Abstract
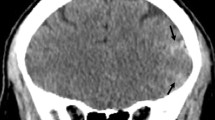
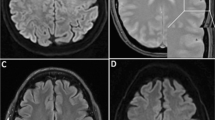
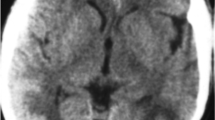
Posterior encephalopathy is characterised by headache, impairment of consciousness, seizures and progressive visual loss. MRI shows bilateral, predominantly posterior, cortical and subcortical lesions with a distribution. Our aim was to analyse the MRI lesion pattern and angiographic findings because the pathophysiology of posterior encephalopathy is incompletely understood. We report three patients with clinical and imaging findings consistent with posterior encephalopathy who underwent serial MRI including diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and construction of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps, and four-vessel digital subtraction angiography (DSA). DWI revealed symmetrical subcortical and cortical parieto-occipital high signal. High and also low ADCs indicated probable vasogenic and cytotoxic oedema. On follow-up there was focal cortical laminar necrosis, while the white-matter lesions resolved almost completely, except in the arterial border zones. DSA revealed diffuse arterial narrowing, slightly more marked in the posterior circulation. These findings suggest that posterior encephalopathy may in some cases be due to diffuse, severe vasospasm affecting especially in the parieto-occipital grey matter, with its higher vulnerability to ischemia. Cerebral vasospasm due to digitoxin intoxication, resulting in posterior encephalopathy, has not yet been described previously.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casey S, Sampaio RC, Michel E, Truwit CL (2000) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: utility of fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in the detection of cortical and subcortical lesions. AJNR 21: 1199–1206
Schwartz RB, Feske SK, Polak JF, et al (2000) Preeclampsia-eclampsia: clinical and neuroradiographic correlates and insights into the pathogenesis of hypertensive encephalopathy. Radiology 217: 371–376
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, et al (1996) A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med 334: 494–500
Schaefer PW, Buonanno FS, Gonzalez RG, Schwamm LH (1997) Diffusion-weighted imaging discriminates between cytotoxic and vasogenic edema in a patient with eclampsia. Stroke 28: 1082–1085
Pavlakis SG, Frank Y, Chusid R (1999) Hypertensive encephalopathy, reversible occipitoparietal encephalopathy, or reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy: three names for an old syndrome. J Child Neurol 14: 277–281
Ay H, Buonanno FS, Schäfer PW, Le DA, Wang B, Gonzales RG, Koroshetz WJ (1998) Posterior leukoencephalopathy without severe hypertension: utility of diffusion-weighted MRI. Neurology 53: 1372–1373
Antunes NL, Small TN, George D, Boulad F, Lis E (1999) Posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome may not be reversible. Pediatr Neurol 20: 241–243
Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG (2002) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. AJNR 23: 1038–1048
Sengar AR, Gupta RA, Dhanuka AK, Roy R, Das K (1997) MR imaging, MR angiography, and MR spectroscopy of the brain in eclampsia. AJNR 18: 1485–1490
Schwartz RB, Bravo SM, Klufas RA, et al (1995) Cyclosporine neurotoxicity and its relationship to hypertensive encephalopathy: CT and MR findings in 16 cases. Am J Roentgenol 165: 627–631
Gijtenbeek JM, van den Bent MJ, Vecht CJ (1999) Cyclosporine neurotoxicity: a review. J Neurol 246: 339–346
Lewis MB (1999) Cyclosporine neurotoxicity after chemotherapy: cyclosporine causes reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Br Med J 319: 54–55
Lin JT, Wang SJ, Fuh JL, Hsiao LT, Lirng JF, Chen PM (2003) Prolonged reversible vasospasm in cyclosporine A-induced encephalopathy. AJNR 24: 102–104
Kastrup O, Maschke M, Wanke I, Diener HC (2002) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome due to severe hypercalcemia. J. Neurol 249: 1563–1566
Utz N, Kinkel B, Hedde JP, Bewermeyer H (2001) MR imaging of acute intermittent porphyria mimicking reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Neuroradiology 43: 1059–1062
Celik M, Forta H, Dalkilic T, Babacan G (2002) MRI reveals reversible lesions resembling posterior reversible encephalopathy in porphyria. Neuroradiology 44: 839–841
Russell MT, Nassif AS, Cacyorin ED, Awwad E, Perman W, Dunphy F (2001) Gemcitabine-associated posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: MR imaging and MR spectroscopy findings. Magn Reson Imaging 19: 129–132
Ito Y, Arahata Y, Goto Y, Hirayama M (1998) Cisplatin neurotoxicity presenting as reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. AJNR 19: 415–417
Raps EC, Galetta SL, Broderick M, Atlas SW (1993) Delayed peripartum vasculopathy: cerebral eclampsia revisited. Ann Neurol 33: 222–225
Lewis LK, Hinshaw DB, Will AD, Hasso AN, Thompson JR (1988) CT and angiographic correlation of severe neurological disease in toxemia of pregnancy. Neuroradiology 30: 59–64
