Abstract
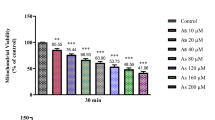
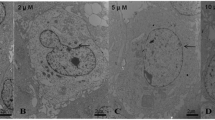
Arsenic is successfully used in cancer chemotherapy and several cancer treatments on account of its apoptogenic effects. However, it is environmentally hazardous with potential for toxicity when distributed in the soil, water, and food, and long exposure to water contaminated with Arsenic may induce cancers. Some research studies have reported that liver is the storage site and an important target organ for Arsenic toxicity. In the present work, a new kind of organic arsenic compound, 4-(2-nitrobenzaliminyl) phenyl arsenoxide (NPA), was synthesized, and its potential involvement of mitochondria was explored. The results presented that the toxicology of NPA, at least in part, mediated mitochondrial function and may thoroughly destroy mitochondrial membrane physiological functions. NPA induced mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mtPTP) opening that induces mitochondrial biochemical abnormalities as evidenced by mitochondrial swelling, mitochondrial membrane potential breakdown, membrane fluidity alterations, and the strikingly remarkable protection of CsA. Meanwhile, both the decreased respiration rate of state 4 and the increased inner membrane H+ permeabilization revealed that the inner membrane function regarding important energy production chain was destroyed. The toxicity of NPA is due to its interaction with mitochondrial membrane thiol protein. This conclusion is based on the protective effects of RR, DTT, and MBM+.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlam VJ, Harrison JC, Porteous CM, James AM, Smith RAJ, Murphy MP, Sammut IA (2005) Targeting an antioxidant to mitochondria decreases cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J 19(9):1088–1095
Bae JH, Park JW, Kwon TK (2003) Ruthenium red, inhibitor of mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter, inhibits curcumin-induced apoptosis via the prevention of intracellular Ca2+ depletion and cytochrome c release. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303(4):1073–1079
Belyaeva EA, Korotkov SM (2003) Mechanism of primary Cd2+-induced rat liver mitochondria dysfunction: discrete modes of Cd2+ action on calcium and thiol-dependent domains. Toxicol Appl Pharm 192(1):56–68
Bustamante J, Nutt L, Orrenius S, Gogvadze V (2005) Arsenic stimulates release of cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria via induction of mitochondrial permeability transition. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207(2):110–116
Castanha Zanoli JC, Maioli MA, Medeiros HC, Mingatto FE (2012) MingattoAbamectin affects the bioenergetics of liver mitochondria: a potential mechanism of hepatotoxicity. Toxicol In Vitro 26(1):51–56
Chen XY, Hu XL, Xia CF, Qin CQ, Liu Y (2013) Antibacterial evaluation of novel organoarsenic compounds by the microcalorimetric method. Biol Trace Elem Res 153(1–3):382–389
Choong TSY, Chuah TG, Robiah Y, Gregory Koay FL, Azni I (2007) Arsenic toxicity, health hazards and removal techniques from water: an overview. Desalination 217:139–166
Dong JX, Zhao GY, Yu QLY, Li R, Yuan L, Chen J, Liu Y (2013) Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by Honokiol. J Membr Biol 246(5):375–381
Eliseev RA, Salter JD, Gunter KK, Gunter TE (2003) Bcl-2 and tBid proteins counter-regulate mitochondrial potassium transport. Biochim Biophys Acta 1604(1):1–5
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48(12):909–930
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Bioenerg Biomenbr 177(2):751–766
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH, Park WH (2008) Arsenic trioxide inhibits the growth of Calu-6 cells via inducing a G2 arrest of the cell cycle and apoptosis accompanied with the depletion of GSH. Cancer Lett 270(1):40–55
Hosseini MJ, Shaki F, Ghazi-Khansari M, Pourahmad J (2013) Toxicity of Arsenic (III) on isolated liver mitochondria: a new mechanistic. Appr Iran J Pharmaceut Res 12:121–138
Kroemer G, Reed JC (2000) Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat Med 6(5):513–519
Leung AW, Varanyuwatana P, Halestrap AP (2008) The mitochondrial phosphate carrier interacts with cyclophilin D and may play a key role in the permeability transition. J Biol Chem Bioenergy 283(39):26312–26323
