Abstract
Introduction
Three cingulate motor areas have been described in monkeys, the rostral, dorsal, and ventral cingulate motor areas, and would control limbic-related motor activity. However, little anatomical data are available in human about the functional networks these cingulate areas underlie. Therefore, networks anchored in the rostral and caudal cingulate motor areas (rCMA and cCMA, respectively) were studied in human using functional connectivity during the brain resting state. Since the rCMA and cCMA are located just under the pre-supplementary and supplementary motor areas (pre-SMA and SMA), the pre-SMA- and SMA-centered networks were also studied to ensure that these four circuits were correctly dissociated.
Methods
Data from 14 right-handed healthy volunteers were acquired at rest and analyzed by region of interest (ROI)-based functional connectivity. The blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) signal fluctuations of separate ROIs located in rCMA, cCMA, pre-SMA, and SMA were successively used to identify significant temporal correlations with BOLD signal fluctuations of other brain regions.
Results
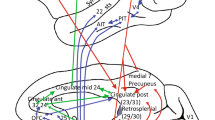
Low-frequency BOLD signal of the CMA was correlated with signal fluctuations in the prefrontal, cingulate, insular, premotor, motor, medial and inferior parietal cortices, putamen and thalamus, and anticorrelated with the default-mode network. rCMA was more in relation with prefrontal, orbitofrontal, and language-associated cortices than cCMA more related to sensory cortex. These cingulate networks were very similar to the pre-SMA- and SMA-centered networks, although pre-SMA and SMA showed stronger correlation with the prefrontal and inferior parietal cortices and with the cerebellum and the superior parietal cortex, respectively.
Conclusion
The human cingulate motor areas constitute an interface between sensorimotor, limbic and executive systems, sharing common cortical, striatal, and thalamic relays with the overlying premotor medial areas.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luppino G, Rizzolatti G (2000) The organization of the frontal motor network. News Physiol Sci 15:219–224
Picard N, Strick PL (1996) Motor areas of the medial wall: a review of their location and functional activation. Cereb Cortex 6:342–353
Morecraft RJ (1993) Van Hoesen GW (1993) Frontal granular cortex input to the cingulate (M3), supplementary (M2) and primary (M1) motor cortices in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 337:669–689
Morecraft RJ (1998) Van Hoesen GW (1998) Convergence of limbic input to the cingulate motor cortex in the rhesus monkey. Brain Res Bull 45:209–232
Morecraft RJ, Rockland KS (2000) Van Hoesen GW (2000) Localization of area prostriata and its projection to the cingulate motor cortices in the rhesus monkey. Cereb Cortex 10:192–203
Shima K (1998) Tanji J (1998) Role for cingulate motor area cells in voluntary movements selection based on reward. Science 282:1335–1338
Russo GS, Backus DA, Ye S (2002) Crutcher MD (2002) Neural activity in monkey dorsal and ventral cingulate motor areas: comparison with the supplementary motor area. J Neurophysiol 88:2612–2629
Picard N, Strick PL (1994) 2-desoxyglucose (2DG) uptake in the medial wall motor areas of behaving monkeys. Society of Neurosciences Abstract 20:986
Hakanawa T, Dimyan MA, Hallett M (2008) The representation of blinking movement in cingulate motor areas: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Cereb Cortex 18:930–937
Stephan KM, Binkofski F, Halsband U, Dohle C, Wunderlich G, Schnitzler A, Tass P, Posse S, Herzog H, Sturm V, Zilles K, Seitz RJ, Freund H-J (1999) The role of ventral medial wall motor areas in bimanual co-ordination. A combined lesion and activation study. Brain 122:351–368
Grafton ST, Schmitt P, Van Norn J, Diedrichsen J (2008) Neural substrates of visuomotor learning based of improved feedback control and prediction. NeuroImage 39:1383–1395
Cross ES, Hamilton AF, Grafton ST (2006) Building a motor simulation de novo: observation of dance by dancers. NeuroImage 31:1257–1267
