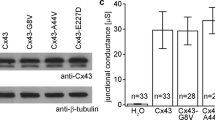
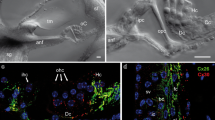
Abstract
A large proportion of recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss is due to mutations in the GJB2 gene encoding connexin 26 (Cx26), a component of a gap junction. Within different ethnic groups there are specific common recessive mutations, each with a relatively high carrier frequency, suggesting the possibility of heterozygous advantage. Carriers of the R143W GJB2 allele, the most prevalent in the African population, present with a thicker epidermis than noncarriers. In this study, we show that (R143W)Cx26-expressing keratinocytes form a significantly thicker epidermis in an organotypic coculture skin model. In addition, we show increased migration of cells expressing (R143W)Cx26 compared to (WT)Cx26-overexpressing cells. We also demonstrate that cells expressing (R143W)Cx26 are significantly less susceptible to cellular invasion by the enteric pathogen Shigella flexneri than (WT)Cx26-expressing cells. These in vitro studies suggest an advantageous effect of (R143W)Cx26 in epithelial cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyer B, Tucker GC, Valles AM, Franke WW, Thiery JP (1989) Rearrangements of desmosomal and cytoskeletal proteins during the transition from epithelial to fibroblastoid organization in cultured rat bladder carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol 109:1495–1509
Brandner JM, Houdek P, Husing B, Kaiser C, Moll I (2004) Connexins 26, 30, and 43: differences among spontaneous, chronic, and accelerated human wound healing. J Invest Dermatol 122:1310–1320
Brobby GW, Muller-Myhsok B, Horstmann RD (1998) Connexin 26 R143W mutation associated with recessive nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness in Africa [letter]. N Engl J Med 338:548–550
Common JE, Di WL, Davies D, Kelsell DP (2004) Further evidence for heterozygote advantage of GJB2 deafness mutations: a link with cell survival. J Med Genet 41:573–575
Deng H, Lin Q, Khavari PA (1997) Sustainable cutaneous gene delivery. Nat Biotechnol 15:1388–1391
Denoyelle F, Weil D, Maw MA, et al. (1997) Prelingual deafness: high prevalence of a 30delG mutation in the connexin 26 gene. Hum Mol Genet 6:2173–2177
Di WL, Rugg EL, Leigh IM, Kelsell DP (2001) Multiple epidermal connexins are expressed in different keratinocyte subpopulations including connexin 31. J Invest Dermatol 117:958–964
Dickson MA, Hahn WC, Ino Y, Ronfard V, Wu JY, Weinberg RA, Louis DN, Li FP, Rheinwald JG (2000) Human keratinocytes that express hTERT and also bypass a p16(INK4a)-enforced mechanism that limits life span become immortal yet retain normal growth and differentiation characteristics. Mol Cell Biol 20:1436–1447
Djalilian AR, McGaughey D, Patel S, Seo EY, Yang C, Cheng J, Tomic M, Sinha S, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Segre JA (2006) Connexin 26 regulates epidermal barrier and wound remodeling and promotes psoriasiform response. J Clin Invest 116:1243–1253
Goliger JA, Paul DL (1995) Wounding alters epidermal connexin expression and gap junction-mediated intercellular communication. Mol Biol Cell 6:1491–1501
Hertle M, Kubler M-D, Leigh IM, Watt FM (1992) Aberrant integrin expression during epidermal wound healing and in psoriatic epidermis. J Clin Invest 89:1892–1901
Hutchin T, Coy NN, Conlon H, Telford E, Bromelow K, Blaydon D, Taylor G, Coghill E, Brown S, Trembath R, Liu XZ, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Mueller R (2005) Assessment of the genetic causes of recessive childhood non-syndromic deafness in the UK – implications for genetic testing. Clin Genet 68:506–512
Kelsell DP, Dunlop J, Stevens HP, Lench NJ, Liang JN, Parry G, Mueller RF, Leigh IM (1997) Connexin 26 mutations in hereditary non-syndromic sensorineural deafness. Nature 387:80–83