Li JH, Zhang Y, Xiao Q, Tian FF, Liu XR, Li R, Zhao GY, Jiang FL, Liu Y (2011) Mitochondria as target of quantum dots toxicity. J Hazard Mater 194:440–444
Liu J, Waalkes MP (2008) Liver is a target of arsenic carcinogenesis. Toxicol Sci 105(1):24–32
Liu XR, Li JH, Zhang Y, Ge YS, Tian FF, Dai J, Jiang FL, Liu Y (2011) Mitochondrial permeability transition induced by different concentrations of Zinc. J Membr Biol 244(3):105–112
Miller WH Jr, Schipper HM, Lee JS, Singer J, Waxman S (2002) Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res 62(14):3893–3903
Murphy MP (2001) How understanding the control of energy metabolism can help investigation of mitochondrial dysfunction, regulation and pharmacology. BBA-Bioenergetics 1504(1):1–11
National Research Council (NRC) (2001) Subcommittee to update the 1999 arsenic in drinking water report. Arsenic in drinking water 2001 update. National Academy Press, Washington, pp 24–74
Newmeyer DD, Ferguson-Miller S (2003) Mitochondria: releasing power for life and unleashing the machineries of death. Cell 112(4):481–490
Niki E, Yoshida Y, Saito Y, Noguchi N (2005) Lipid peroxidation: mechanisms, inhibition, and biological effects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338(1):668–676
Nordstrom DK (2002) Worldwide occurrences of arsenic in ground water. Science 296(5576):2143–2145
Paul MK, Kumar R, Mukhopadhyay AK (2008) Dithiothreitol abrogates the effect of arsenic trioxide on normal rat liver mitochondria and human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharm 226(2):140–152
Puntel RL, Roos DH, Folmer V, Nogueira CW, Galina A, Aschner M, Rocha JB (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by different organochalchogens is mediated by thiol oxidation and is not dependent of the classical mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. Toxicol Sci 117(1):133–143
Ricchelli F, Beghetto C, Gobbo S, Tognon G, Moretto V, Crisma M (2003) Structural modifications of the permeability transition pore complex in resealed mitochondria induced by matrix-entrapped disaccharides. Arc Biochem Biophys 410(1):155–160
Robson LP, Daniel HR, Vanderlei F, Cristina WN, Antonio G, Michael A, João BTR (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by different organochalchogens is mediated by thiol oxidation and is not dependent of the classical mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. Toxicol Sci 117(1):133–143
Rojewski MT, Korper S, Thiel E, Schrezenmeier H (2004) Depolarization of mitochondria and activation of caspases are common features of arsenic(III)-induced apoptosis in myelogenic and lymphatic cell lines. Chem Res Toxicol 17(1):119–128
Vaseva AV, Marchenko ND, Ji K, Tsirka SE, Holzmann S, Moll UM (2012) p53 opens the mitochondrial permeability transition pore to trigger necrosis. Cell 149(7):1536–1548
Wu DD, Xiao YF, Geng Y, Hou J (2010) Antitumor effect and mechanisms of arsenic trioxide on subcutaneously implanted human gastric cancer in nude mice. Cancer Genet Cytogen 198(2):90–96
Yu SP (2003) Regulation and critical role of potassium homeostasis in apoptosis. Prog Neurobiol 70(4):363–386
Zhang TD, Chen GQ, Wang ZG, Zhen YW, Chen SJ, Chen Z (2001) Arsenic trioxide, a therapeutic agent for APL. Oncogene 20(49):7146–7153
Zhang Y, Li JH, Liu XR, Jiang FL, Tian FF, Liu Y (2011) Spectroscopic and microscopic studies on the mechanisms of mitochondrial toxicity induced by different concentrations of cadmium. J Membr Biol 241(1):39–49
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21225313); Hubei Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 3013CFC027); B Plan of Hubei Provincial Education Office of China (No. B20114404) and the Hubei Polytechnic University Program of China (No.14xjz03A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, YH., Zhang, Q., Pan, LL. et al. Rat Liver Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by an Organic Arsenical Compound 4-(2-Nitrobenzaliminyl) Phenyl Arsenoxide. J Membrane Biol 248, 1071–1078 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-015-9818-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-015-9818-5