Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of this study was to create morphologically reproducible elastase-induced model aneurysms in rabbits.
Methods
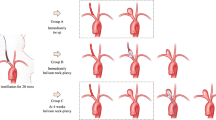
We created 120 elastase-induced aneurysms in rabbits using two different methods: the standard technique (group 1, n=62) and a modified technique (group 2, n=58). In the standard technique a small cutdown with a focal area of exposure of the mid-right common carotid artery (RCCA) was employed, while in the modified technique the RCCA was completely exposed to its origin. We measured aneurysm sizes (neck diameter, width and height) in the two groups. The aneurysm sizes were compared between the two groups using Student’s t test, and the standard deviations of the aneurysm sizes were compared between the groups using the F test.
Results
The mean aneurysm neck size, width and height in group 1 were 3.4±1.2 mm, 3.8±1.0 mm and 8.0±1.7 mm, respectively, and in group 2, were 3.2±0.9 mm, 3.7±0.6 mm and 9.1±1.8 mm, respectively. The differences in mean aneurysm neck and width between the two groups were not significant (P>0.05). However, there were significant differences in the standard deviation of these two parameters between the two groups (P<0.05 and P<0.01, respectively). The mean aneurysm height in group 2 was larger than in group 1 (P<0.001), but no significant difference in the standard deviation of this parameter between the two groups was found (P>0.05).
Conclusion
The results indicate that more consistent aneurysm diameters can be created using the modified technique.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hashimoto N, Handa H, Hazama F (1979) Experimentally induced cerebral aneurysms in rats: part III. Pathology. Surg Neurol 11:299–304
Cloft HJ, Altes TA, Marx WF, et al (1999) Endovascular creation of an in vivo bifurcation aneurysm model in rabbits. Radiology 213:223–228
Strother CM, Graves VB, Rappe A (1992) Aneurysm hemodynamics: an experimental study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 13:1089–1095
Guglielmi G, Ji C, Massoud TF, et al (1994) Experimental saccular aneurysms. II. A new model in swine. Neuroradiology 36:547–550
Stehbens WE (1997) Histological changes in chronic experimental aneurysms surgically fashioned in sheep. Pathology 29:374–379
Reul J, Weis J, Spetzger U, Konert T, Fricke C, Thoron A (1997) A long-term angiographic and histopathologic findings in experimental aneurysms of the carotid bifurcation embolized with platinum and tungsten coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:35–42
Altes TA, Cloft HJ, Short JG, et al (1999) ARRS Executive Council Award: creation of saccular aneurysms in the rabbit: a model suitable for testing endovascular devices: American Roentgen Ray Society. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:349–354
Fujiwara NH, Cloft HJ, Marx WF, Short JG, Jensen ME, Kallmes DF (2001) Serial angiography in an elastase-induced aneurysm model in rabbits: evidence for progressive aneurysm enlargement after creation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:698–703
Short JG, Fujiwara NH, Marx WF, Helm GA, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF (2001) Elastase-induced saccular aneurysms in rabbits: comparison of geometric features with those of human aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1833–1837
Kallmes DF, Fujiwara NH, Berr SS, Helm GA, Cloft HJ (2002) Elastase-induced saccular aneurysms in rabbits: a dose-escalation study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:295–298
Kallmes DF, Helm GA, Hudson SB, et al (1999) Histologic evaluation of platinum coil embolization in an aneurysm model in rabbits. Radiology 213:217–222
Kallmes DF, Fujiwara NH (2002) New expandable hydrogel-platinum coil hybrid device for aneurysm embolization. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1580–1588
Kallmes DF, Fujiwara NH, Yuen D, Dai D, Li ST (2003) A collagen-based coil for embolization of saccular aneurysms in a New Zealand White rabbit model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:591–596
Fujiwara NH, Kallmes DF (2002) Healing response in elastase-induced rabbit aneurysms after embolization with a new platinum coil system. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1137–1144
Marx WF, Cloft HJ, Helm GA, et al (2001) Endovascular treatment of experimental aneurysms by use of biologically modified embolic devices: coil-mediated intraaneurysmal delivery of fibroblast tissue allografts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:323–333
De Gast AN, Altes TA, Marx WF, et al (2001) Transforming growth factor beta-coated platinum coils for endovascular treatment of aneurysms: an animal study. Neurosurgery 49:690–696
Moller-Hartmann W, Krings T, Hans FJ, et al (2002) Endovascular treatment of experimental aneurysms in rabbits using Guglielmi detachable coils – a feasibility study. Neuroradiology 44:946–949
Hoh BL, Rabinov JD, Pryor JC, Ogilvy CS (2004) A modified technique for using elastase to create saccular aneurysms in animals that histologically and hemodynamically resemble aneurysms in human. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:705–711
Krings T, Moller-Hartmann W, Hans FJ, et al (2003) A refined method for creating saccular aneurysms in the rabbit. Neuroradiology 45:423–429
Thiex R, Moller-Hartmann W, Hans FJ, Scherer K, Krings T (2004) Are the configuration and neck morphology of experimental aneurysms predictable? A technical approach. Neuroradiology 46:571–576
Thiex R, Hans FJ, Krings T, et al (2004) Haemorrhagic tracheal necrosis as a lethal complication of an aneurysm model in rabbits via endoluminal incubation with elastase. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:285–289
Moller-Hartmann W, Krings T, Stein KP, et al (2003) Aberrant origin of the superior thyroid artery and the tracheoesophageal branch from the common carotid artery: a source of failure in elastase-induced aneurysms in rabbits. AJR Am J Roentgenol 181:739–741
Ding YH, Dai D, Lewis DA, et al (2005) Can neck size in elastase-induced aneurysms be controlled? A prospective study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2364–2367
Carsten CG 3rd, Calton WC, Johanning JM, et al (2001) Elastase is not sufficient to induce experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 33:1255–1262
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health grant NS42646. The authors thank Brian Hoh, MD, for his ongoing collaborative efforts.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors’ contributions
-
Guarantor of integrity of the entire study: Yonghong Ding and David F. Kallmes
-
Study concepts: Yonghong Ding and David F. Kallmes
-
Study design: David F. Kallmes and Yonghong Ding
-
Definition of intellectual content: Yonghong Ding and David F. Kallmes
-
Literature research: Yonghong Ding and David F. Kallmes
-
Clinical studies: not applicable
-
Experimental studies: Yonghong Ding, Mark A. Danielson, Ramanathan Kadirvel, Daying Dai, Debra A. Lewis, and David F. Kallmes
-
Data acquisition: Yonghong Ding, Daying Dai, Mark A. Danielson
-
Data analysis: Yonghong Ding and David F. Kallmes
-
Statistical analysis: Debra A. Lewis and Yonghong Ding
-
Manuscript preparation: Yonghong Ding
-
Manuscript editing: Yonghong Ding and David F. Kallmes
-
Manuscript review: David F. Kallmes and Harry J. Cloft
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y.H., Danielson, M.A., Kadirvel, R. et al. Modified technique to create morphologically reproducible elastase-induced aneurysms in rabbits. Neuroradiology 48, 528–532 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0093-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0093-0