Abstract
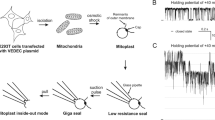
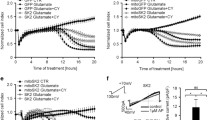
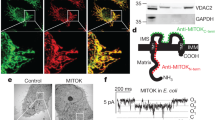
Our aim was to determine the subcellular localization and functional roles of the KATP channel subunit Kir6.1 in intracellular membranes. Specifically, we focused on the potential role of Kir6.1 as a subunit of the mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channel. Cell imaging showed that a major proportion of heterologously expressed Kir6.1-GFP and endogenously expressed Kir6.1 was distributed in the endoplasmic reticulum with little in the mitochondria or plasma membrane. We used pharmacological and molecular tools to investigate the functional significance of this distribution. The KATP channel opener diazoxide increased reactive oxygen species production, and glibenclamide abolished this effect. However, in cells lacking Kir6.1 or expressing siRNA or dominant negative constructs of Kir6.1, the same effect was seen. Ca2+ handling was examined in the muscle cell line C2C12. Transfection of the dominant negative constructs of Kir6.1 significantly reduced the amplitude and rate of rise of [Ca2+] c transients elicited by ATP. This study suggests that Kir6.1 is located in the endoplasmic reticulum and plays a role in modifying Ca2+ release from intracellular stores.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardehali H, Chen Z, Ko Y, Mejia-Alvarez R, Marban E (2004) Multiprotein complex containing succinate dehydrogenase confers mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channel activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11880–11885
Ashcroft FM, Gribble FM (1998) Correlating structure and function in ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Trends Neurosci 21:288–294
Babenko AP, AguilarBryan L, Bryan J (1998) A view of SUR/KIR6.X, KATP channels. Annu Rev Physiol 60:667–687
Bolsover S, Ibrahim O, O’luanaigh N, Williams H, Cockcroft S (2001) Use of fluorescent Ca2+ dyes with green fluorescent protein and its variants: problems and solutions. Biochem J 356:345–352
Coronado R, Miller C (1980) Decamethonium and hexamethonium block K+ channels of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature 288:495–497
Costa AD, Garlid KD (2008) Intramitochondrial signaling: interactions among mitoKATP, PKCepsilon, ROS, and MPT. Am J Physiol 295:H874–H882
Costa AD, Pierre SV, Cohen MV, Downey JM, Garlid KD (2008) cGMP signalling in pre- and post-conditioning: the role of mitochondria. Cardiovasc Res 77:344–352
Cui Y, Giblin JP, Clapp LH, Tinker A (2001) A mechanism for ATP-sensitive potassium channel diversity: functional coassembly of two pore forming subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:729–734
Cuong DV, Kim N, Joo H, Youm JB, Chung JY, Lee Y, Park WS, Kim E, Park YS, Han J (2005) Subunit composition of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in mitochondria of rat hearts. Mitochondrion 5:121–133
Das M, Parker JE, Halestrap AP (2003) Matrix volume measurements challenge the existence of diazoxide/glibencamide-sensitive KATP channels in rat mitochondria. J Physiol 547:893–902
Doyle DA, Cabral JM, Pfuetzner RA, Kuo A, Gulbis JM, Cohen SL, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (1998) The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 280:69–77
Fialka I, Pasquali C, Lottspeich F, Ahorn H, Huber LA (1997) Subcellular fractionation of polarized epithelial cells and identification of organelle-specific proteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 18:2582–2590
Forbes RA, Steenbergen C, Murphy E (2001) Diazoxide-induced cardioprotection requires signaling through a redox-sensitive mechanism. Circ Res 88:802–809
Foster DB, Rucker JJ, Marban E (2008) Is Kir6.1 a subunit of mitoK(ATP)? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 366:649–656
Fryer RM, Eells JT, Hsu AK, Henry MM, Gross GJ (2000) Ischemic preconditioning in rats: role of mitochondrial K(ATP) channel in preservation of mitochondrial function. Am J Physiol 278:H305–H312
