Abstract
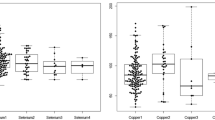
Trace elements are essential components of biological structures, but alternatively, they can be toxic at concentrations beyond those necessary for their biological functions. Changes in the concentration of essential trace elements and heavy metals may affect acute hemorrhagic stroke. The aim of this study was to measure serum levels of essential trace elements [iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), copper (Cu), and magnesium (Mg)] and heavy metals [cobalt (Co), cadmium (Cd), and lead (Pb)] in patients with acute hemorrhagic stroke. Twenty-six patients with acute hemorrhagic stroke and 29 healthy controls were enrolled. Atomic absorption spectrophotometry (UNICAM-929) was used to measure serum Fe, Cu, Pb, Cd, Zn, Co, Mn and Mg concentrations. Serum Cd, Pb and Fe levels were significantly higher in patients with acute hemorrhagic stroke than controls (p < 0.001), while serum Cu, Zn, Mg and Mn levels were significantly lower (all p < 0.001). However, there was no significant difference between the groups with respect to serum Co levels (p > 0.05). We first demonstrate increased Cd, Pb, and Fe levels; and decreased Cu, Zn, Mg, and Mn levels in patients with acute hemorrhagic stroke. These findings may have diagnostic and prognostic value for acute hemorrhagic stroke. Further studies are required to elucidate the roles of trace elements and heavy metals in patients with acute hemorrhagic stroke.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams H, Bendixen B, Kappelle L, Biller J, Love B, Gordon D, Marsh EE 3rd (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke 24:35–41
Aggett PJ (1999) An overview of the metabolism of copper. Eur J Med Res 4:214–216
Altamura C, Squitti R, Pasqualetti P, Gaudino C, Palazzo P, Tibuzzi F, Lupoi D, Cortesi M, Rossini PM, Vernieri F (2009) Ceruloplasmin/Transferrin system is related to clinical status in acute stroke. Stroke 40:1282–1288
Anderson MB, Pedigo NG, Katz RP, George WJ (1992) Histopathology of testes from mice chronically treated with cobalt. Reprod Toxicol 6:41–50
Arslan M, Demir H, Arslan H, Gokalp AS, Demir C (2011) Trace elements, heavy metals and other biochemical parameters in malignant glioma patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 12(2):447–451
Atasoy N, Mercan U, Alacabey I, Kul AR (2011) Levels of heavy metals and certain macro elements in potable and tap water at Van City Center. Hacettepe J Biol Chem 39:391–396
Beard J, Connor J, Jones B (1993) Iron in the brain. Nutr Rev 51:157–170
Benmoyal-Segal L, Vander T, Shifman S, Bryk B, Ebstein RP, Marcus EL, Stessman J, Darvasi A, Herishanu Y, Friedman A, Soreq H (2005) Acetylcholinesterase/paraoxonase interactions increase the risk of insecticide-induced Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J 19:452–454
Bradbury MW (1992) An approach to study of transport of trace metals at the blood-brain barrier. Prog Brain Res 91:133–138
Bureau I, Anderson RA, Arnaud J, Raysiguier Y, Favier AE, Roussel AM (2002) Trace mineral status in post menopausal women: impact of hormonal replacement therapy. J Trace Elem Med Biol 16:9–13
Cartwright GE, Wintrobe MM (1964) Copper metabolism in normal subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 14:224–232
Dayani PN, Bishop MC, Black K, Zeltzer PM (2004) Desferoxamine (DFO)-mediated iron chelation: rationale for a novel approach to therapy for brain cancer. J Neurooncol 67:367–377
Demirdogen BC, Demirkaya S, Türkanoglu A, Bek S, Arinc E, Adali O (2009) Analysis of paraoxonase 1 (PON1) genetic polymorphisms and activities as risk factors for ischemic stroke in Turkish population. Cell Biochem Funct 27(8):558–567
