C, Minar E, Lammer J, Buceck RA (2008) Assessment of intima–media thickness of carotid arteries: evaluation of an automated computer software. Neuroradiology 50:849–853
Wendelhag I, Liang Q, Gustavsson T, Wikstrand J (1997) A new automated computerizing analyzing system simplifies readings and reduces the variability in ultrasound measurement of intima–media-thickness. Stroke 28:2195–2200
Joakimsen O, Bonaa KH, Stensland-Bugge E (1997) Reproducibility of ultrasound assessment of carotid plaque occurrence, thickness and morphology; the Tromso Study. Stroke 28:2201 2207
Warlaw JM, Chappel FM, Stevenson M, De Nigris E, Thomas S, Gillard J et al (2002) Accurate, practical and cost-effective assessment of carotid stenosis in UK. Health Technol Assess 2006:10 1–182
Acknowledgements
We are deeply indebted to Tiziana Langella MS and Giancarlo Caddeo MD for their precious help. We would like to thank also Aldo Saitz, Ermanno Saitz and Clements Atzeni.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saba, L., Sanfilippo, R., Montisci, R. et al. Carotid artery wall thickness: comparison between sonography and multi-detector row CT angiography. Neuroradiology 52, 75–82 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0589-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0589-5