Ito T, Sakai T, Inagawa S, Utsu M, Bun T (1995) MR angiography of cerebral vasospasm in preeclampsia. AJNR 16: 1344–1346
Coughlin WF, McMurdo K, Reeves T (1989) MR imaging of postpartum cortical blindness. J Comput Assist Tomogr 13: 572–576
Zunker P, Golombeck K, Brossmann J, Georgiadis D, Deuschl G (2002) Post-partum cerebral angiopathy: repetitive TCD, MRI, MRA and EEG examinations. Neurol Res 24: 570–572
Schäfer PW, Gonzales RG, Hunter G, Wang B, Koroshetz WJ, Schwamm LH (2001) Diagnostic value of apparent diffusion coefficient hyperintensity in selected patients with acute neurologic deficits. J Neuroimaging 11: 369–380
Engelter ST, Provenzale JM, Petrella JR (2000) Assessment of vasogenic edema in eclampsia using diffusion imaging. Neuroradiology 42: 818–820
Provenzale JM, Petrella JR, Cruz LCH, Wong JC, Engelter S, Barboriak DB (2001) Quantitative assessment of diffusion abnormalities in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR 22: 1455–1461
Manfredi M, Beltramello A, Bongiovanni LG, Polo A, Pistoia L, Rizzuto N (1997) Eclamptic encephalopathy: imaging and pathogenetic considerations. Acta Neurol Scand 96: 277–282
Port JD, Beauchamp NJ (1998) Reversible intracerebral pathologic entities mediated by vascular autoregulatory dysfunction. Radiographics 18: 353–367
Higman MA, Port JD, Beauchamp NJ, Chen AR (2000) Reversible leukoencephalopathy associated with re-infusion of DMSO preserved stem cells. Bone Marrow Transplant 26: 797–800
Giminez-Mesa E, Martinez-Salio A, Porta-Etessam J, Berbel Garcia A, Cedena Romero T, Salam Bendoyan P (2001) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy in a patient with non-Hodgkin lymphoma after treatment with CHOP. Ann Med Intern 18: 591–593
Dillon WP, Rowley H (1998) The reversible posterior cerebral edema syndrome. AJNR 19: 591
Sundgren PC, Edvardsson B, Holtås S (2002) Serial investigation of perfusion disturbances and vasogenic oedema in hypertensive encephalopathy by diffusion and perfusion weighted imaging. Neuroradiology 44: 299–304
Henderson RD, Rajah T, Nicol AJ, Read SJ (2003) Posterior leukoencephalopathy following intrathecal chemotherapy with MRA-documented vasospasm. Neurology 60: 326–328
Heo K, Park SA, Lee JY, Lee BI, Lee SK (2003) Post-transfusion posterior leukoencephalopathy with cytotoxic and vasogenic edema precipitated by vasospasm. Cerebrovasc Dis 15: 230–233
Cunningham FG, Fernandez CO, Hernandez C (1995) Blindness associated with preeclampsia and eclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 172: 1291–1298
Trommer BL, Homer D, Mikhael MA (1988) Cerebral vasospasm and eclampsia. Stroke 19: 326–329
Coley SC, Porter DA, Calamante F, Chong WK, Connelly A (1999) Quantitative MR diffusion mapping and cyclosporine-induced neurotoxicity. AJNR 20: 1507–1510
Mukherjee P, McKinstry RC (2001) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: evaluation with diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology 219: 756–765
Sticherling C, Berkefeld J, Auch-Schwelk W, Lanfermann H (1998) Transient bilateral cortical blindness after coronary angiography. Lancet 351: 570
Zwicker JC, Sila CA (2002) MRI findings in a case of transient cortical blindness after cardiac catheterisation. Cathet Cardiovasc Intervent 57: 47–49
Tuxhorn I, Holthausen H, Ebener A, Noachtar S (1994) Reversible cortical edema mimicking cortical dysplasia in mitochondrial disorder. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57: 1439
Yaffe K, Ferriero D, Barkovich AJ, Rowley H (1995) Reversible MRI abnormalities following seizures. Neurology 45: 104–108
de Bruijn SFTM, de Haan RJ, Stam J (2001) Clinical features and prognostic factors of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in a prospective series of 59 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70: 105–108
Caplan LR (1980) “Top of the basilar” syndrome. Neurology 30: 72–79
Uson-Martin M, Gracia-Naya M (1999) Top of the basilar artery syndrome: clinico-radiological aspects of 25 patients. Rev Neurol 28: 698–701
Osborn AG (1994) Diagnostic neuroradiology. Mosby, St Louis, pp 373–378
Harris KG, Tran DD, Sickels WJ, Cornell SH, Yuh WTC (1994) Diagnosing intracranial vasculitis: the roles of MR and angiography. AJNR 15: 317–330
Moore PM, Richardson B (1998) Neurology of the vasculitides and connective tissue diseases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 65: 10–22
Pomper MG, Miller TJ, Stone HJ, Tidmore WC, Hellmann DB (1999) CNS vasculitis in autoimmune disease: MR imaging findings and correlation with angiography. AJNR Neuroradiol 20: 75–85
Ohkuma H, Suzuki S, Shimamura N, Nakano T (2003) Dissecting aneurysms of the middle cerebral artery: neuroradiological and clinical features. Neuroradiology 45: 143–148
Acknowledgements
We thank Marina Heibel for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weidauer, S., Gaa, J., Sitzer, M. et al. Posterior encephalopathy with vasospasm: MRI and angiography. Neuroradiology 45, 869–876 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1059-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1059-0