Dexter DT, Wells FR, Lees AJ, Agid F, Agid Y, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1989) Increased nigral iron content and alterations in other metal ions occuring in brain in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 52:1830–1836
Dexter DT, Jenner P, Schapira AH, Marsden CD (1992) Alterations in levels of ıron, ferritin, and other trace metals in neurodegeneretive diseases affecting the basal ganglia. Ann Neurol 32:94–100
Dexter DT, Sian J, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1993) Implications of alterations in trace element levels in brain in Parkinson’s disease and other neurological disorders affecting the basal ganglia. Adv Neurol 60:273–281
Donma O, Donma MM (2002) Association of headaches and the metals. Biol Trace Elem Res 90:1–14
Ertekin A, DeGer Y, Mert H, Mert N, Yur F, Dede S, Demir H (2006) An investigation of the effects of alpha-tocopherol on the levels Fe, Cu, Zn, Mn and carbonic anhydrase in rats with bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Biol Trace Elem Res 114:1–12
Forte G, Bocca B, Senofonte O, Petrucci F, Brusa L, Stanzione P, Zannino S, Violante N, Alimonti A, Sancesario G (2004) Trace and major elements in whole blood, serum, cerebrospinal fluid and urine of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 111:1031–1040
Fraga Cesar G (2005) Relevance, essentiality and toxicity of trace elements in human health. Mol Aspect Med 26:235–244
Hickenbottom SL, Grotta J (1998) Neuroprotective therapy. Sem Neurol 18:485–492
Jomova K, Valko M (2011) Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 283:65–87
Kang YJ (2011) Copper and homocysteine in cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol Ther 129(3):321–331
Kayan M, Nazıroglu M, Barak C (2010) Effects of vitamin C and E combination on trace element levels in blood of smokers and nonsmokers radiology X-ray technicians. Biol Trace Elem Res 136:140–148
Kirchvink N, Martin N, Fievez L, Smith N, Marlin D, Gustin P (2006) Airway inflammation in cadmium-exposed rats is associated with pulmonary oxidative stress and emphysema. Free Radic Res 40:241–250
Klos A (2001) Lead, cadmium and mercury content in meals planned for consumption in selected kindergartens in Warsaw: IV International Scientific-Technical Conference, Warsaw, p 4–5
Kowalczyk E, Kopff A, Fijalkowski P, Kopff M, Niedworok J, Blaszczyk J, Kêdziora J, Tyoelerowicz P (2003) Effect of anthocyanins on selected biochemical parameters in rats exposed to cadmium. Acta Bio Pol 50:543–548
Leach RM Jr (1971) Role of manganese in mucopolysaccharide metabolism. Fed Proc 30:991–994
Levenson CW (2005) Trace metal regulation of neuronal apoptosis: from genes to behavior. Physiol Behav 15:399–406
Lichy C, Hacke W (2010) Stroke. Internist (Berl) 51(8):1003–1011
Lustberg M, Silbergeld E (2002) Blood lead levels and mortality. Arch Intern Med 162:2443–2449
Mahabir S, Spitz MR, Barrera SL, Beaver SH, Etzel C, Forman MR (2007) Dietary zinc, copper and selenium, and risk of lung cancer. Int J Cancer 120:1108–1115
Manca D, Ricard AC, Tra HV, Chevalier G (1994) Relation between lipid peroxidation and inflammation in the pulmonary toxicity of cadmium. Arch Toxicol 68:364–369
Meller L, Tage S, Kristensen TS (1992) Blood lead as a cardiovascular risk factor. Am J Epidemiol 136:1091–1100
Mertz W (1981) The essential trace elements. Science 213:1332–1338
Messner B, Knoflach M, Seubert A, Ritsch A, Pfaller K, Henderson B, Shen YH, Zeller I, Willeit J, Laufer G, Wick G, Kiechl S, Bernhard D (2009) Cadmium is a novel and independent risk factor for early atherosclerosis mechanisms and in vivo relevance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:1392–1394
