Abstract
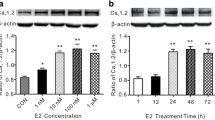
TASK channels, an acid-sensitive subgroup of two pore domain K+ (K2P) channels family, were widely expressed in a variety of neural tissues, and exhibited potent functions such as the regulation of membrane potential. The steroid hormone estrogen was able to interact with K+ channels, including voltage-gated K+ (Kv) and large conductance Ca2+-activated (BK) K+ channels, in different types of cells like cardiac myocytes and neurons. However, it is unclear about the effects of estrogen on TASK channels. In the present study, the expressions of two members of acid-sensitive TASK channels, TASK-1 and TASK-2, were detected in mouse neuroblastoma N2A cells by RT-PCR. Extracellular acidification (pH 6.4) weakly but statistically significantly inhibited the outward background current by 22.9 % at a holding potential of 0 mV, which inactive voltage-gated K+ currents, suggesting that there existed the functional TASK channels in the membrane of N2A cells. Although these currents were not altered by the acute application of 100 nM 17β-estradiol, incubation with 10 nM 17β-estradiol for 48 h reduced the mRNA level of TASK-1 channels by 40.4 % without any effect on TASK-2 channels. The proliferation rates of N2A cells were also increased by treatment with 10 nM 17β-estradiol for 48 h. These data implied that N2A cells expressed functional TASK channels and chronic exposure to 17β-estradiol downregulated the expression of TASK-1 channels and improved cell proliferation. The effect of 17β-estradiol on TASK-1 channels might be an alternative mechanism for the neuroprotective action of 17β-estradiol.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller MI, Veale EL, Linden AM, Sandu C, Schwaninger M, Evans LJ, Korpi ER, Mathie A, Wisden W, Brickley SG (2005) Modifying the subunit composition of TASK channels alters the modulation of a leak conductance in cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurosci 25:11455–11467
Barrett-Connor E, Bush TL (1991) Estrogen and coronary heart disease in women. JAMA 265:1861–1867
Bayliss DA, Barrett PQ (2008) Emerging roles for two-pore-domain potassium channels and their potential therapeutic impact. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:566–575
Brickley SG, Aller MI, Sandu C, Veale EL, Alder FG, Sambi H, Mathie A, Wisden W (2007) TASK-3 two-pore domain potassium channels enable sustained high-frequency firing in cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurosci 27:9329–9340
Burg ED, Remillard CV, Yuan JX (2006) K+ channels in apoptosis. J Membr Biol 209:3–20
Carrer HF, Araque A, Buno W (2003) Estradiol regulates the slow Ca2+-activated K+ current in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 23:6338–6344
Decher N, Wemhoner K, Rinne S, Netter MF, Zuzarte M, Aller MI, Kaufmann SG, Li XT, Meuth SG, Daut J, Sachse FB, Maier SK (2011) Knock-out of the potassium channel TASK-1 leads to a prolonged QT interval and a disturbed QRS complex. Cell Physiol Biochem 28:77–86
Druzin M, Malinina E, Grimsholm O, Johansson S (2011) Mechanism of estradiol-induced block of voltage-gated K+ currents in rat medial preoptic neurons. PLoS One 6:e20213
Duprat F, Lesage F, Fink M, Reyes R, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M (1997) TASK, a human background K+ channel to sense external pH variations near physiological pH. EMBO J 16:5464–5471
Enyedi P, Czirjak G (2010) Molecular background of leak K+ currents: two-pore domain potassium channels. Physiol Rev 90:559–605
Fatehi M, Kombian SB, Saleh TM (2005) 17β-estradiol inhibits outward potassium currents recorded in rat parabrachial nucleus cells in vitro. Neuroscience 135:1075–1086
Green PS, Simpkins JW (2000) Neuroprotective effects of estrogens: potential mechanisms of action. Int J Dev Neurosci 18:347–358
Kelly MJ, Levin ER (2001) Rapid actions of plasma membrane estrogen receptors. Trends Endocrinol Metab 12:152–156
Lauritzen I, Zanzouri M, Honore E, Duprat F, Ehrengruber MU, Lazdunski M, Patel AJ (2003) K+-dependent cerebellar granule neuron apoptosis. Role of task leak K+ channels. J Biol Chem 278:32068–32076
Lesage F, Guillemare E, Fink M, Duprat F, Lazdunski M, Romey G, Barhanin J (1996) TWIK-1, a ubiquitous human weakly inward rectifying K+ channel with a novel structure. EMBO J 15:1004–1011