Gamper N, Shapiro MS (2007) Regulation of ion transport proteins by membrane phosphoinositides. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:921–934
Garcia AM, Miller C (1984) Channel-mediated monovalent cation fluxes in isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Gen Physiol 83:819–839
Hanley PJ, Mickel M, Loffler M, Brandt U, Daut J (2002) K(ATP) channel-independent targets of diazoxide and 5-hydroxydecanoate in the heart. J Physiol 542:735–741
Inoue I, Nagase H, Kishi K, Higuti T (1991) ATP-sensitive K+ channel in the mitochondrial inner membrane. Nature 352:244–247
Lacza Z, Snipes JA, Miller AW, Szabo C, Grover G, Busija DW (2003) Heart mitochondria contain functional ATP-dependent K+ channels. J Mol Cell Cardiol 35:1339–1347
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Leaney JL, Dekker LV, Tinker A (2001) Regulation of a G-protein gated inwardly rectifying potassium channel by a Ca2+-independent protein kinase C. J Physiol Lond 534:367–379
Liu Y, Ren G, O’Rourke B, Marban E, Seharaseyon J (2001) Pharmacological comparison of native mitochondrial K(ATP) channels with molecularly defined surface K(ATP) channels. Mol Pharmacol 59:225–230
Ma D, Zerangue N, Lin YF, Collins A, Yu M, Jan YN, Jan LY (2001) Role of ER export signals in controlling surface potassium channel numbers. Science 291:316–319
Paucek P, Mironova G, Mahdi F, Beavis AD, Woldegiorgis G, Garlid KD (1992) Reconstitution and partial purification of the glibenclamide-sensitive, ATP-dependent K+ channel from rat liver and beef heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem 267:26062–26069
Quinn KV, Cui Y, Giblin JP, Clapp LH, Tinker A (2003) Do anionic phospholipids serve as cofactors or second messengers for the regulation of activity of cloned ATP-sensitive K+ channels? Circ Res 93:646–655
Rodrigo GC, Standen NB (2005) ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Curr Pharm Des 11:1915–1940
Salkoff L, Wei AD, Baban B, Butler A, Fawcett G, Ferreira G, Santi CM (2005) Potassium channels in C. elegans. WormBook 1–15
Seino S (1999) ATP-sensitive potassium channels: a model of heteromultimeric potassium channel/receptor assemblies. Annu Rev Physiol 61:337–362
Suzuki M, Kotake K, Fujikura K, Inagaki N, Suzuki T, Gonoi T, Seino S, Takata K (1997) Kir6.1: a possible subunit of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 241:693–697
Tinker A, Lindsay AR, Wlliams AJ (1992) A model for ionic conduction in the ryanodine receptor channel of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol 100:495–517
Urabe M, Kume A, Tobita K, Ozawa K (2000) DNA/calcium phosphate precipitates mixed with medium are stable and maintain high transfection efficiency. Anal Biochem 278:91–92
Voelker DR (1996) Lipid assembly into cell membranes. In: Vance DE, Vance JE (eds) Biochemistry of lipids, lipoproteins and membranes. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 391–423
Wang Y, Ashraf M (1999) Role of protein kinase C in mitochondrial KATP channel-mediated protection against Ca2+ overload injury in rat myocardium. Circ Res 84:1156–1165
White SM, Constantin PE, Claycomb WC (2004) Cardiac physiology at the cellular level: use of cultured HL-1 cardiomyocytes for studies of cardiac muscle cell structure and function. Am J Physiol 286:H823–H829
Yellon DM, Downey JM (2003) Preconditioning the myocardium: from cellular physiology to clinical cardiology. Physiol Rev 83:1113–1151
Zhou M, Tanaka O, Sekiguchi M, He HJ, Yasuoka Y, Itoh H, Kawahara K, Abe H (2005) ATP-sensitive K+-channel subunits on the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum of rat cardiomyocytes. J Histochem Cytochem 53:1491–1500
Acknowledgement
This work was funded by the British Heart Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, KE., Schwarzer, S., Duchen, M.R. et al. The Intracellular Localization and Function of the ATP-Sensitive K+ Channel Subunit Kir6.1. J Membrane Biol 234, 137–147 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-010-9241-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-010-9241-x