Berkowitz AL, Ansari D (2008) Generation of novel motor sequences: the neural correlates of musical improvisation. NeuroImage 41:535–543
Mueller VA, Brass M, Waszak F, Prinz W (2007) The role of the preSMA and the rostral cingulate zone in internally selected actions. NeuroImage 37:1354–1361
Mars RB, Coles MG, Grol MJ, Holroyd CB, Nieuwenhuis S, Hulstijn W, Toni I (2005) Neural dynamics of error processing in medial frontal cortex. NeuroImage 28:1007–1013
Chassagnon S, Minotti L, Kremer S, Hoffmann D, Kahane P (2008) Somatosensory, motor and reaching/grasping responses to direct electrical stimulation of the human cingulate motor areas. J Neurosurg 109:593–604
Paus T (2001) Primate anterior cingulate cortex: where motor control, drive and cognition interface. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:417–424
Brazdil M, Kuba R, Rektor I (2006) Rostral cingulate motor area and paroxysmal alien hand syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:992–1000
Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM (1995) Hyde JS(1995) Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34:537–541
Fox MD, Raischle ME (2007) Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:700–711
Greicius M (2008) Resting-state functional connectivity in neuropsychiatric disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 21:424–430
Morecraft RJ, Cipolloni PB, Stilwell-Morecraft KS, Gedney MT, Pandya DN (2004) Cytoarchitecture and cortical connections of the posterior cingulate and adjacent somatosensory fields in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 469:37–69
Nieuwenhuys R, Voogt J, vanHuijzen C (eds) (2008) The human central nervous system. A synopsis and atlas, 4th revised edn. Springer, Berlin
Hatanaka N, Tokuno H, Hamada I, Inase M, Ito Y, Imanishi M, Hasegawa N, Akazawa T, Nambu A, Takada M (2003) Thalamocortical and intracortical connections of monkey cingulate motor areas. J Comp Neurol 462:121–138
Vogt BA, Berger G, Derbyshire SWG (2003) Structural and functional dichotomy of human midcingulate cortex. Eur J NeuroSci 18:3134–3144
Cavanna AE, Trimble MR (2006) The precuneus: a review of its functional anatomy and behavioural correlates. Brain 129:564–583
Calvaraza R, Mailly P, Haber SN (2007) Relationship between the corticostriatal terminals from areas 9 and 46, and those from area 8A, dorsal and rostral premotor cortex and area 24c: an anatomical substrate for cognition and action. Eur J NeuroSci 26:2005–2024
Takada M, Tokuno H, Hamada I, Inase M, Ito Y, Imanishi M, Hasegawa N, Akazawa T, Nambu A (2001) Organization of inputs from cingulate motor areas to basal ganglia in macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol 14:1633–1650
Nachev P, Kennard C, Husain M (2008) Functional role of the supplementary and pre-supplementary motor areas. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:856–859
Middleton FA, Strick PL (2000) Basal ganglia and cerebellar loops: motor active and cognitive circuits. Brains Res Rev 21:236–250
Krieghoff V, Brass M, Prinz W, Waszak F (2009) Dissociating what and when of intentional actions. Frontiers in Human Neurosciences 3:3
Hattori N, Shibasaki H, Wheaton L, Wu T, Matsuhashi M, Hallett M (2009) Discrete parieto-frontal functional connectivity related to grasping. J Neurophysiol 101:1267–1282
Margulies DS, Kelly AMC, Uddin LQ, Castellanos BBB, FX MMP (2007) Mapping the functional connectivity of anterior cingulate cortex. NeuroImage 37:579–588
Beckmann M, Johansen-Berg H, Rushworth FS (2009) Connectivity-based parcellation of human cingulate cortex and its relation to functional specialization. J Neurosci 29:1175–1190
Conflict of interest statement
I declare that I have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habas, C. Functional connectivity of the human rostral and caudal cingulate motor areas in the brain resting state at 3T. Neuroradiology 52, 47–59 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0572-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0572-1