Leung YM, Huang CF, Chao CC, Lu DY, Kuo CS, Cheng TH, Chang LY, Chou CH (2011) Voltage-gated K+ channels play a role in cAMP-stimulated neuritogenesis in mouse neuroblastoma N2A cells. J Cell Physiol 226:1090–1098
Li X, Dong X, Zheng S, Xiao J (2013a) Expression and localization of TASK-1, -2 and -3 channels in MG63 human osteoblast-like cells. Oncol Lett 5:865–869
Li X, Zheng S, Dong X, Xiao J (2013b) 17β-Estradiol inhibits outward voltage-gated K(+) currents in human osteoblast-like MG63 cells. J Membr Biol 246:39–45
Medhurst AD, Rennie G, Chapman CG, Meadows H, Duckworth MD, Kelsell RE, Gloger II, Pangalos MN (2001) Distribution analysis of human two pore domain potassium channels in tissues of the central nervous system and periphery. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 86:101–114
Mendez P, Garcia-Segura LM (2006) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and glycogen synthase kinase 3 regulate estrogen receptor-mediated transcription in neuronal cells. Endocrinology 147:3027–3039
Moller C, Netzer R (2006) Effects of estradiol on cardiac ion channel currents. Eur J Pharmacol 532:44–49
Naftolin F, Cutmann JN, Decherney AH, Sarrel PM (1990) Ovarian secretions and cardiovascular and neurological function. Raven, New York
Nishimura I, Ui-Tei K, Saigo K, Ishii H, Sakuma Y, Kato M (2008) 17beta-estradiol at physiological concentrations augments Ca(2+)-activated K+ currents via estrogen receptor beta in the gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuronal cell line GT1-7. Endocrinology 149:774–782
Prediger ME, Gamaro GD, Crema LM, Fontella FU, Dalmaz C (2004) Estradiol protects against oxidative stress induced by chronic variate stress. Neurochem Res 29:1923–1930
Reyes R, Duprat F, Lesage F, Fink M, Salinas M, Farman N, Lazdunski M (1998) Cloning and expression of a novel pH-sensitive two pore domain K+ channel from human kidney. J Biol Chem 273:30863–30869
Runnebaum B, Raube T (1987) Gynaekologische endokrinologie. Springer, New York
Sawada H, Ibi M, Kihara T, Urushitani M, Honda K, Nakanishi M, Akaike A, Shimohama S (2000) Mechanisms of antiapoptotic effects of estrogens in nigral dopaminergic neurons. FASEB J 14:1202–1214
Sullivan JM, Vander Zwaag R, Lemp GF, Hughes JP, Maddock V, Kroetz FW, Ramanathan KB, Mirvis DM (1988) Postmenopausal estrogen use and coronary atherosclerosis. Ann Intern Med 108:358–363
Tanabe S, Hata T, Hiraoka M (1999) Effects of estrogen on action potential and membrane currents in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol 277:H826–H833
Torgerson DJ, Bell-Syer SE (2001) Hormone replacement therapy and prevention of nonvertebral fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. JAMA 285:2891–2897
Valen-Sendstad A, Engedal K, Stray-Pedersen B, Strobel C, Barnett L, Meyer N, Nurminemi M (2010) Effects of hormone therapy on depressive symptoms and cognitive functions in women with Alzheimer disease: a 12 month randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of low-dose estradiol and norethisterone. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 18:11–20
Valverde MA, Rojas P, Amigo J, Cosmelli D, Orio P, Bahamonde MI, Mann GE, Vergara C, Latorre R (1999) Acute activation of Maxi-K channels (hSlo) by estradiol binding to the beta subunit. Science 285:1929–1931
Watson CS, Gametchu B (2003) Proteins of multiple classes may participate in nongenomic steroid actions. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 228:1272–1281
White RE, Han G, Maunz M, Dimitropoulou C, El-Mowafy AM, Barlow RS, Catravas JD, Snead C, Carrier GO, Zhu S, Yu X (2002) Endothelium-independent effect of estrogen on Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res 53:650–661
Wroolie TE, Kenna HA, Williams KE, Powers BN, Holcomb M, Khaylis A, Rasgon NL (2011) Differences in verbal memory performance in postmenopausal women receiving hormone therapy: 17β-estradiol versus conjugated equine estrogens. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 19:792–802
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grants from Academic team of SCUN (CTZ12017 and CTZ 13017) and Basic Research Project of SCUN (YCZY12019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, X., Li, X. & Li, X. 17β-Estradiol Downregulated the Expression of TASK-1 Channels in Mouse Neuroblastoma N2A Cells. J Membrane Biol 247, 273–279 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9632-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9632-5