Millan M, Sobrino T, Castellanos M, Nombela F, Arenillas JF, Riva E, Cristobo I, García MM, Vivancos J, Serena J, Moro MA, Castillo J, Dávalos A (2007) Increased body iron stores are associated with poor outcome after thrombolytic treatment in acute stroke. Stroke 38(1):90–95
Moos T (2002) Brain iron homeostasis. Dan Med Bull 49:279–301
Muir KW, Lees KR (1995) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial of ıntravenous magnesium sulfate in acute stroke. Stroke 26:1183–1188
Munshi A, Babu S, Kaul S, Shafi G, Rajeshwar K, Alladi S, Jyothy A (2010) Depletion of serum zinc in ischemic stroke patients. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 32(6):433–436
Nawrot TS, Thijs L, Den Hond EM, Roels HA, Staessen JA (2002) An epidemiological re-appraisal of the association between blood pressure and blood lead: a meta-analysis. J Hum Hypertens 16:123–131
No authors listed (1990) Special report From The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Classification of cerebrovascular diseases III. Stroke 21:637–676
Nordberg M (1978) Studies on metallothionein and cadmium. Environ Res 15:381–404
Ozkaya MO, Nazıroğlu M, Barak C, Berkkanoğlu M (2011) Effects of multivitamin/mineral supplementation on trace element levels in serum and follicular fluid of women undergoing in vitrofertilization (IVF). Biol Trace Elem Res 139:1–9
Pérez de la Ossa N, Sobrino T, Silva Y, Blanco M, Millán M, Gomis M, Agulla J, Araya P, Reverté S, Serena J, Dávalos A (2010) Iron-related brain damage in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 41(4):810–813
Rahnama M, Marcınıak A (2002) Influence of Estrogen Deficiency on the level of magnesium in rat mandible and teeth. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 46:267–271
Shenkin A (1997) Micronutrients and outcome. Nutrition 13:825–828
Sokolov DL, Bailey MR, Crum LA, Blomgren PM, Connors BA, Evan AP (2002) Prefocal alignment improves stone comminution in shockwave lithotripsy. J Endourol 16:709–715
Solioz M, Odermatt A, Krapf R (1994) Copper pumping ATPases: common concept in bacteria and man. FEBS Lett 346:44–47
Stabel JR, Spears JW, Brown TT (1993) Effect of copper deficiency on tissue, blood characteristics and immune function of calves challenged with infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus and Pasteurella hemolytica. J Anim Sci 71:1247–1255
Tapiero H, Townsend DM, Tew KD (2003) Trace elements in human physiology and pathology. Biomed Pharmacother 57:399–411
Teasdale G, Jenett B (1974) Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness: a practical scale. Lancet 2:81–83
Uza G, Comes L, Uza D, Pop O (1995) Serum zinc and copper in patients with cerebral vascular disease. Rom J Intern Med 33:19–26
Waisberg M, Joseph P, Hale B, Beyersmann D (2003) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology 192:95–117
Wenstrup D, Ehmann WD, Markesbery WR (1990) Trace element imbalances in isolated subcellular fractions of Alzheimer’s disease brains. Brain Res 533:125–131
Wu T, Sempos CT, Freudenheim JL, Muti P, Smit E (2004) Serum iron, copper and zinc concentrations and risk of cancer mortality in US adults. Ann Epidemiol 14:195–201
Zangieva ZK, Torshin IIu, Gromova OA, Nikonov AA (2013) Trace elements in the nervous tissue and ischemic stroke. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova 113:30–36
Acknowledgments
The authors do not report any conflicts of interest regarding this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karadas, S., Sayın, R., Aslan, M. et al. Serum Levels of Trace Elements and Heavy Metals in Patients with Acute Hemorrhagic Stroke. J Membrane Biol 247, 175–180 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9621-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-013-9621-0