Abstract
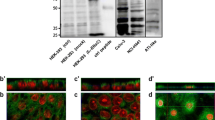
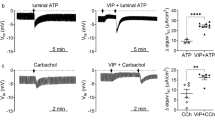
Potassium channels play an important role in providing a driving force for anion secretion from secretory epithelia. To investigate the role of KCNQ K+ channels in mediating rates of basal anion secretion across the human airway submucosal gland serous cell model, the Calu-3 cell, we examined the expression, localization and function of these channels. In addition to our previous knowledge that Calu-3 cells express KCNQ1, using reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction we determined expression of KCNQ3, KCNQ4 and KCNQ5 mRNA transcripts. Immunoblotting detected KCNQ1, KCNQ3 and KCNQ5 proteins, while KCNQ4 protein was not found. Immunolocalization using polarized Calu-3 cell monolayers revealed that KCNQ1 and KCNQ3 were located in or toward the apical membrane of the cells, while KCNQ5 was detected in the apical and lateral membranes. Transepithelial transport studies revealed a small chromanol 293B-sensitive current at the apical membrane, likely KCNQ1. Application of XE991, an inhibitor of all members of the KCNQ channel family, inhibited the basal short-circuit current when applied to both sides of the cells to a greater extent than 293B, with the largest inhibition seen upon apical application. This result was confirmed using linopiridine, a less potent analogue of XE991, and suggests that functional KCNQ3 and KCNQ5, in addition to KCNQ1, are present at the apical aspect of these cells. These results demonstrate the role of a number of KCNQ channel members in controlling basal anion secretion across Calu-3 cells, while also demonstrating the importance of apically located K+ channels in mediating anion secretion in the airway epithelium.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard K, Bogliolo S, Soriani O, Ehrenfeld J (2003) Modulation of calcium-dependent chloride secretion by basolateral SK4-like channels in a human bronchial cell line. J Membr Biol 196:15–31
Bett GCL, Morales MJ, Beahm DL, Duffey ME, Rasmusson RL (2006) Ancillary subunits and stimulation frequency determine the potency of chromanol 293B for the KCNQ1 potassium channel. J Physiol 576:755–767
Bleich M, Briel M, Busch AE, Lang HJ, Geriach U, Gögelein H, Greger R, Kunzelmann K (1997) KvLQT channels are inhibited by the K+ channel blocker 293B. Pfluegers Arch 434:499–501
Bleich M, Warth R (2000) The very small-comductance K+ channel KvLQT1 and epithelial function. Pfluegers Arch 440:202–206
Cook DI, Young JA (1989) Effect of K+ channels in the apical plasma membrane on epithelial secretion based on secondary active Cl- transport. J Membr Biol 110:139–146
Cooper EC, Jan LY (2003) M-channels. Neurological diseases, neuromodulation and drug development. Arch Neurol 60:496–500
Cowley EA, Linsdell P (2002) Characterization of basolateral K+ channels underlying anion secretion in the human airway cell line Calu-3. J Physiol 538:747–757
Currid A, Ortega B, Valverde MA (2003) Chloride secretion in a morphologically differentiated human colonic cell line that expresses the epithelial Na+ channel. J Physiol 555:241–250
Davis KA, Cowley EA (2006) Two-pore domain potassium channels support anion secretion from human airway Calu-3 epithelial cells. Pfluegers Arch 451:631–641
Devor DC, Singh AK, Frizzell RA, Bridges RJ (1996) Modulation of Cl- secretion by benzimidazolones. I. Direct activation of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel. Am J Physiol 271:L775–L784
Devor DC, Singh AK, Lambert LC, DeLuca A, Frizzell RA, Bridges RJ (1999) Bicarbonate and chloride secretion in Calu-3 human airway epithelial cells. J Gen Physiol 113:743–760
Elmedyb P, Calloe K, Schmidt N, Hansen RS, Grunner M, Olesen SP (2007) Modulation of ERG channels by XE991. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 100:316–322