Kenneson A, Van Naarden Braun K, Boyle C (2002) GJB2 (connexin 26) variants and nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss: a HuGE review. Genet Med 4:258–274
Kudo T, Ikeda K, Kure S, Matsubara Y, Oshima T, Watanabe K, Kawase T, Narisawa K, Takasaka T (2000) Novel mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) responsible for childhood deafness in the Japanese population. Am J Med Genet 90:141–145
Labarthe MP, Bosco D, Saurat JH, Meda P, Salomon D (1998) Upregulation of connexin 26 between keratinocytes of psoriatic lesions. J Invest Dermatol 111:72–76
Leigh IM, Navsaria H, Purkis PE, McKay IA, Bowden PE, Riddle PN (1995) Keratins (K16 and K17) as markers of keratinocyte hyperproliferation in psoriasis in vivo and in vitro. Br J Dermatol 133:501–511
Lucke T, Choudhry R, Thom R, Selmer IS, Burden AD, Hodgins MB (1999) Upregulation of connexin 26 is a feature of keratinocyte differentiation in hyperproliferative epidermis, vaginal epithelium, and buccal epithelium. J Invest Dermatol 112:354–361
Matoltsy AG, Viziam CB (1970) Further observations on epithelialization of small wounds: an autoradiographic study of incorporation and distribution of 3H-thymidine in the epithelium covering skin wounds. J Invest Dermatol 55:20–25
Mese G, Londin E, Mui R, Brink PR, White TW (2004) Altered gating properties of functional Cx26 mutants associated with recessive non-syndromic hearing loss. Hum Genet 115:191–199
Meyer CG, Amedofu GK, Brandner JM, Pohland D, Timmann C, Horstmann RD (2002) Selection for deafness? Nat Med 8:1332–1333
Ojeh NO, Frame JD, Navsaria HA (2001) In vitro characterization of an artificial dermal scaffold. Tissue Eng 7:457–472
Palmada M, Schmalisch K, Bohmer C, Schug N, Pfister M, Lang F, Blin N (2006) Loss of function mutations of the GJB2 gene detected in patients with DFNB1-associated hearing impairment. Neurobiol Dis 22:112–118
Richard G (2005) Connexin disorders of the skin. Clin Dermatol 23:23–32
Rivas MV, Jarvis ED, Morisaki S, Carbonaro H, Gottlieb AB, Krueger JG (1997) Identification of aberrantly regulated genes in diseased skin using the cDNA differential display technique. J Invest Dermatol 108:188–194
Snoeckx RL, Huygen PL, Feldmann D, et al. 2005. GJB2 mutations and degree of hearing loss: a multicenter study. Am J Hum Genet 77:945–957
Stark HJ, Willhauck MJ, Mirancea N, Boehnke K, Nord I, Breitkreutz D, Pavesio A, Boukamp P, Fusenig NE (2004) Authentic fibroblast matrix in dermal equivalents normalises epidermal histogenesis and dermoepidermal junction in organotypic coculture. Eur J Cell Biol 83:631–645
Tran Van Nhieu G, Clair C, Bruzzone R, Mesnil M, Sansonetti P, Combettes L (2003) Connexin-dependent inter-cellular communication increases invasion and dissemination of shigella in epithelial cells. Nat Cell Biol 5:720–726
Wang HL, Chang WT, Li AH, Yeh TH, Wu CY, Chen MS, Huang PC (2003) Functional analysis of connexin−26 mutants associated with hereditary recessive deafness. J Neurochem 84:735–742
Wiszniewski L, Limat A, Saurat JH, Meda P, Salomon D (2000) Differential expression of connexins during stratification of human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 115:278–285
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Research Advisory Board of Barts and the London, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) and the Wellcome Trust to D. P. K. We express special thanks to Dr. Jash Vyas for advice and help with the migration assays and Professor Tom MacDonald for the normal human colon and help with interpretation of Cx26 localization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first two authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Man, Y.K.S., Trolove, C., Tattersall, D. et al. A Deafness-Associated Mutant Human Connexin 26 Improves the Epithelial Barrier In Vitro . J Membrane Biol 218, 29–37 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-007-9025-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-007-9025-0