Abstract
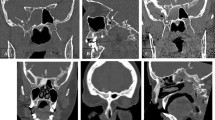
Our purpose was to evaluate the utility of intrathecal gadopentetate dimeglumine -enhanced magnetic resonance cisternography (GdMRC). We injected 0.5 ml contrast medium into the subarachnoid space via lumbar puncture in 20 patients with suspected cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) rhinorrhoea. MRC showed CSF leakage in 14 patients with rhinorrhoea at the time of the examination, into the ethmoid air cells in nine, the sphenoid sinus in three and the frontal sinus in two cases. In 12 of these the site leakage was confirmed during surgical repair of the fistula. No leakage was observed in four patients with intermittent rhinorrhoea, not present at the time of the examination. GdMRC showed leakage in two patients with negative CT cisternography. GdMRC may prove better than CT cisternography, especially with slow CSF flow. We also showed low-dose GdMRC to be a feasible and relative safe way of confirming the presence of and localising active CSF leaks prior to surgical repair.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park J, Strelzow V, Friedman W (1983) Current management of cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea. Laryngoscope 93: 1924–1300
Stafford-Johnson DB, Brennan P, Toland J, O’Dwyer AJ (1996) Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of the cerebrospinal fluid fistula. Clin Radiol 51: 837–841
Colquhoun IR (1993) CT cisternography in the investigation of cerebrospinal rhinorrhoea. Clin Radiol 47: 403–408
Manelfe C, Cellerier P, Sobel D, Prevost C, Bonafé A (1982) Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea: evaluation with metrizamide cisternography. Am J Roentgenol 138: 471–476
Nickaus P, Dutcher PO, Kido DK, Hengerer AS, Nelson CN (1998) New imaging techniques in the diagnosis of cerebrospinal fluid fistula. Laryngoscope 98: 1065–1068
Lloyd MNH, Kimber PM, Burrows EH (1994) Posttraumatic cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhoea: modern high-resolution computed tomography is all that is required for effective demonstration of the site of leakage. Clin Radiol 49: 100–103
Ahmadi J, Weiss MH, Segall HD, Schultz DH, Zee CS, Giannotta SL (1985) Evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea by metrizamide computed tomography. Neurosurgery 16: 54–59
Drayer BP, Wilkins RH, Boehnke M, Horton JA, Rosenbaum AE (1977) Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea demonstrated by metrizamide CT cisternography. Am J Roentgenol 129: 149–151
Stone JA, Castillo M, Neelon B Mukherji SK (1999) Evaluation of CSF leaks: high-resolution CT compared with contrast-enhanced CT and radionuclide cisternography. AJNR 20: 706–712
Eljamel MS, Pidgeon CN, Toland JB, Phillips J, O’Dwyer AJ (1994) MRI cisternography and the localization of CSF fistulae. Br J Neurosurg 8: 433–437
El Gammal T, Brooks BS (1994) MR cisternography: initial experience in 41 cases. AJNR 15: 1647–1656
Eberhardt KEW, Hollenbach HP, Deimling M, Tomandl BF, Huk WJ (1997) MR cisternography: a new method for the diagnosis of CSF fistulae. Eur Radiol 7: 1485–1491
Muftah S, Eljamel M, Christopher N, et al (1994) MRI cisternography, and the localization of CSF fistula. Br J Neurosurg 8: 433–437
Hegarty SE, Millar JS (1997) MRI in the localization of CSF fistulae: is it of any value? Clin Radiol 52: 768–770
Sand T, Myhr G, Stovner LJ, Dale LG (1990) Side effects after lumbar iohexol myelography: relation to radiological diagnosis, sex and age. Neuroradiology 31: 523–528
Van de Kelft E, Bosmans J, Paziel P, Van Vyve PM, Selosse P (1991) Intracerebral hemorrhage after lumbar myelography with iohexol: report of a case and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 28: 570–574
Di Chiro G, Knop RH, Girton MR, et al (1985) MR cisternography and myelography with Gd-GTPA in monkeys. Radiology 157: 373–377
Jinkins JR, Williams RF, Xiong L (1999) Evaluation of gadopentetate dimeglumine magnetic resonance cisternography in an animal model. Invest Radiol 34: 156–159
Jinkins JR, Rudwan M, Krumina G, Tali T (2002) Intrathecal gadolinium-enhanced MR cisternography in the evaluation of clinically suspected cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea in humans: early experience. Radiology 222: 555–559
Ray DE, Cavanagh JB, Nolan CC, Williams SCR (1996) Neurotoxic effects of gadopentetate dimeglumine: behavioral disturbance and morphology after intracerebroventricular injection in rats. AJNR 17: 365–373
Ray DE, Holton JL, Nolan CC, Cavanagh JB, Harpur ES (1998) Neurotoxic potential of gadodiamide after injection into the lateral cerebral ventricle of rats. AJNR 19: 1455–1462
Skalpe IO, Tang GJ (1997) Magnetic resonance imaging contrast media in the subarachnoid space: a comparison between gadodiamide injection and gadopentetate dimeglumine in an experimental study in pigs. Invest Radiol 32: 140–148
Zeng Q, Xiong L, Jinkins JR, Fan Z, Liu Z (1999) Intrathecal gadolinium (gadopentetate dimeglumine)-enhanced MR myelography: a pilot study in human patients. Am J Roentgenol 173: 1109–1115
Siebner HR, Grafin von Einsiedel H, Conrad B (1997) Magnetic resonance ventriculography with gadolinium DTPA: report of two cases. Neuroradiology 39: 418–422
Shetty PG, Shroff MM, Sahani DV, Kirtane MV(1998) Evaluation of high-resolution CT and MR cisternography in the diagnosis of cerebrospinal fluid fistula. AJNR 19: 633–639
Wenzel R, Leppien A (2000) Gadolinium-myelocisternography for cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhoea. Neuroradiology 42: 874–880
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aydin, K., Guven, K., Sencer, S. et al. MRI cisternography with gadolinium-containing contrast medium: its role, advantages and limitations in the investigation of rhinorrhoea. Neuroradiology 46, 75–80 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1004-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1004-2