Englehardt JF, Yankaskas JR, Ernst SA, Yang Y, Marino CR, Boucher RC, Cohn JA, Wilson JM (1992) Submucosal glands are the predominant site of CFTR expression in the human bronchus. Nat Genet 2:240–248
Erovic BM, Pammer J, Hollemann D, Woegerbauer M, Geleff S, Fischer MB, Burian M, Frommlet F, Neuchrist C (2003) Motility-related protein-1/CD9 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 25:848–857
Grahammer F, Warth R, Barhanin J, Bleich M, Hug MJ (2001) The small conductance K+ channel, KCNQ1 expression, function and subunit composition in murine trachea. J Biol Chem 276:42268–42275
Haws C, Finkbeiner WE, Widdicombe JH, Wine JJ (1994) CFTR in Calu-3 human airway cells: channel properties and role in cAMP-activated Cl- conductance. Am J Physiol 266:L502–L512
Heitzmann D, Grahammer F, von Hahn T, Schmitt-Gräff A, Romeo E, Nitschke R, Gerlach U, Lang HJ, Verry F, Barhanin J, Warth R (2004) Heteromeric KCNE2/KCNQ1 potassium channels in the luminal membrane of gastric parietal cells. J Physiol 561:547–557
Hoshi N, Zhang J-S, Omaki M, Takeuchi T, Yokoyama S, Wanaverbecq N, Langeberg LK, Yoneda Y, Scott JD, Brown DA, Higashida H (2003) AKAP150 signaling promotes suppression of the M-current by muscarinic agonists. Nat Neurosci 6:564–571
Hwang T-H, Suh D-J, Bae H-R, Lee S-H, Jung J-S (1996) Characterization of K+ channels in the basolateral membrane of rat tracheal epithelia. J Membr Biol 154:251–257
Kharkovets T, Dedek K, Maier H, Schweizer M, Khimich D, Nouvian R, Vardanyan V, Leuwer R, Jentsch TJ (2006) Mice with altered KCNQ4 K+ channels implicate sensory outer hair cells in human progressive deafness. EMBO J 25:642–652
Lan W-Z, Abbas H, Lemay A-M, Briggs MM, Hill CE (2005) Electrophysiological and molecular identification of hepatocellular volume-activated K+ channels. Biochim Biophys Acta 1668:223–233
Lerche C, Scherer CR, Seebohm G, Derst C, Wei AD, Busch AE, Steinmeyer K (2000) Molecular cloning and functional expression of KCNQ5, a potassium channel subunit that may contribute to neuronal M-current diversity. J Biol Chem 275:22395–22400
Lohrmann E, Burhoff I, Nitscke RB, Lang HJ, Mania D, Englert HC, Hropot M, Warth R, Rohm W, Bleich M, Greger R (1995) A new class of inhibitors of cAMP-mediated Cl- secretion in rabbit colon, acting by the reduction of cAMP-activated K+ conductance. Pfluegers Arch 429:517–530
MacVinish LJ, Hickman ME, Mufti DAH, Durrington HJ, Cuthbert AW (1998) Importance of basolateral K+ conductance in maintaining Cl- secretion in murine nasal and colonic epithelia. J Physiol 510:237–247
MacVinish LJ, Guo Y, Dixon AK, Murrell-Lagnado RD, Cuthbert AW (2001) XE991 reveals differences in K+ channels regulating chloride secretion in murine airway and colonic epithelium. Mol Pharmacol 60:753–760
Mall M, Wissner A, Schreiber R, Kuehr J, Seydewitz HH, Brandis M, Greger R, Kunzelmann K (2000) Role of KvLQT1 in cyclic adenosine monophosphate-mediated Cl- secretion in human airway epithelia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23:283–289
Marx S (2003) Ion channel macromolecular complexes in the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 35:37–44
Marx SO, Kurokawa J, Reiken S, Motoike H, D’Armiento J, Marks AR, Kass RS (2002) Requirement of a macromolecular signaling complex for β-adrenergic receptor modulation of the KCNQ1-KCNE1 potassium channel. Science 295:496–499
McCann JD, Welsh MJ (1990) Basolateral K+ channels in airway epithelia. II. Role in Cl- secretion and evidence for two types of K+ channel. Am J Physiol 258:L343–L348
Moon S, Singh M, Krouse ME, Wine JJ (1997) Calcium-stimulated Cl- secretion in Calu-3 human airway cells requires CFTR. Am J Physiol 273:L1208–L1219
Naren AP, Cobb B, Li C, Roy K, Nelson D, Heda GD, Liao J, Kirk KL, Sorscher EJ, Hanrahan J, Clancy JP (2003) A macromolecular complex of adrenergic receptor, CFTR, and ezrin/radixin/moesin-binding phosphoprotein 50 is regulated by PKA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:342–346
Nickolson VJ, Tam SW, Meyers MJ, Cook L (1990) DuP 996 (3,3-bis(4-pyrindinylmethyl)-1-phenylindolin-2-one) enhances the stimulus-induced release of acetylcholine from rat brain in vitro and in vivo. Drug Dev Res 19:285–300
Pilewski JM, Frizzell RA (1999) Role of CFTR in airway disease. Physiol Rev 79(Suppl 1):S215–S255
Robbins J (2001) KCNQ potassium channels: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Ther 90:1–19
Roy J, Denovan-Wright EM, Linsdell P, Cowley EA (2006) Exposure to sodium butyrate leads to functional down-regulation of calcium-activated potassium channels in human airway epithelial cells. Pfluegers Arch 453:167–176
Schroeder BC, Hechenberger M, Weinreich F, Kubisch C, Jentsch TJ (2000a) KCNQ5, a novel potassium channel broadly expressed in brain, mediates M-type currents. J Biol Chem 275:24089–24095
Schroeder BC, Waldegger S, Fehr S, Bleich M, Warth R, Greger R, Jentsch TJ (2000b) A constitutively open potassium channel formed by KCNQ1 and KCNE3. Nature 403:196–199
Shen BQ, Finkbeiner WE, Wine JJ, Mrsny RJ, Widdicombe JH (1994) Calu-3: a human airway epithelial cell line that shows a cAMP-dependent Cl- secretion. Am J Physiol 266:L493–L501
Silva P, Stoff J, Field M, Fine L, Forrest JN, Epstein FH (1977) Mechanism of active chloride secretion by shark rectal gland: role of Na-K-ATPase in chloride transport. Am J Physiol 233:F298–F306
Singh M, Krouse M, Moon S, Wine J (1997) Most basal Isc in Calu-3 human airway cells is bicarbonate-dependent Cl- secretion. Am J Physiol 272:L690–L698
Smith PL, Frizzell RA (1984) Chloride secretion by canine tracheal epithelium: IV. Basolateral membrane K permeability parallels secretion rate. J Membr Biol 77:187–199
Strutz-Seebohm N, Seebohm G, Fedorenko O, Baltaev R, Engel J, Knirsch M, Lang F (2006) Functional coassembly of KCNQ4 with KCNE beta-subunits in Xenopus oocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 18:57–66
Tinel N, Diochot S, Borsotto M, Lazdunski M, Barhanin J (2000) KCNE2 confers background current characteristics to the cardiac KCNQ1 potassium channel. EMBO J 19:6326–6330
Wang H-S, Brown BS, McKinnon D, Cohen IS (2000) Molecular basis for differential sensitivity of KCNQ and IKs channels to the cognitive enhancer XE991. Mol Pharmacol 57:1218–1223
Warth R (2003) Potassium channels in epithelial transport. Pfluegers Arch 446:505–513
Wu JV, Krouse ME, Rustagi A, Joo NS, Wine JJ (2004) An inwardly rectifying potassium channel in apical membrane of Calu-3 cells. J Biol Chem 279:46558–46565
Yus-Nájera E, Muñoz A, Salvador N, Jensen BS, Rasmussen HB, Defelipe J, Villarroel A (2003) Localization of KCNQ5 in the normal and epileptic human temporal neocortex and hippocampal formation. Neuroscience 120:353–364
Zaczek R, Chorvat RJ, Saye JA, Pierdomenico ME, Maciag CM, Logue AR, Fisher BN, Rominger DH, Earl RA (1998) Two new potent neurotransmitter release enhancers, 10, 10-bis(4-pyridinylmethyl)-9(10H)-anthracenone: comparison to linopirdine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:724–730
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Dieter Gruenert for the 16HBE14o- and CFBE41o- cells and Dr. Paul Murphy for the human testis cDNA sample. Brenna vanTol provided excellent technical assistance. As always, we are indebted to Dr. Paul Linsdell for discussion and criticism. This work was supported by the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moser, S.L., Harron, S.A., Crack, J. et al. Multiple KCNQ Potassium Channel Subtypes Mediate Basal Anion Secretion from the Human Airway Epithelial Cell Line Calu-3. J Membrane Biol 221, 153–163 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-008-9093-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-008-9093-9